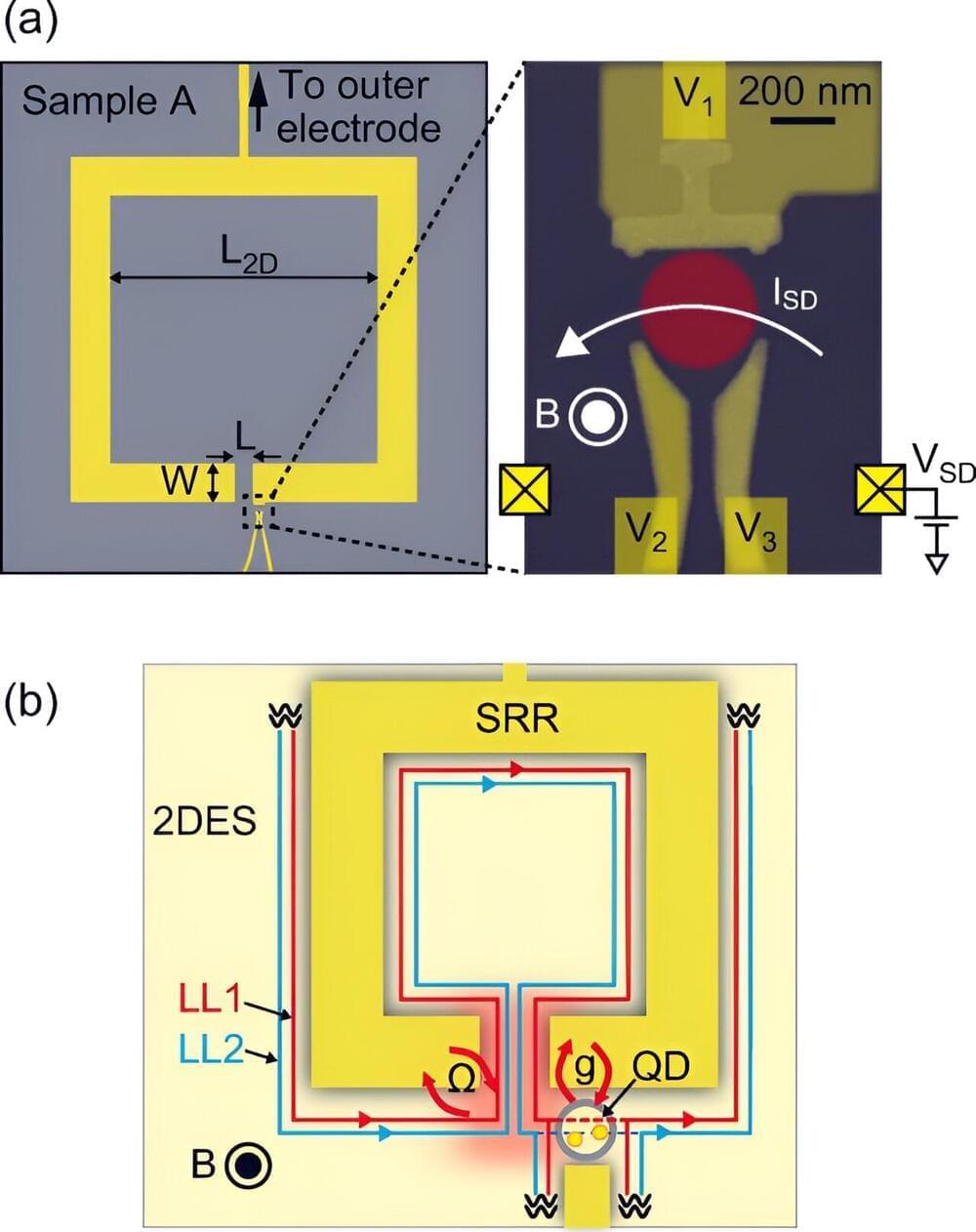
Future quantum electronics will differ substantially from conventional electronics. Whereas memory in the latter is stored as binary digits, the former is stored as qubits, which can take many forms, such as entrapped electrons in nanostructures known as quantum dots. However, challenges in transmitting this information to anything further than the adjacent quantum dot have limited qubit design.
Now, in a study recently published in Physical Review Letters, researchers from the Institute of Industrial Science at the University of Tokyo are solving this problem, They developed a new technology for transmitting quantum information over perhaps tens to a hundred micrometers. This advance could improve the functionality of upcoming quantum electronics.
How can researchers transmit quantum information, from one quantum dot to another, on the same quantum computer chip? One way might be to convert electron (matter) information into light (electromagnetic wave) information—by generating light–matter hybrid states.