Learn how we’re advancing quantum computing by developing 4D error-correction codes that are applicable to many types of qubits.

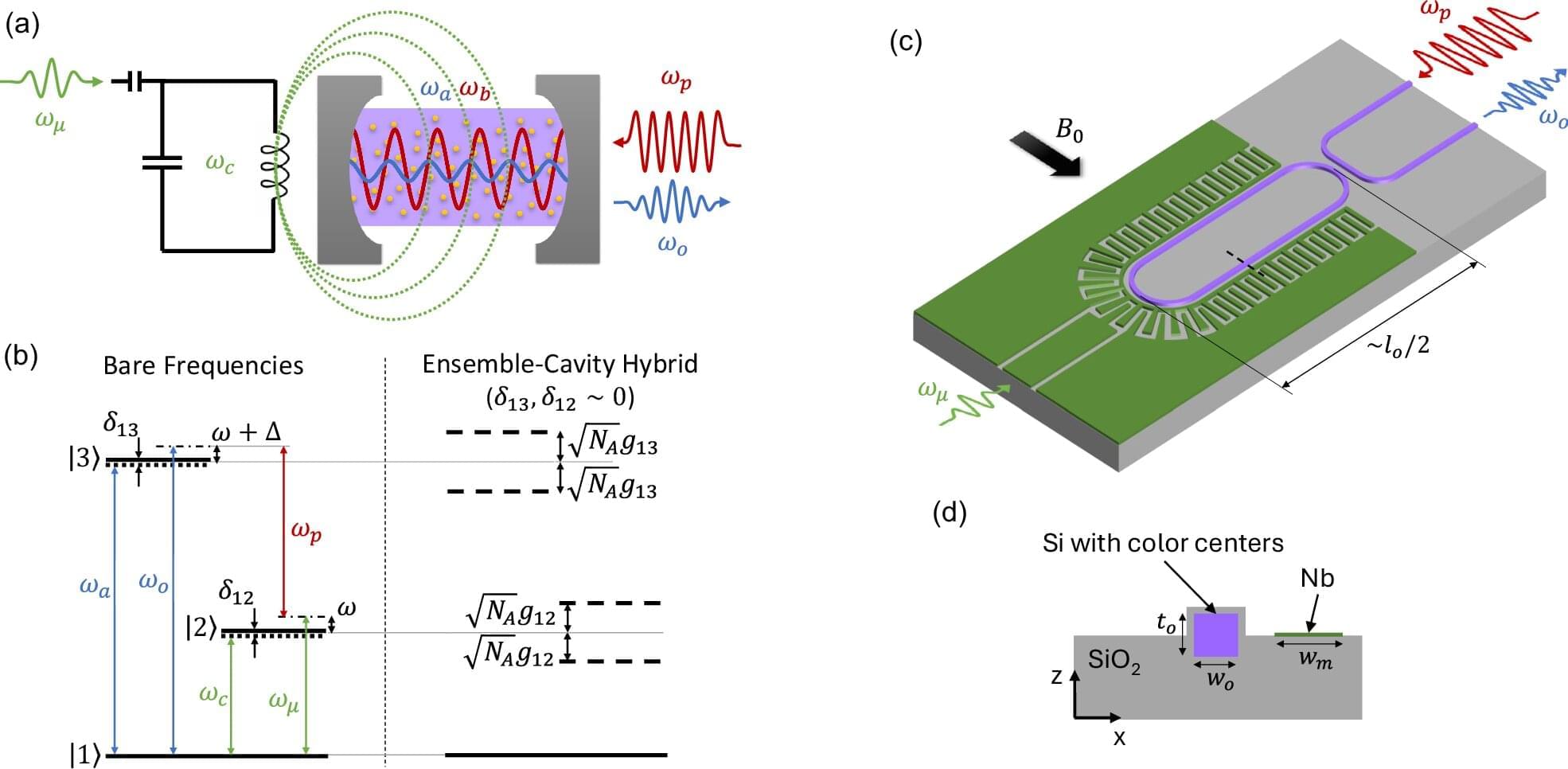
UBC researchers are proposing a solution to a key hurdle in quantum networking: a device that can “translate” microwave to optical signals and vice versa.
