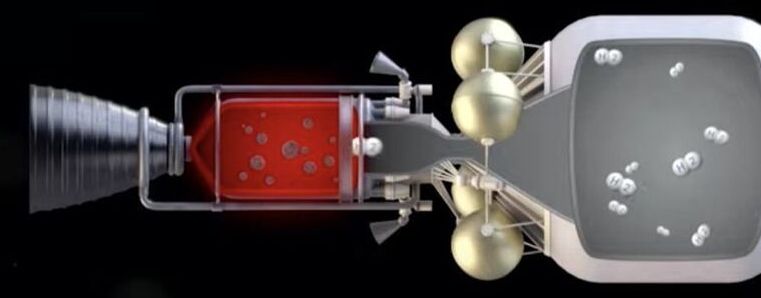
Tensions are flaring between the powers of the world evoking many to ponder the worst. Yet some are already wondering how to manage a path to peace. Looks like that consideration needs a bit more work! Watch and find out!
Support my channel by clicking the links below (or copy and paste in your browser) and shopping with my partner programs:
See the Special Deals at My Patriot Supply: www.PrepWithGreg.com.
Awesome deals for long term food supplies!
Green Gregs has teamed up with True Leaf Market to bring you a great selection of seed for your spring planting. Check it out: http://www.pntrac.com/t/TUJGRklGSkJGTU1IS0hCRkpIRk1K
To join Green Greg’s Tribe movement email: [email protected].
Put Tribe in the Title.
To join the Freedom Restoration Foundation (FRF) email: [email protected].
Put Freedom in the Title.
FRF On FaceBook: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1017608155367475
FRF On MeWe: https://mewe.com/group/5f809034e1276c18d7f3497d.
Buy worms at: Shutting down temporarily (www.GreenGregs.com will be back)