The future of VPNs may be fighting quanta with quanta.


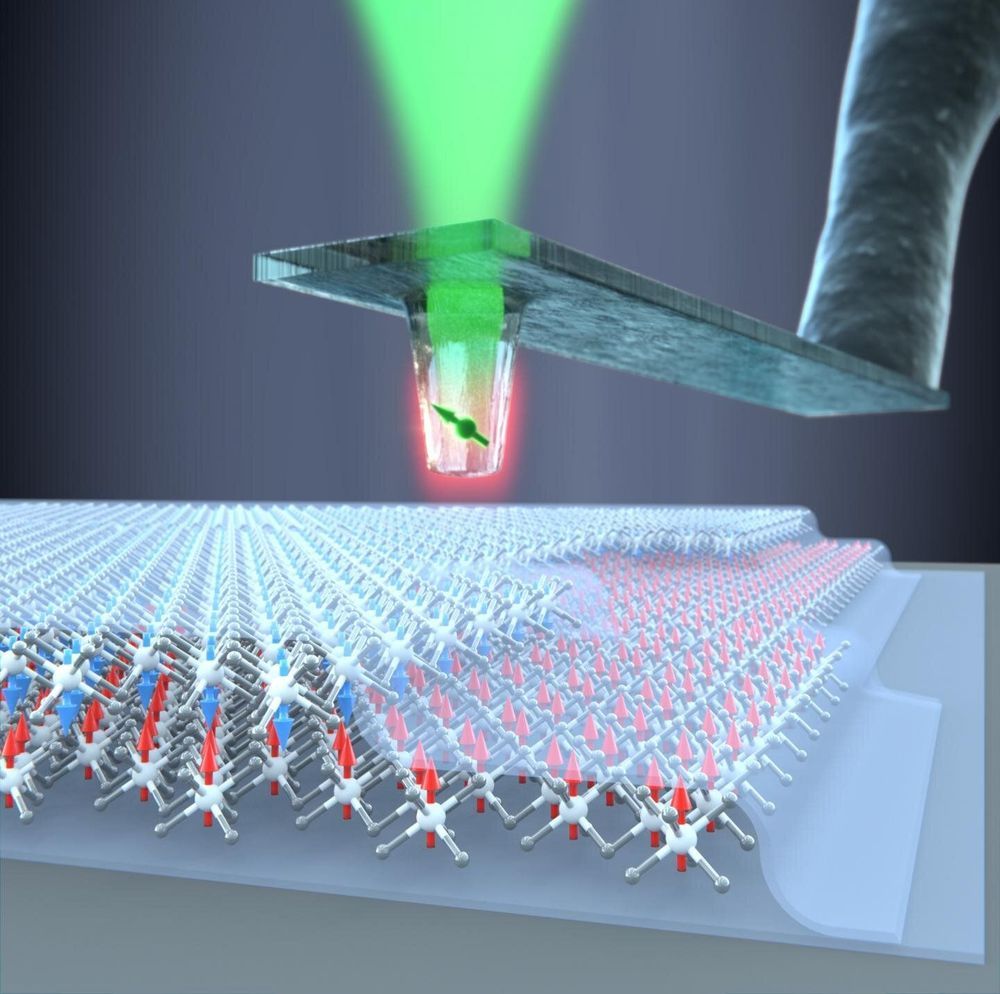
For the first time, physicists at the University of Basel have succeeded in measuring the magnetic properties of atomically thin van der Waals materials on the nanoscale. They used diamond quantum sensors to determine the strength of the magnetization of individual atomic layers of the material chromium triiodide. In addition, they found a long-sought explanation for the unusual magnetic properties of the material. The journal Science has published the findings.
The use of atomically thin, two-dimensional van der Waals materials promises innovations in numerous fields in science and technology. Scientists around the world are constantly exploring new ways to stack different single atomic layers and thus engineer new materials with unique, emerging properties.
