When it comes to microelectronics, there is one chemical element like no other: silicon, the workhorse of the transistor technology that drives our information society. The countless electronic devices we use in everyday life are a testament to how today very high volumes of silicon-based components can be produced at very low cost. It seems natural, then, to use silicon also in other areas where the properties of semiconductors—as silicon is one—are exploited technologically, and to explore ways to integrate different functionalities. Of particular interest in this context are diode lasers, such as those employed in barcode scanners or laser pointers, which are typically based on gallium arsenide (GaAs). Unfortunately though, the physical processes that create light in GaAs do not work so well in silicon. It therefore remains an outstanding, and long-standing, goal to find an alternative route to realizing a ‘laser on silicon.’
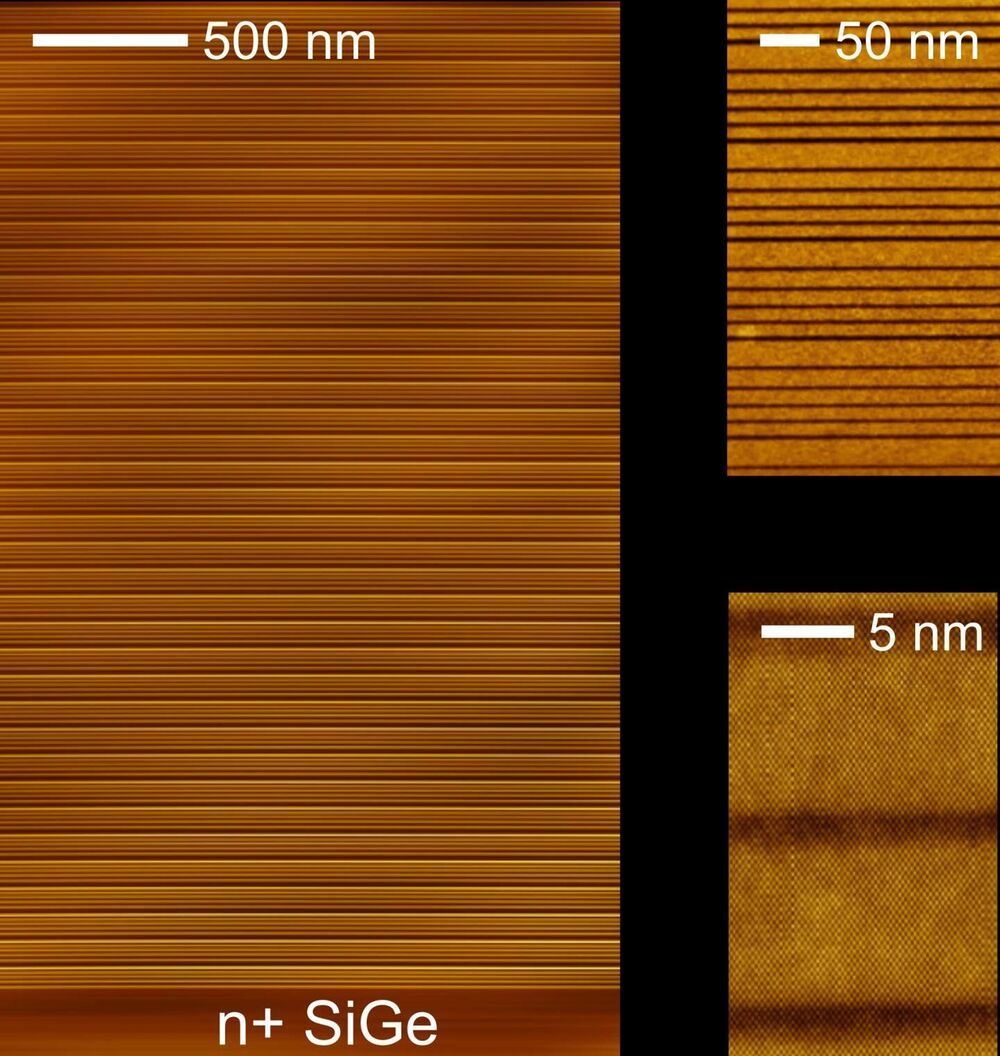
Writing today in Applied Physics Letters, an international team led by Professors Giacomo Scalari and Jérôme Faist from the Institute for Quantum Electronics present an important step towards such a device. They report electroluminescence—electrical light generation—from a semiconductor structure based on silicon-germanium (SiGe), a material that is compatible with standard fabrication processes used for silicon devices. Moreover, the emission they observed is in the terahertz frequency band, which sits between those of microwave electronics and infrared optics, and is of high current interest with a view to a variety of applications.