Scientists from the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy (MBI) in Berlin combined state-of-the-art experiments and numerical simulations to test a fundamental assumption underlying strong-field physics. Their results refine our understanding of strong-field processes such as high harmonic generation (HHG) and laser-induced electron diffraction (LIED).
Strong infrared laser pulses can extract an electron from a molecule (ionization), accelerate it away into free space, then turn it around (propagation), and finally collide it with the molecule (recollision). This is the widely used three-step model of strong-field physics. In the recollision step, the electron may, for example, recombine with the parent ion, giving rise to high harmonic generation, or scatter elastically, giving rise to laser-induced electron diffraction.
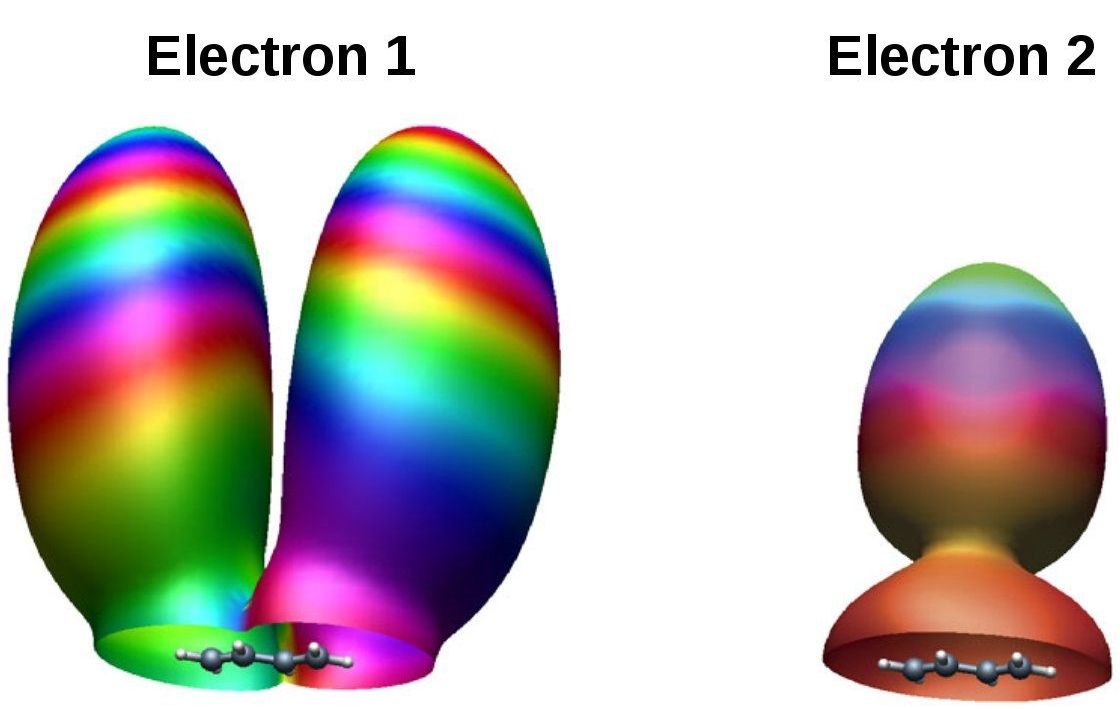
One of the commonly used assumptions underlying attosecond physics is that, in the propagation step, the initial structure of the ionized electron is “washed out”, thus losing the information on the originating orbital. So far, this assumption was not experimentally verified in molecular systems.