Last year, I edhost a thrilling conversation between @SabineHossenfelder, Carlo Rovelli, and Eric Weinstein as they debate quantum physics, consciousness and the mystery of reality. \
\
IAI Live is a monthly event featuring debates, talks, interviews, documentaries and music. LIVE. \
Watch the original video \
\
See the world’s leading thinkers debate the big questions for real, LIVE in London. Tickets: https://howthelightgetsin.org/\
\
To discover more talks, debates, interviews and academies with the world’s leading speakers visit https://iai.tv/\
\
We imagine physics is objective. But quantum physics found the act of human observation changes the outcome of experiment. Many scientists assume this central role of the observer is limited to just quantum physics. But is this an error? As Heisenberg puts it, \.
Category: quantum physics – Page 435
Why Quantum Mechanics Defies Physics
The full, weird story of the quantum world is much too large for a single article, but the period from 1905, when Einstein first published his solution to the photoelectric puzzle, to the 1960’s, when a complete, well-tested, rigorous, and insanely complicated quantum theory of the subatomic world finally emerged, is quite the story.
This quantum theory would come to provide, in its own way, its own complete and total revision of our understanding of light. In the quantum picture of the subatomic world, what we call the electromagnetic force is really the product of countless microscopic interactions, the work of indivisible photons, who interact in mysterious ways. As in, literally mysterious. The quantum framework provides no picture as to how subatomic interactions actually proceed. Rather, it merely gives us a mathematical toolset for calculating predictions. And so while we can only answer the question of how photons actually work with a beleaguered shrug, we are at least equipped with some predictive power, which helps assuage the pain of quantum incomprehensibility.
Doing the business of physics – that is, using mathematical models to make predictions to validate against experiment – is rather hard in quantum mechanics. And that’s because of the simple fact that quantum rules are not normal rules, and that in the subatomic realm all bets are off.
Finding meaning at the quantum level
Kmele steps inside Fermilab, America’s premiere particle accelerator facility, to find out how the smallest particles in the universe can teach us about its biggest mysteries.\
\
This video is an episode from @The-Well, our publication about ideas that inspire a life well-lived, created with the @JohnTempletonFoundation.\
\
Watch the full podcast now ► • Dispatches from The Well \
\
