Scientists have uncovered some preliminary evidence for a nuclear physics effect first predicted back in the 1970s. The physics universe you’re about to enter into in order to understand it is especially mind-bending.


One of the more well-known rules in physics is that light can only ever go one speed, so long as nothing stands in its way.
But new research has found there could be an interesting exception to this rule, where the mixing of light waves could bring them to a complete standstill.
The discovery hints at new ways of wrangling not just photons but nearly any kind of wave, which could be useful in technology that relies on information sent and stored using light.
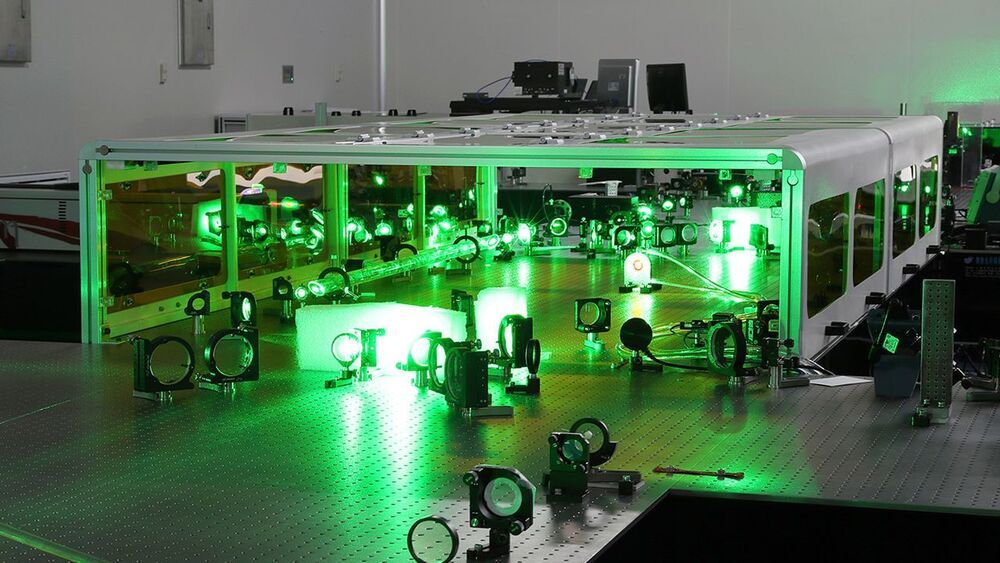



“This unexpected behavior has led to a serious buzz in the scientific community, with astronomers trying to come up with explanations as to what type of physics could be driving these emissions.”
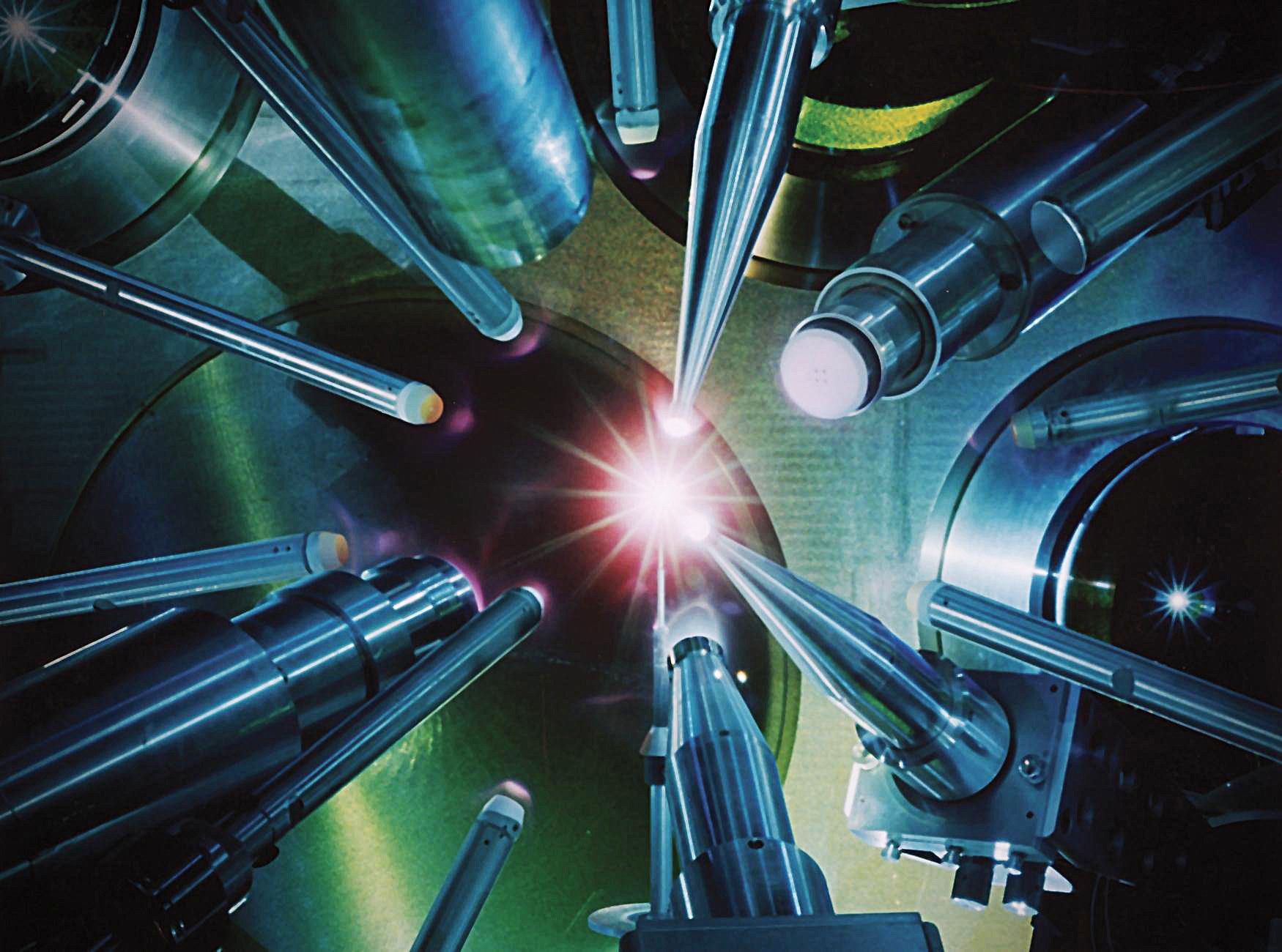
The development of ultra-intense lasers delivering the same power as the entire U.S. power grid has enabled the study of cosmic phenomena such as supernovae and black holes in earthbound laboratories. Now, a new method developed by computational astrophysicists at the University of Chicago allows scientists to analyze a key characteristic of these events: their powerful and complex magnetic fields.
In the field of high-energy density physics, or HEDP, scientists study a wide range of astrophysical objects—stars, supermassive black holes at the center of galaxies and galaxy clusters—with laboratory experiments as small as a penny and lasting only a few billionths of a second. By focusing powerful lasers on a carefully designed target, researchers can produce plasmas that reproduce conditions observed by astronomers in our sun and distant galaxies.