These super-thin composite materials are held together by van der Waals forces and often behave differently to bulk crystals of the same material. Atomically thin van der Waals materials include insulators, semiconductors, superconductors and a few materials with magnetic properties. Their use in spintronics or ultra-compact magnetic memory media is highly promising.
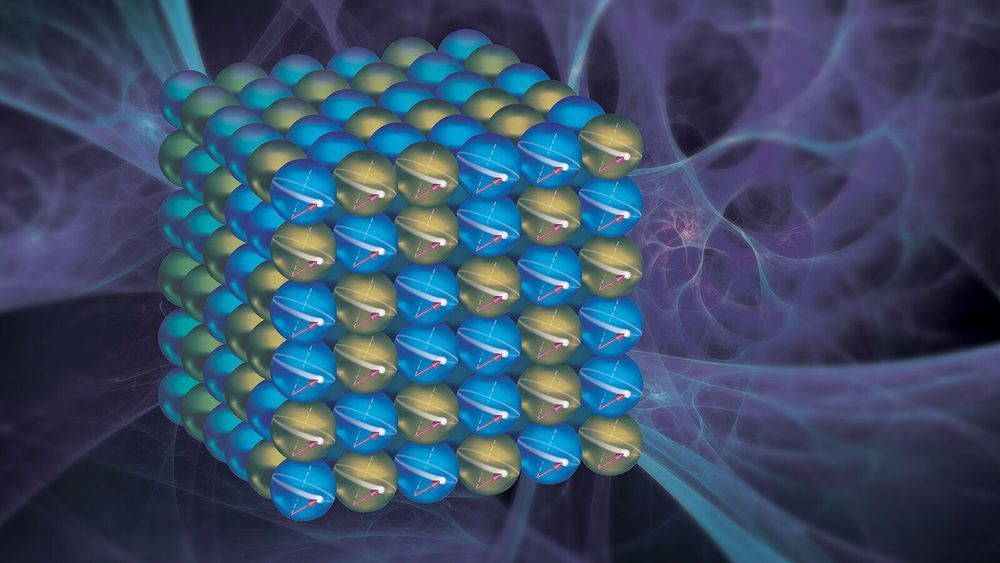
Scientists find surprising way to affect information storage properties in metal alloy.
Sometimes scientific discoveries can be found along well-trodden paths. That proved the case for a cobalt-iron alloy material commonly found in hard disk drives.
As reported in a recent issue of Physical Review Letters, researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, along with Oakland University in Michigan and Fudan University in China, have found a surprising quantum effect in this alloy.

Particles travelling through empty space can emit bright flashes of gamma rays by interacting with the quantum vacuum, according to a new study by researchers at the University of Strathclyde.
It has long been known that charged particles, such as electrons and protons, produce the electromagnetic equivalent of a sonic boom when their speeds exceed that of photons in the surrounding medium. This effect, known as Cherenkov emission, is responsible for the characteristic blue glow from water in a nuclear reactor, and is used to detect particles at the CERN Large Hadron Collider.
According to Einstein, nothing can travel faster than light in vacuum. Because of this, it is usually assumed that the Cherenkov emission cannot occur in vacuum. But according to quantum theory, the vacuum itself is packed full of “virtual particles”, which move momentarily in and out of existence.