According to Fermilab’s Bonnie Flemming, the pursuit of scientific understanding is “daunting in an inspiring way.” What makes it daunting? The seemingly infinite number of questions, with their potentially inaccessible answers.\
\
In this episode of Dispatches from The Well, host Kmele Foster tours the grounds of America’s legendary particle accelerator to discover how exploring the mysteries at the heart of particle physics help us better understand some of the most profound mysteries of our universe.\
\
Read the video transcript ► https://bigthink.com/the-well/dispatc…\
\
00:00:00 — The Miracle of Birth\
00:04:48 — Exploring the Universe’s Mysteries\
00:09:20 — Building Blocks of Matter and the Standard Model\
00:13:35 — The Evolving Body of Knowledge\
00:17:39 — Understanding the Early Universe\
00:22:05 — Reflections on Particle Physics\
00:25:34 — The Extraordinary Effort to Understand the Small\
00:29:59 — From Paleontology to Astrophysics\
00:33:40 — The Importance of the Scientific Method and Being Critical\
\
\
About Kmele Foster:\
\
Kmele Foster is a media entrepreneur, commentator, and regular contributor to various national publications. He is the co-founder and co-host of The Fifth Column, a popular media criticism podcast.\
\
He is the head of content at Founders Fund, a San Francisco based venture capital firm investing in companies building revolutionary technologies, and a partner at Freethink, a digital media company focused on the people and ideas changing our world.\
\
Kmele also serves on the Board of Directors of the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression (FIRE).\
\
\
Read more from The Well: \
Actually, neuroscience suggests “the self” is real\
► https://bigthink.com/the-well/actuall…\
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein can illuminate the debate over generative AI\
► https://bigthink.com/the-well/mary-sh…\
Few of us desire true equality. It’s time to own up to it\
► https://bigthink.com/the-well/few-des…\
\
\
About The Well\
Do we inhabit a multiverse? Do we have free will? What is love? Is evolution directional? There are no simple answers to life’s biggest questions, and that’s why they’re the questions occupying the world’s brightest minds.\
\
Together, let’s learn from them.\
\
\
\
Join The Well on your favorite platforms:\
► Facebook: https://bit.ly/thewellFB \
► Instagram: https://bit.ly/thewellIG

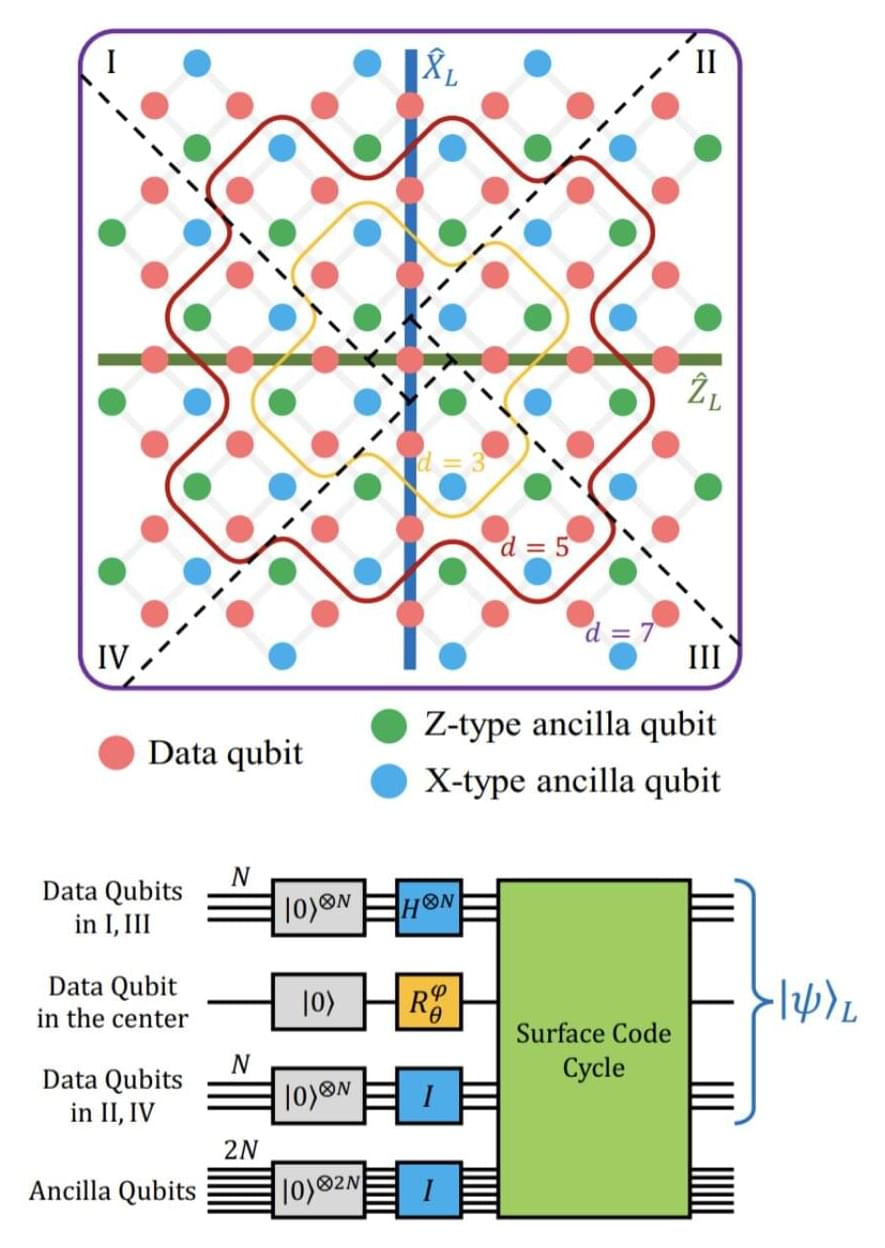
A logical magic state with fidelity beyond distillation threshold realized on superconducting quantum processor
Quantum computers have the potential to outperform conventional computers on some tasks, including complex optimization problems. However, quantum computers are also vulnerable to noise, which can lead to computational errors.
