Physicists have seen signs that a mystery force is interacting with other particles in a manner never witnessed before. It may explain some of the deepest physics puzzles.



Two teams of researchers have independently found that there exists a certain type of graphene system where electrons freeze as the temperature rises. The first team, with members from Israel, the U.S. and Japan, found that placing one layer of graphene atop another and then twisting the one on top resulted in a graphene state in which the electrons would freeze as temperatures rose. And in attempting to explain what they observed, they discovered that the entropy of the near-insulating phase was approximately half of what would be expected from free-electron spins. The second team, with members from the U.S., Japan and Israel, found the same graphene system and in their investigation to understand their observations, they noted that a large magnetic moment arose in the insulator. Both teams have published their results in the journal Nature. Biao Lian with Princeton University has published a News and Views piece outlining the work by both teams in the same journal issue.
As temperatures around most substances rise, the particles they are made of are excited. This results in solids melting to liquids and liquids turning to a gas. This is explained by thermodynamics—higher temperatures lead to more entropy, which is a description of disorder. In this new effort, both teams found an exception to this rule—a graphene system in which electrons freeze as the temperature rises.
The graphene system was very simple. Both teams simply laid one sheet of graphene on top of another and then twisted the top sheet very slightly. But it had to be twisted at what they describe as the “magic angle,” describing a twist of just 1 degree. The moiré pattern that resulted led to lower velocity of the electrons in the system, which in turn led to more resistance, bringing the system close to being an insulator.


Researchers have used a quantum mechanical property to overcome some of the limitations of conventional holograms. The new approach, detailed in Nature Physics, employed quantum entanglement, allowing two photons to become a single “non-local particle.” A series of entangled photon pairs is key to producing new and improved holograms.
Classical holograms work by using a single light beam split into two. One beam is sent towards the object you’re recreating and is reflected onto a special camera. The second beam is sent directly onto the camera. By measuring the differences in light, its phase, you can reconstruct a 3D image. A key property in this is the wave’s coherence.
The quantum hologram shares some of these principles but its execution is very different. It starts by splitting a laser beam in two, but these two beams will not be reunited. The key is in the splitting. As you can see in the image below, the blue laser hits a nonlinear crystal, which creates two beams made of pairs of entangled photons.

PARIS: Scientists believe they may have discovered a “brand-new force of nature” at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider that could explain why certain atomic particles behave unexpectedly and which may transform our understanding the rudiments of physics.
Authors of the research said this week that their results should “get physicists’ hearts beating just a little faster” after they discovered evidence of a “brand-new” type of particle.
Since its inception over a decade ago, the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) has sought to delve into the secrets of the universe by studying the smallest discreet particles of matter as they collide at nearly the speed of light.

This is the best estimate scientists have made for the size of the invisible Higgs sector. The next step is to collect more data and hone their techniques to narrow in on these invisible decays.
“It’s like looking at something very small,” Rifki says. “Right now, we can’t see anything other than what we already know. But that doesn’t mean there is nothing new there. It could just mean that we need a more powerful lens.”
Lindert sees this collaboration as a good example of what theorists and experimentalists can accomplish when they combine their skills and work together.
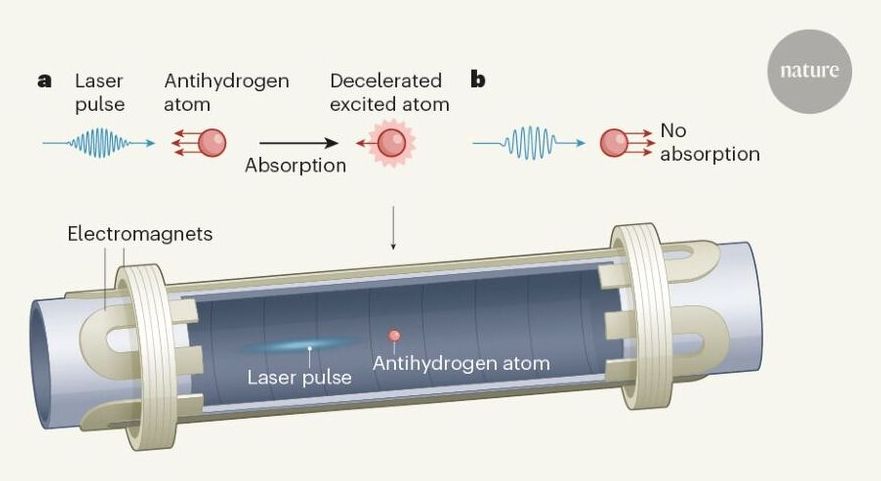
A step towards ultra-precise measurements of antihydrogen.