The technology could serve as a universal translator for quantum computers—enabling them to talk to one another over long distances and converting up to 95% of a signal with virtually no noise. And it all fits on a silicon chip, the same material found in everyday computers.
“It’s like finding a translator that gets nearly every word right, keeps the message intact and adds no background chatter,” says study author Mohammad Khalifa, who conducted the research during his Ph.D. at UBC’s faculty of applied science and the Stewart Blusson Quantum Matter Institute (SBQMI).

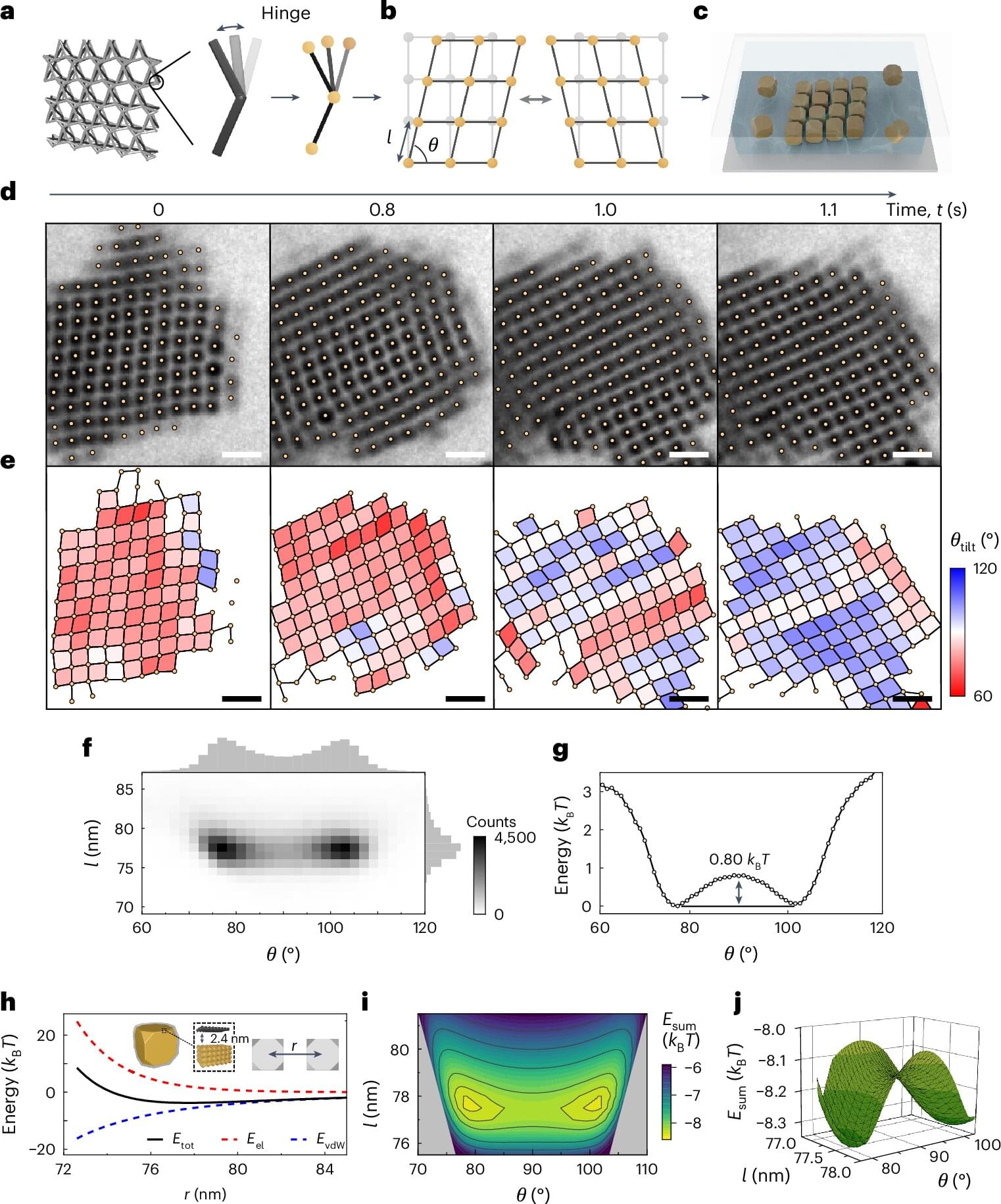
A research team including members from the University of Michigan have unveiled a new observational technique that’s sensitive to the dynamics of the intrinsic quantum jiggles of materials, or phonons.