Planning these complex and expensive experiments requires large-scale, high-fidelity computer simulation beforehand. Since 2012, the Flash Center for Computational Science of the Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics at UChicago has provided the leading open computer code, called FLASH, for these HEDP simulations, enabling researchers to fine-tune experiments and develop analysis methods before execution at sites such as the National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory or the OMEGA Laser Facility in Rochester, N.Y.
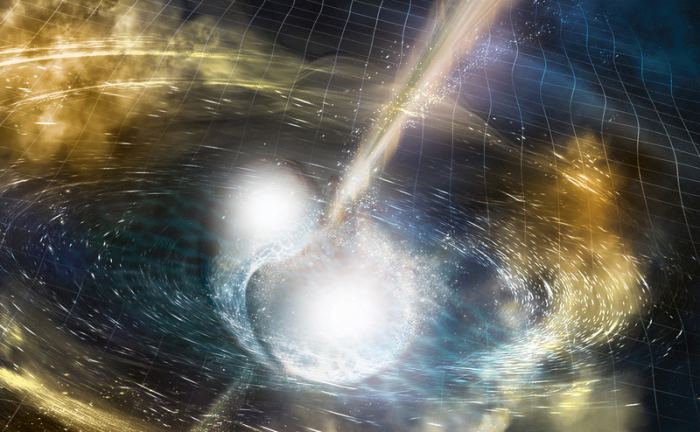
Each year, Science’s editors and writers highlight a top research achievement as their Breakthrough of the Year. For 2017, the honor goes to the first full observation of a neutron-star merger, made possible by detecting gravitational waves created by the stars as they spiraled into each other. But there a lot of other advances to talk about, from the oldest ice to the newest ape. Check them all out in this video rundown.
A video compilation of some of the biggest advances of 2017.
Excitonium has a team of researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign… well… excited! Professor of Physics Peter Abbamonte and graduate students Anshul Kogar and Mindy Rak, with input from colleagues at Illinois, University of California, Berkeley, and University of Amsterdam, have proven the existence of this enigmatic new form of matter, which has perplexed scientists since it was first theorized almost 50 years ago.
The team studied non-doped crystals of the oft-analyzed transition metal dichalcogenide titanium diselenide (1T-TiSe2) and reproduced their surprising results five times on different cleaved crystals. University of Amsterdam Professor of Physics Jasper van Wezel provided crucial theoretical interpretation of the experimental results.