These two constraints are so fundamental that it would be difficult to formulate a consistent understanding of nature without them. Nevertheless, it is worth testing whether they really hold up in ultra-precise measurements carried out using the most modern technologies, because any deviation, however small, would force scientists to radically rethink the basis of our theories of physics. Writing in Nature, Baker et al.1 (members of the ALPHA collaboration) report a major step towards this goal. They have slowed down atoms of antihydrogen — the antimatter counterpart of hydrogen — to unprecedentedly low velocities by bathing them in a beam of ultraviolet laser light. This could allow measurements of the atoms to be made with exceptionally high precision.
Antihydrogen is the simplest stable atom that consists only of antimatter particles, namely an antiproton and an antielectron (a positron). Measurements of antihydrogen therefore provide an ideal way to test the symmetry between matter and antimatter, but such experiments present formidable obstacles. In 1995, 11 antihydrogen atoms were produced from reactions in a particle accelerator at CERN, Europe’s particle-physics laboratory near Geneva, Switzerland, and hurtled down a 10-metre-long vacuum tube at nine-tenths of the speed of light2. Each atom existed for barely a few tens of nanoseconds before being destroyed by striking a particle detector.
Much of the ensuing research into antihydrogen has involved inventing new ways of producing samples of increasingly slower-moving atoms. This was eventually achieved by confining and mixing clouds of antiprotons and positrons in magnetic fields that acted as ion traps to produce antihydrogen atoms. The atoms were then confined by another complex configuration of magnetic fields that acted as a neutral-atom trap3,4. The ALPHA collaboration at CERN’s Antiproton Decelerator facility can now routinely trap 1000 antihydrogen atoms for many hours in this way. This has allowed an atomic frequency of antihydrogen, which corresponds to the energy of a characteristic atomic transition, to be measured5 with a fractional precision of 2 parts in 1012. No deviation from the corresponding frequency of hydrogen was observed, which is exactly the outcome expected from CPT symmetry.
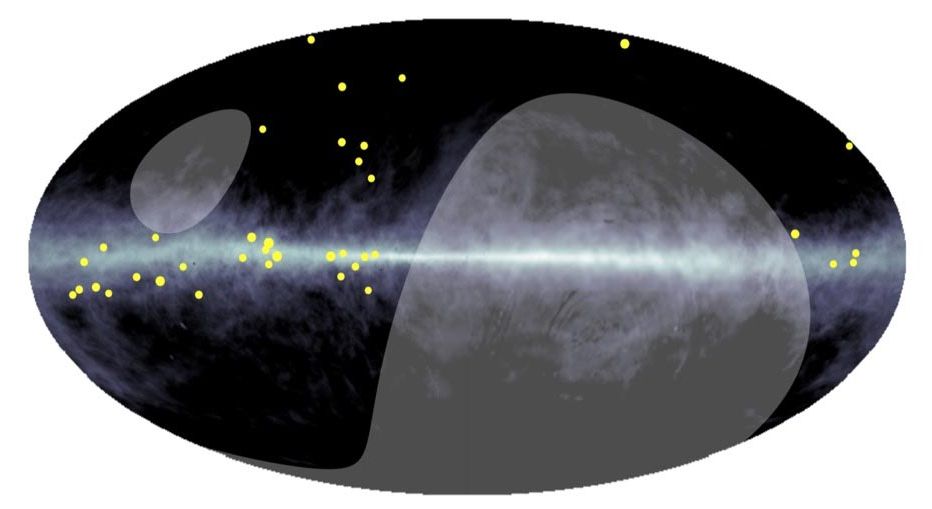
The Tibet ASγ experiment, a China-Japan joint research project on cosmic-ray observation, has discovered ultra-high-energy diffuse gamma rays from the Milky Way galaxy. The highest energy detected is estimated to be unprecedentedly high, nearly 1 Peta electronvolts (PeV, or one million billion eV).