This work will help scientists and engineers better design metamaterials—substances that possess exotic properties that rarely exist in nature—that are reconfigurable and made from solutions containing nanoparticles that self-assemble into larger structures, the researchers said. These materials have wide-ranging applications, from shock absorption to devices that guide acoustic and optical energy in high-powered computer applications.
“This opens a new research area where nanoscale building blocks—along with their intrinsic optical, electromagnetic and chemical properties —can be incorporated into mechanical metamaterials, enabling emerging technologies in multiple fields from robotics and mechanical engineering to information technology,” said Xiaoming Mao, U-M professor of physics and co-author of the new study.
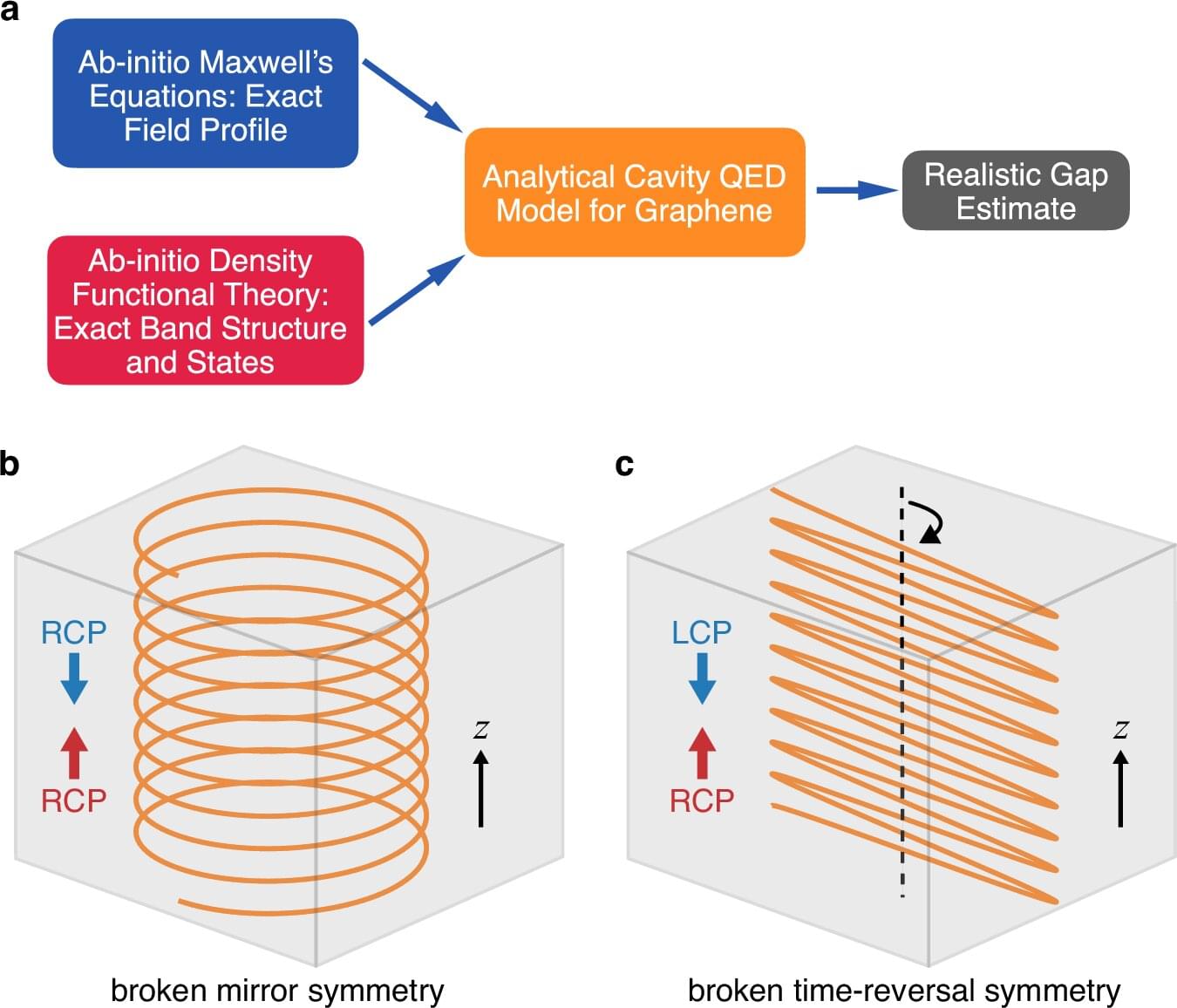
Vacuum is often thought of as empty, but in fact it is teeming with fleeting energy fluctuations—virtual photons popping in and out of existence that can interact with matter, giving rise to new, potentially useful properties.
Researchers use optical cavities, structures made of mirrors facing one another, to confine these fluctuations, harnessing their effects to engineer new forms of matter.
Conventional optical cavities boost fluctuations, or vacuum fields, for both right-and left-handed circularly polarized light. Rice University researchers and collaborators have developed a new cavity design that selectively enhances the quantum vacuum fluctuations of circularly polarized light in a single direction, achieving chirality—a feat that typically requires the use of a strong magnetic field.


The answer, it turns out, is yes. In a breakthrough experiment, scientists have observed signs of anyons in a one-dimensional ultracold gas for the first time. The research, published in Nature, involved teams from the University of Innsbruck, Université Paris-Saclay, and Université Libre de Bruxelles.
To reveal the presence of anyons, the scientists carefully injected and accelerated a mobile impurity into a tightly controlled gas of bosons at near absolute zero.