So what exactly is excitonium?
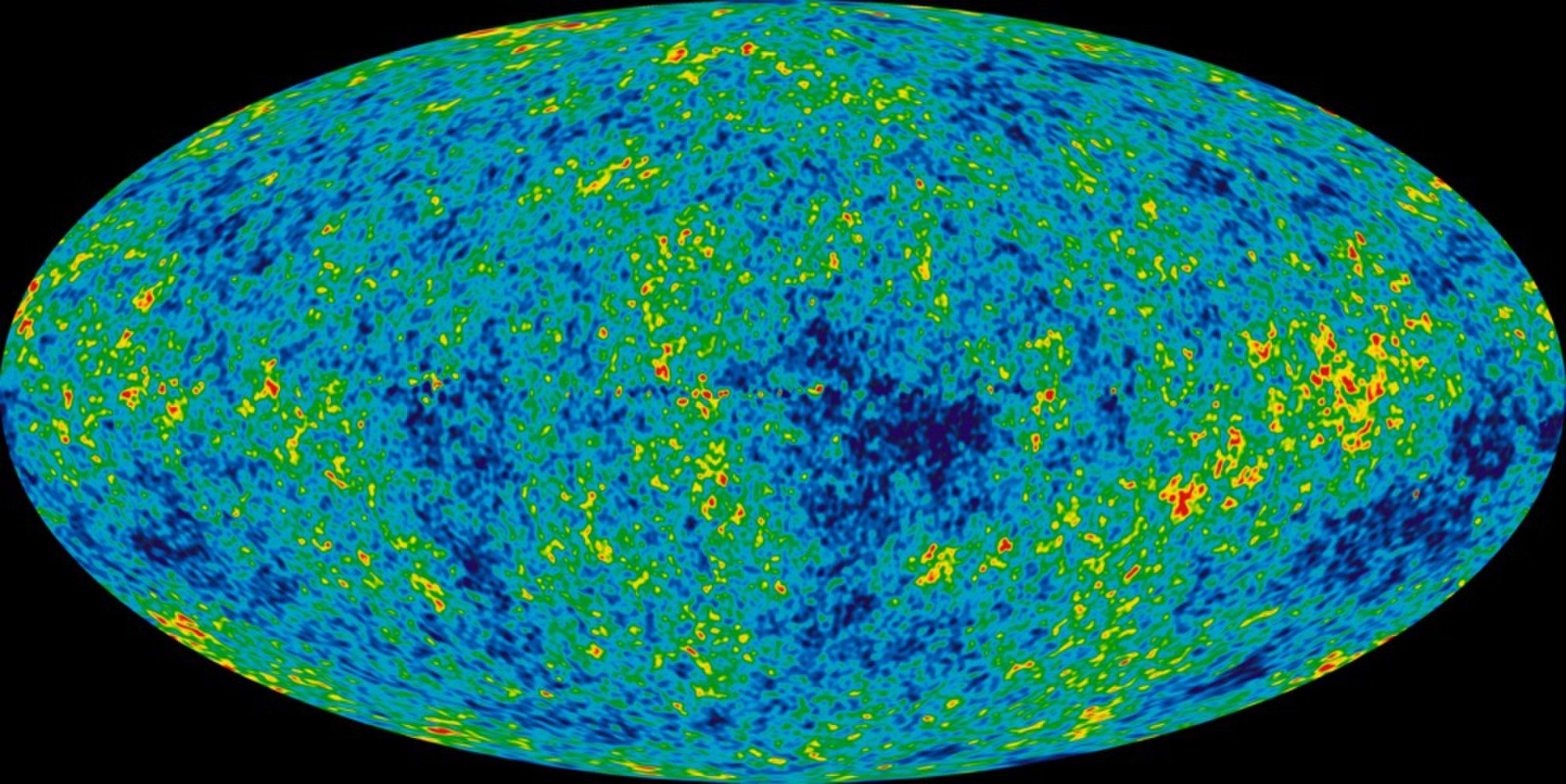

A team of researchers who helped shape our understanding of the origin, evolution and nature of the cosmos is now $3 million richer.
Those folks worked on NASA’s WMAP space mission, which was awarded the 2018 Breakthrough Prize in Fundamental Physics today (Dec. 3) during a ceremony in Palo Alto, California.
From 2001 to 2009, WMAP mapped the cosmic microwave background (CMB) — the light left over from the Big Bang — with unprecedented precision. This work allowed scientists to nail down the age of the universe (about 13.8 billion years), its rate of accelerating expansion (roughly 70 kilometers per second per megaparsec) and its basic composition (about 5 percent “normal” matter, 24 percent dark matter and 71 percent dark energy). [Dark Matter and Dark Energy: The Mystery Explained (Infographic)].