Surprisingly, these gamma rays do not point back to known high-energy gamma-ray sources, but are spread out across the Milky Way (see Figure 1).
Scientists believe these gamma rays are produced by the nuclear interaction between cosmic rays escaping from the most powerful galactic sources (“PeVatrons”) and interstellar gas in the Milky Way galaxy. This observational evidence marks an important milestone in revealing the origin of cosmic rays, which has puzzled mankind for more than a century.
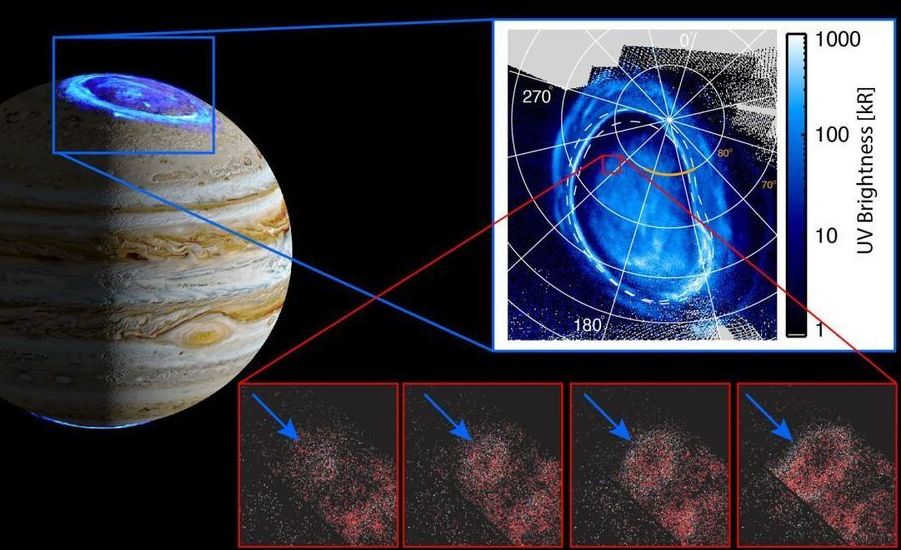
NASA’s Juno spacecraft captured a new aurora feature on Jupiter that is characterized by faint ring-shaped emissions that expand rapidly over time. These auroral emissions are believed to be triggered by charged particles coming from the edge of the planet’s magnetosphere.
NASA’s Juno mission has detected new auroral emissions on Jupiter which appear to ripple over the planet’s poles.
The Ultraviolet Spectrograph (UVS) on the Juno spacecraft captured this glowing phenomenon, which is characterized by faint ring-shaped emissions that expand rapidly over time at speeds between 2 and 4.8 miles per second (3.3 and 7.7 kilometers per second). Researchers from the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), where Juno’s UVS instrument was built, suggest these auroral emissions are triggered by charged particles coming from the edge of Jupiter’s massive magnetosphere, according to a statement from the institute.
The European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) involves 23 countries, 15000 researchers, billions of dollars a year, and the biggest machine in the world: the Large Hadron Collider. Even with so much organizational and mechanical firepower behind it, though, CERN and the LHC are outgrowing their current computing infrastructure, demanding big shifts in how the world’s biggest physics experiment collects, stores and analyzes its data. At the 2021 EuroHPC Summit Week, Maria Girone, CTO of the CERN openlab, discussed how those shifts will be made.
The answer, of course: HPC.
The Large Hadron Collider – a massive particle accelerator – is capable of collecting data 40 million times per second from each of its 150 million sensors, adding up to a total possible data load of around a petabyte per second. This data describes whether a detector was hit by a particle, and if so, what kind and when.