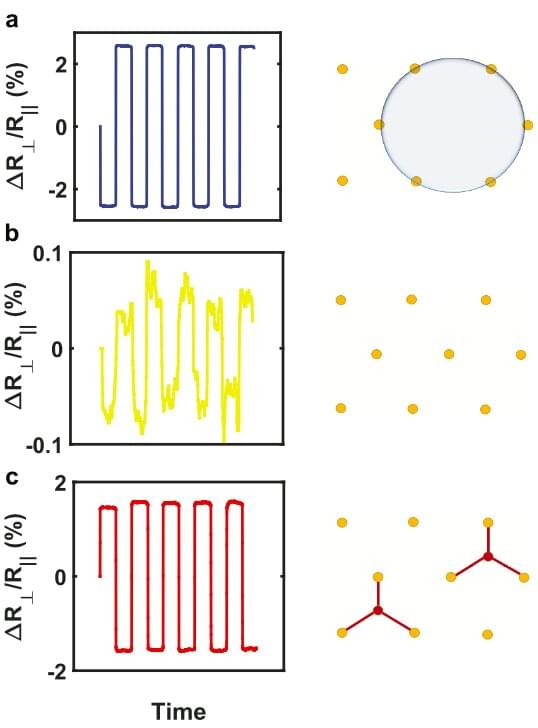
Over the past decade or so, physicists and engineers have been trying to identify new materials that could enable the development of electronic devices that are faster, smaller and more robust. This has become increasingly crucial, as existing technologies are made of materials that are gradually approaching their physical limits.
Antiferromagnetic (AFM) spintronics are devices or components for electronics that couple a flowing current of charge to the ordered spin ‘texture’ of specific materials. In physics, the term spin refers to the intrinsic angular momentum observed in electrons and other particles.
The successful development of AFM spintronics could have very important implications, as it could lead to the creation of devices or components that surpass Moore’s law, a principle first introduced by microchip manufacturer Gordon Earle Moore’s law essentially states that the memory, speed and performance of computers may be expected to double every two years due to the increase in the number of transistors that a microchip can contain.