Absolute zero is the theoretical lowest temperature on the thermodynamic scale, corresponding to 0.00 K (−273.15 °C or −459.67 °F). At this point, atomic motion ceases entirely, and the substance no longer emits or absorbs thermal energy.
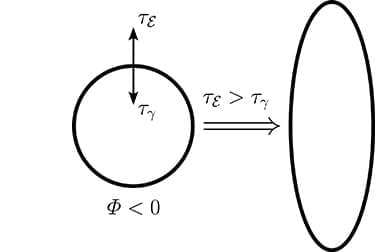
This theoretical and numerical study investigates the impact of electrostatic stresses on the shape of charged water structures (grains) in weakly ionized plasmas. We developed an analytic model to predict the conditions under which a grain in a plasma is deformed. We find that electrostatic stresses can overcome the opposing surface tension stresses on nanometer-scale grains, causing initially spherical clusters to elongate and become ellipsoidal. The exact size limit of the grain for which electrostatic stress will dominate depends on the floating potential, surface tension, and local radius of curvature. Clusters larger than this limit are not affected by electrostatic stresses due to an insufficient number of electrons on the surface. The model is compared to Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations performed with a calculated solvated electron potential on initially spherical grains of 2.5 nm radius charged with 0.5%–1% electrons. We find excellent agreement between MD simulations and the analytic theory. We also carried out Quantum Mechanics (QM) computations showing that the surface tension increases with decreasing size of the water molecule cluster and increases even more with the addition of solvated electrons. This increase in surface tension can hinder the elongation of the grains. Our QM computations also show that on the nanosecond time scale, the binding force of electrons to water molecule clusters is stronger than the electrostatic repulsion between adjacent electrons and thus the cluster behaves as an insulator. However, consideration of the very small conductivity of ice shows that on time scales of a fraction of a second, ice clusters behave as conductors, so their surface may be considered to be at an equipotential.
