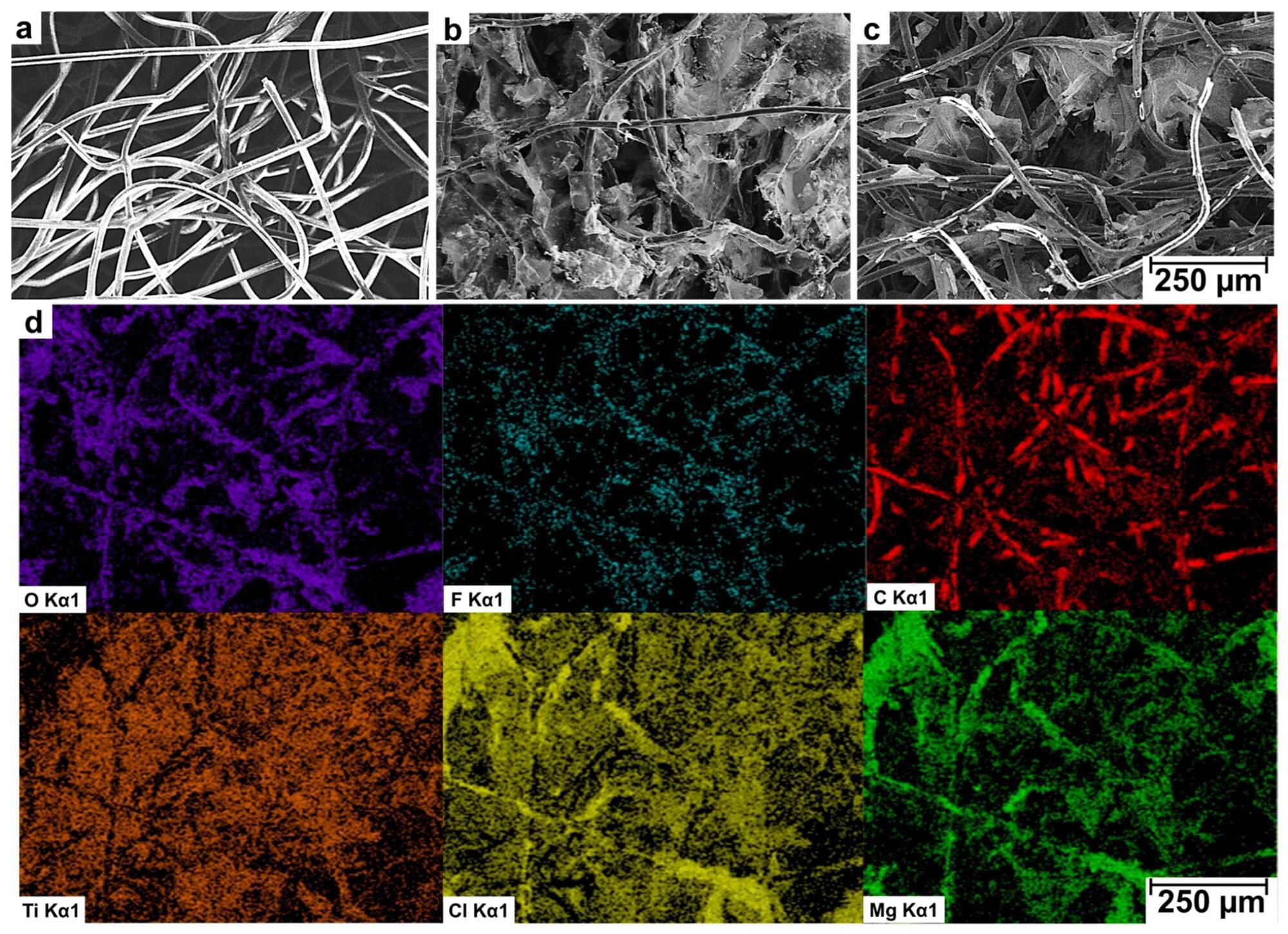
Despite improvements to air filtration technology in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, some of the smallest particles—those of automobile and factory emissions—can still make their way through less efficient, but common filters. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from Drexel University’s College of Engineering have introduced a new way to improve textile-based filters by coating them with a type of two-dimensional nanomaterial called MXene.
Recently published in the journal C—Journal of Carbon Research, the team’s research reports that a non-woven polyester textile—a low-cost material with low filtration efficiency—coated with a thin layer of MXene nanomaterial can turn it into a potent filter capable of pulling some of the finest nanoparticles from the air.
“It can be challenging for common filters to contend with particles less than 100 nanometers, which include those emitted by industrial processes and automobiles,” said Michael Waring, Ph.D., a professor in Drexel’s College of Engineering, and co-author of the research. “Being able to augment a filter, through a simple coating process, to make it effective against these emissions is a significant development.”