Engineers have been trying to devise fault-tolerant quantum computing approaches that could be more resistant to noise and could thus be scaled up more robustly. One common approach to attain fault-tolerance is the preparation of magic states, which introduce so-called non-Clifford gates.
Researchers at University of Science and Technology of China, the Henan Key Laboratory of Quantum Information and Cryptography and the Hefei National Laboratory recently demonstrated the preparation of a logical magic state with fidelity beyond the distillation threshold on a superconducting quantum processor. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, outlines a viable and effective strategy to generate high-fidelity logical magic states, an approach to realize fault-tolerant quantum computing.

We Just Got a Major Step Closer to Teleporting Images Using Only Light
Teleportation of quantum states promises to play a central role in securing the information superhighway of tomorrow.
In spite of the headway that’s been made, the process remains slow and kind of clunky. That could change, with scientists using a new process that could efficiently teleport states of light to form an image using a single pair of entangled photons.
The team, from South Africa, Germany, and Spain, is hopeful that the innovation may help build the secure networks of the future: if the key data isn’t transmitted, then it can’t be stolen.
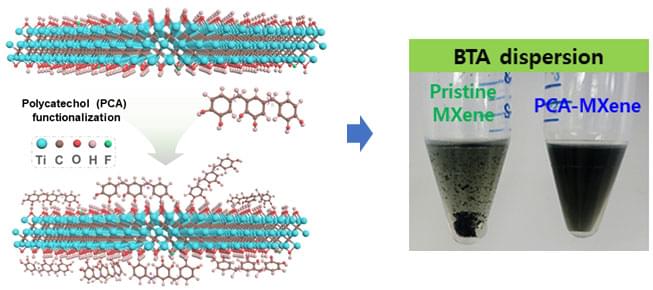
Applying MXene to quantum dot photovoltaic cells simultaneously increases efficiency and stability
A research team led by Professor Jong-min Choi of the Department of Energy Engineering has developed a technology that can significantly improve the efficiency of quantum dot photovoltaic cells by introducing organic solvent dispersible MXene.
The findings were published in Advanced Energy Materials (“Organic solvent dispersible MXene integrated colloidal quantum dot photovoltaics”).
Comparison of the dispersibility of quantum dot solar cell ink organic solvent according to surface modification of MXene. (Image: DGIST)


How A Laser-Plasma Collider Can Turn Light Into Matter In A Matter Of Seconds
A team led by researchers at Osaka University and University of California, San Diego has conducted simulations of creating matter solely from collisions of light particles. Their method circumvents what would otherwise be the intensity limitations of modern lasers and can be readily implemented by using presently available technology. This work might help experimentally test long-standing theories such as the Standard Model of particle physics, and possibly the need to revise them.
One of the most striking predictions of quantum physics is that matter can be generated solely from light (i.e., photons), and in fact, the astronomical bodies known as pulsars achieve this feat. Directly generating matter in this manner has not been achieved in a laboratory, but it would enable further testing of the theories of basic quantum physics and the fundamental composition of the universe.
In a study published in Physical Review Letters, a team led by researchers at Osaka University has simulated conditions that enable photon–photon collisions, solely by using lasers. The simplicity of the setup and ease of implementation at presently available laser intensities make it a promising candidate for near-future experimental implementation.

Shapes of one million galaxies hint at the universe’s origins
A recent study published in the journal Physical Review D marks a significant advancement in cosmology. A team of researchers has analyzed over one million galaxies to delve into the origins of the universe’s current cosmic structures.
This study contributes to the understanding of the ΛCDM model, the standard framework for the universe, which posits the significance of cold dark matter (CDM) and dark energy (the cosmological constant, Λ).
The model theorizes that primordial fluctuations, originating at the universe’s inception, acted as catalysts for the formation of all celestial objects, including stars, galaxies, and galaxy clusters.