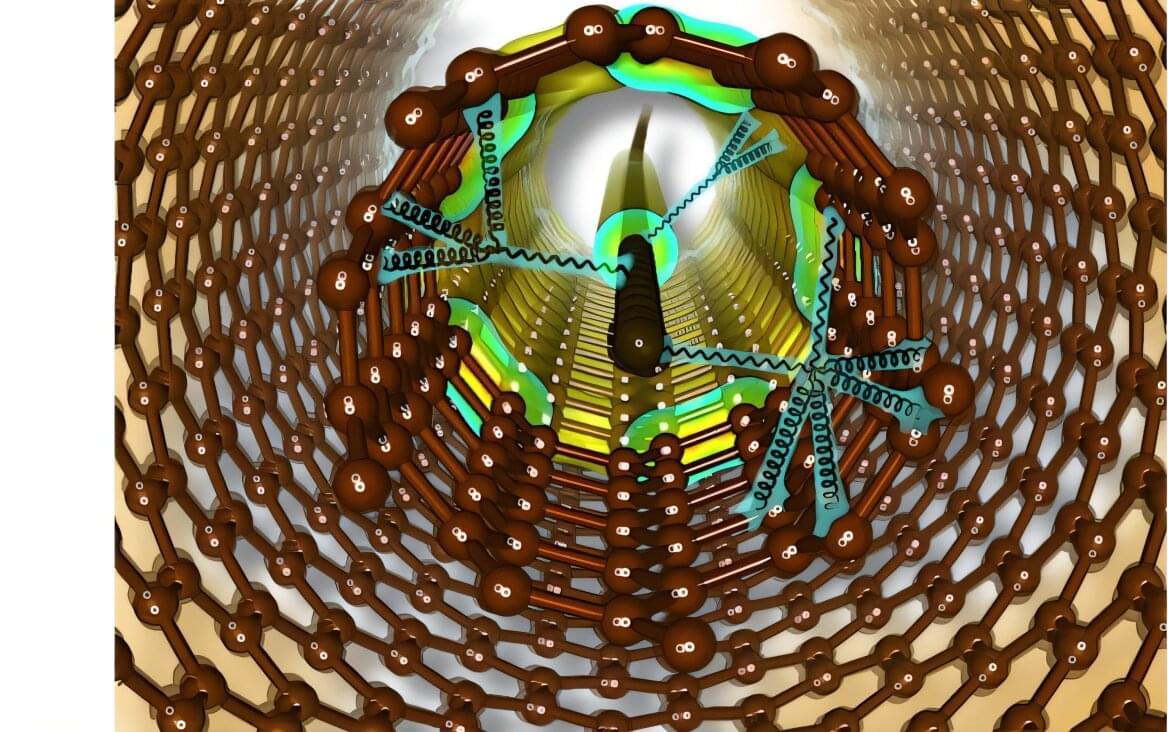
For the design of future materials, it is important to understand how the individual atoms inside a material interact with each other quantum mechanically. Previously inexplicable vibrational states between carbon chains (carbyne) and nanotubes have puzzled materials scientists.
Researchers from Austria, Italy, France, China and Japan led by the University of Vienna have now succeeded in getting to the bottom of this phenomenon with the help of Raman spectroscopy, innovative theoretical models and the use of machine learning. The results, published in Nature Communications, show the universal applicability of carbyne as a sensor due to its sensitivity to external influences.
For the design of future materials, it is important to understand how matter interacts on an atomic scale. These quantum mechanical effects determine all macroscopic properties of matter, such as electrical, magnetic, optical or elastic properties. In experiments, scientists use Raman spectroscopy, in which light interacts with matter, to determine the vibrational eigenstates of the atomic nuclei of the samples.