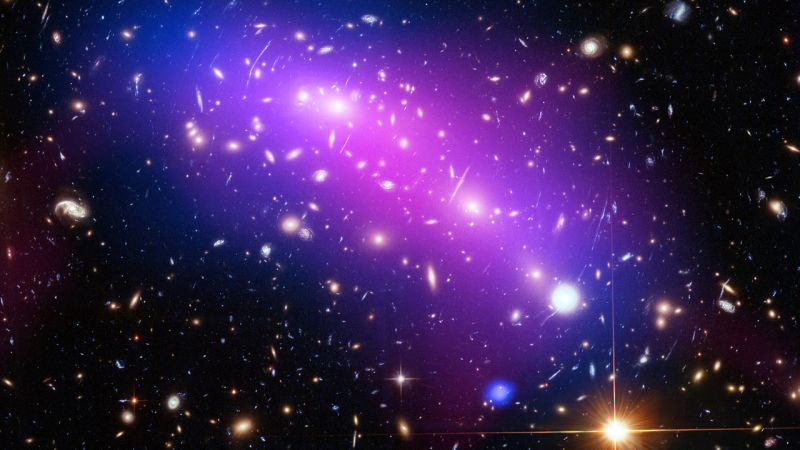
Theoretical physicists and astrophysicists, investigating irregularities in the cosmic microwave background (the ‘afterglow’ of the Big Bang), have found that there is substantial evidence of our universe being a vast and complex hologram. A UK, Canadian and Italian study has provided what researchers believe is the first observational evidence supporting a holographic explanation of the universe. The researchers from the University of Southampton (UK), University of Waterloo (Canada), Perimeter Institute (Canada), INFN, Lecce (Italy) and the University of Salento (Italy) have published their findings in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Category: physics – Page 358

Will the LHC Prove the Existence of Higher Dimensions?
And possibly an elegant Theory of Everything.
Help Me, Obi-Wan! New Hologram Technology Mimics ‘Star Wars’
Princess Leia’s holographic plea in the classic film “Star Wars” inspired researchers to work toward a device that could project real-life sci-fi holograms. Now, the futuristic 3D imaging may be one step closer to reality.
A team of physicists at the Australian National University (ANU) invented a tiny device that creates the highest-quality holographic images ever achieved, the scientists said.
Study lead researcher Lei Wang, a Ph.D. student at the ANU Research School of Physics and Engineering, said he first learned about the concept of holographic imaging from the “Star Wars” movies. However, these futuristic-looking 3D images could be used for more practical ends than sending messages from a galaxy far, far away. [Photos: Microsoft’s HoloLens Transforms Surroundings with Holographic Tech].
Physicists ‘have substantial evidence’ our universe is a HOLOGRAM
The researchers from the University of Southampton, working with colleagues in Canada and Italy, claim there is as much evidence for this theory as for traditional explanations for these irregularities.
A holographic universe, an idea first suggested in the 1990s, is one where all the information, which makes up our 3D ‘reality’is contained in a 2D surface on its boundaries.
Until now the bizarre theory had rarely been tested, but recent mathematical models suggest that the mind-boggling principle could be true.

Scientists Have Finally Created Metallic Hydrogen
In Brief
- By applying 4.95 million atmospheres of pressure to liquid hydrogen, Harvard physicists have claimed they were able to make it metallic, a state of hydrogen that had never existed on Earth before.
- Physicists predict that metallic hydrogen is an authentic superconductor, so if stabilized, it could revolutionize everything from energy storage to rocketry.
As reported back in September, two studies, each with a different approach, were attempting to created metallic hydrogen, and now, more than 80 years after it was predicted to be possible, the Harvard University team has finally managed to produce the elusive state. Physicists Isaac Silvera, who has been working on this problem for 45 years, and Ranga Dias published their study’s results this week in the journal Science.
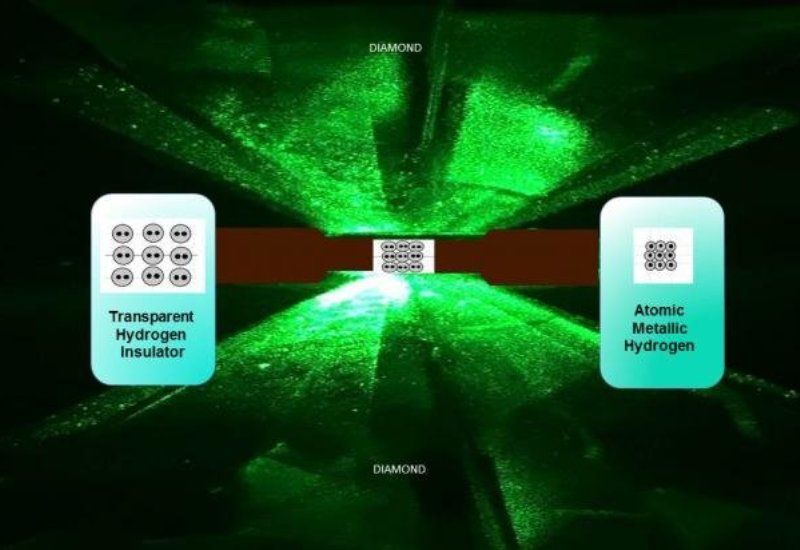
To develop metallic hydrogen, Silvera’s team squeezed two opposing heavy-duty diamonds together to compress gaseous hydrogen, and then they transitioned it into its liquid state by lowering the temperature [hydrogen liquifies at a temperature of −252°C (−423°F)]. They then gradually increased the applied pressure on the solid hydrogen by twisting a steel screw to exert force on the diamond anvil. It was then that changes were noticed.

U.S. scientists could have squeezed hydrogen all the way into a potentially superconducting metal
For over 80 years, scientists all round the world have dreamt of converting hydrogen, the first element of the periodic table, into a metal. And now, after hundreds of failed attempts in the history, scientists from U.S. have finally managed the feat by compressing hydrogen so profoundly that it has turned into a metal!
Back in 1935, physicists Hillard Bell Huntington and Eugene Wigner proposed a theory that hydrogen, which normally exists in a gaseous state, could transform into metallic state once exposed to extreme pressure. Since then many scientists have tried to practically prove the theory — albeit unsuccessfully. However, this discovery, which was published in the journal ‘Science’ on Thursday, is the first confirmation of the theory.
The metallic hydrogen is a potential superconductor, a material with extraordinary electricity conducting capabilities, a quality which makes it a very expensive metal. But it holds the ability of revolutionizing the world of ultra fast super computers, high speed levitation trains, or any other thing which involves conduction of electricity.
Harvard Physicists Say Hydrogen Finally Turns Into Metal, But Not Everyone Is Convinced
Squeezed between two pieces of man-made diamond in the laboratory, hydrogen has finally been transformed into a metallic form that is believed to exist inside planets such as Jupiter, scientists revealed last Thursday.
Metallic hydrogen, deemed the rarest and potentially among the most valuable on Earth, was theorized almost a century ago. If certain theoretical predictions hold true, the hydrogen could turn into a solid metal that can remain solid once crushing pressure is removed. It could also serve as a room-temperature superconductor, conducting electricity sans resistance.
“This is the holy grail of high-pressure physics,” said Harvard physics professor Isaac Silvera, who created the material along with postdoctoral fellow Ranga Dias.