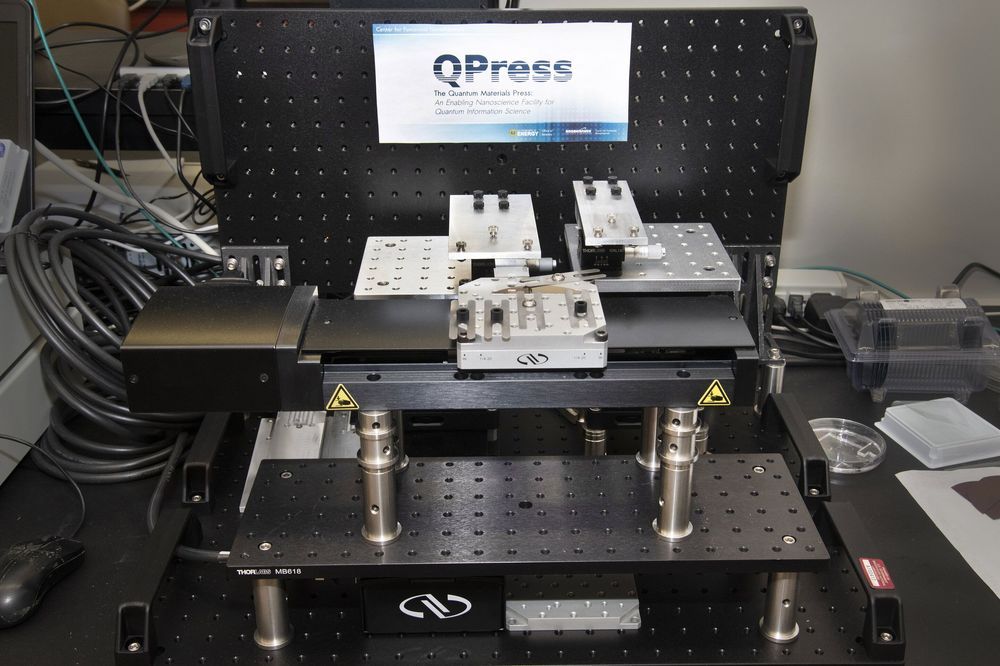

Checking out a stack of books from the library is as simple as searching the library’s catalog and using unique call numbers to pull each book from their shelf locations. Using a similar principle, scientists at the Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN)—a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility at Brookhaven National Laboratory—are teaming with Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) to create a first-of-its-kind automated system to catalog atomically thin two-dimensional (2-D) materials and stack them into layered structures. Called the Quantum Material Press, or QPress, this system will accelerate the discovery of next-generation materials for the emerging field of quantum information science (QIS).
Structures obtained by stacking single atomic layers (“flakes”) peeled from different parent bulk crystals are of interest because of the exotic electronic, magnetic, and optical properties that emerge at such small (quantum) size scales. However, flake exfoliation is currently a manual process that yields a variety of flake sizes, shapes, orientations, and number of layers. Scientists use optical microscopes at high magnification to manually hunt through thousands of flakes to find the desired ones, and this search can sometimes take days or even a week, and is prone to human error.
Once high-quality 2-D flakes from different crystals have been located and their properties characterized, they can be assembled in the desired order to create the layered structures. Stacking is very time-intensive, often taking longer than a month to assemble a single layered structure. To determine whether the generated structures are optimal for QIS applications—ranging from computing and encryption to sensing and communications—scientists then need to characterize the structures’ properties.

Graphene quantum dots drawn from common coal may be the basis for an effective antioxidant for people who suffer traumatic brain injuries, strokes or heart attacks.
Their ability to quench oxidative stress after such injuries is the subject of a study by scientists at Rice University, the Texas A&M Health Science Center and the McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
Quantum dots are semiconducting materials small enough to exhibit quantum mechanical properties that only appear at the nanoscale.

University of Copenhagen researchers have developed a nanocomponent that emits light particles carrying quantum information. Less than one-tenth the width of a human hair, the miniscule component makes it possible to scale up and could ultimately reach the capabilities required for a quantum computer or quantum internet. The research result puts Denmark at the head of the pack in the quantum race.
Teams around the world are working to develop quantum technologies. The focus of researchers based at the Center for Hybrid Quantum Networks (Hy-Q) at the University of Copenhagen’s Niels Bohr Institute is on developing quantum communication technology based on light circuits, known as nanophotonic circuits. The UCPH researchers have now achieved a major advancement.
“It is a truly major result, despite the component being so tiny,” says Assistant Professor Leonardo Midolo, who has been working towards this breakthrough for the past five years.