Scientists have achieved a major breakthrough by creating the world’s first next-generation betavoltaic cell. This advanced power source was made by directly connecting a radioactive isotope electrode to a perovskite absorber layer, a cutting-edge material known for its efficiency.
To boost performance, the team embedded carbon-14-based quantum dots into the electrode and improved the structure of the perovskite layer. These innovations led to a highly stable power output and impressive energy conversion efficiency.
The findings were published in the journal Chemical Communications and led by Professor Su-Il In of the Department of Energy Science & Engineering at DGIST (President Kunwoo Lee).
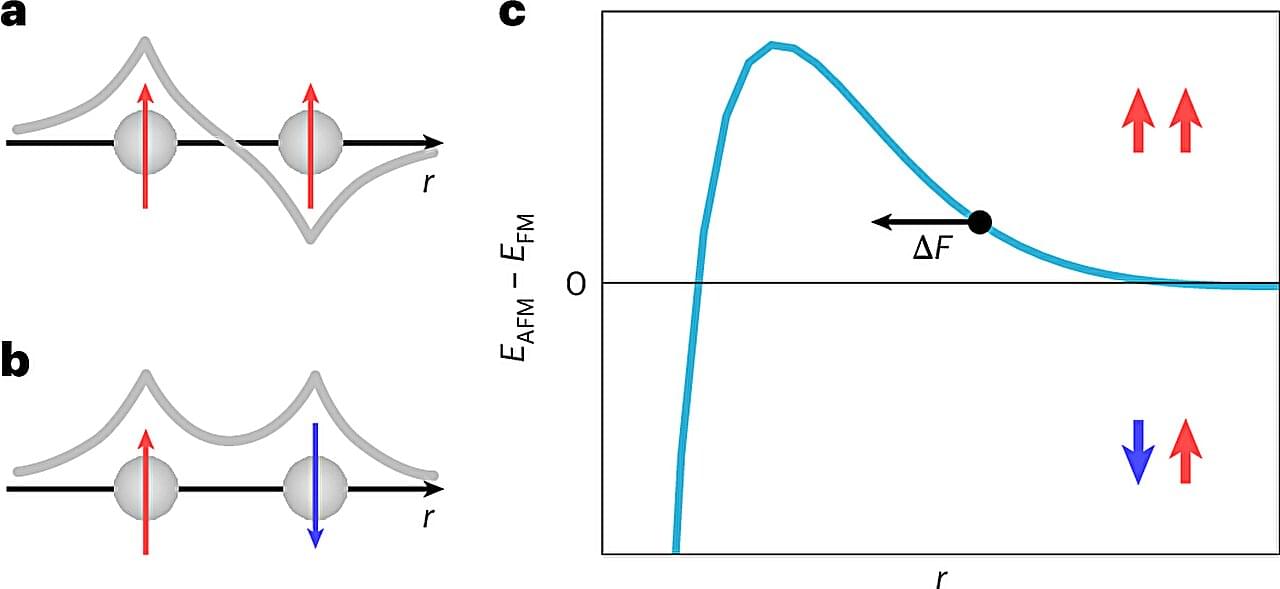
Research from the University of St Andrews has set a new benchmark for the precision with which researchers can explore fundamental physics in quantum materials. The work has implications extending from materials science to advanced computing, as well as confirming a nearly 100-year-old prediction.
The researchers explored magnetoelastic coupling, which is the change in the size or shape of a material when exposed to a magnetic field. It is usually a small effect, but one that has technological consequences.
A team from the School of Physics and Astronomy at the University of St Andrews has now discovered that this effect is remarkably large in a case where one wouldn’t have expected it—in a transition metal oxide. Oxides are a chemical compound containing at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula. High-temperature superconductors are one of the most prominent examples of a transition metal oxide.