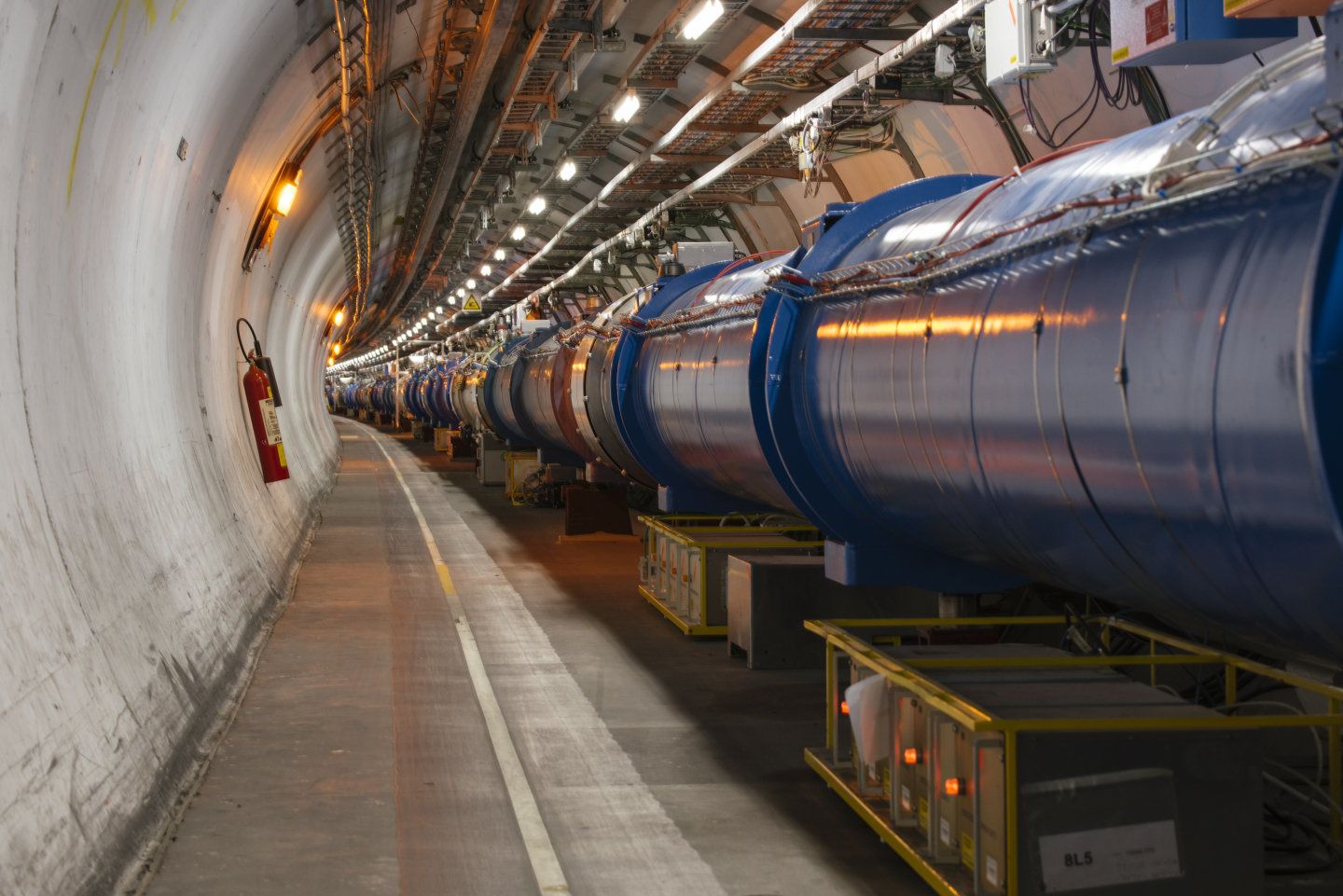

It’s the end of the road for the protons this year after a magnificent performance from the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). On Friday, the final beams of the 2017 proton run circulated in the LHC. The run ended, as it does every year, with a round up of the luminosity performance, the indicator by which the effectiveness of a collider is measured and on which the operators keep a constant eye.
The LHC has far exceeded its target for 2017. It has provided its two major experiments, ATLAS and CMS, with 50 inverse femtobarns of data, i.e. 5 billion million million collisions. The inverse femtobarn (fb-1) is the unit used to measure integrated luminosity, or the cumulative number of potential collisions over a given period.
This result is all the more remarkable because the machine experts had to overcome a serious setback. A vacuum problem in the beam pipe of a magnet cell limited the number of bunches that could circulate in the machine. Several teams were brought in to find a solution. Notably, the arrangement of the bunches in the beams was changed. After a few weeks, luminosity started to increase again.