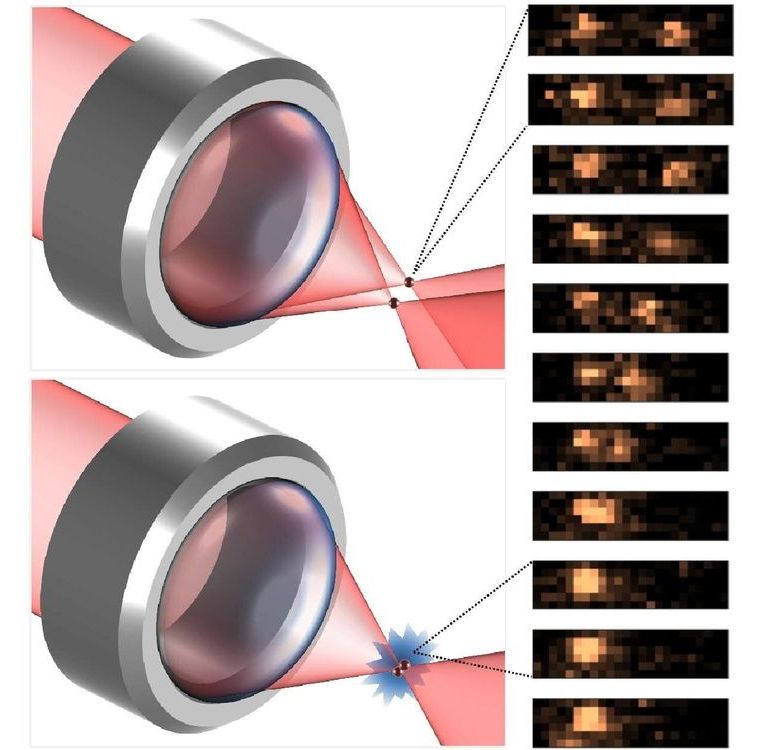
By breaking with conventionality, University of Otago physicists have opened up new research and technology opportunities involving the basic building block of the world—atoms.
In a study, just published in Nature Communications, researchers put one atom inside each of two laser beams before moving them together until they started to interact with each other.
Co-author Associate Professor Mikkel F. Andersen, of the Department of Physics, says this allows the atoms to exchange properties in a way which could be “very useful” for future quantum technologies.
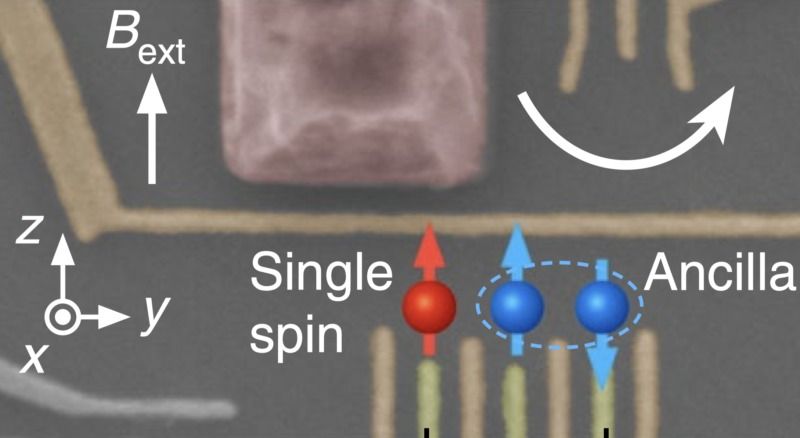
I suspect that if you asked an engineer at Intel about quantum computing, they probably wouldn’t want to know about it unless the chips could be fabricated using standard fabrication technology. Using standard processes means using electrons as the basis for quantum computing.
Electrons are lovely in many respects, but they are rather extroverted. It doesn’t matter what you do, they will run off and play with the neighbors. The constantly interacting electron does not look after its quantum state, so quantum information is rapidly lost, making processing really difficult. This makes the achievement of a quantum non-demolition measurement in an electron system rather remarkable.