A massive study of medical and genetic data shows that people with a particular version of a gene involved in immune response had a lower risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Category: neuroscience – Page 606

New insights on why epilepsy develops, potential treatments in world’s largest genetic study
Specific changes in our DNA that increase the risk of developing epilepsy have been discovered, in the largest genetic study of its kind for epilepsy coordinated by the International League Against Epilepsy, which includes scientists from the University of Melbourne and WEHI (Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research).
Published today in Nature Genetics, this research advances our understanding of why epilepsy develops and could inform the development of new epilepsy treatments. The research was produced by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) Consortium on Complex Epilepsies.
Epilepsy is a common brain disorder estimated to effect more than 50 million people worldwide, where nerve cell activity in the brain is disturbed, causing seizures. It has a genetic component that sometimes runs in families. In this study, researchers compared the DNA from almost 30,000 people with epilepsy to the DNA of 52,500 people without epilepsy from around the world. The differences between the two groups highlighted areas of DNA that may be involved in the development of epilepsy.
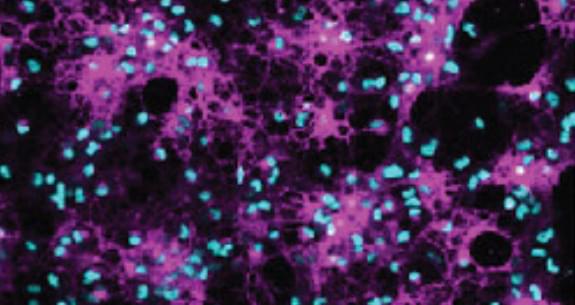
A new biological mechanism to regenerate and repair myelin
A neonatal hypoxic-injury animal model revealed that CK2α mediated Daam2 phosphorylation, which plays a protective role in developmental and behavioral recovery after neonatal hypoxia, a form of brain injury seen in cerebral palsy and other conditions. Additionally, it facilitates remyelination after white matter injury in adult animals.
Together, these findings have identified a novel regulatory node connecting CK2α and Daam2 in the Wnt pathway that regulates stage-specific oligodendrocyte development and offers insights into a new biological mechanism to regenerate myelin.
“This study opens exciting therapeutic avenues we could develop in the future to repair and restore myelin, which has the potential to alleviate and treat several neurological issues that are currently untreatable,” Lee said.
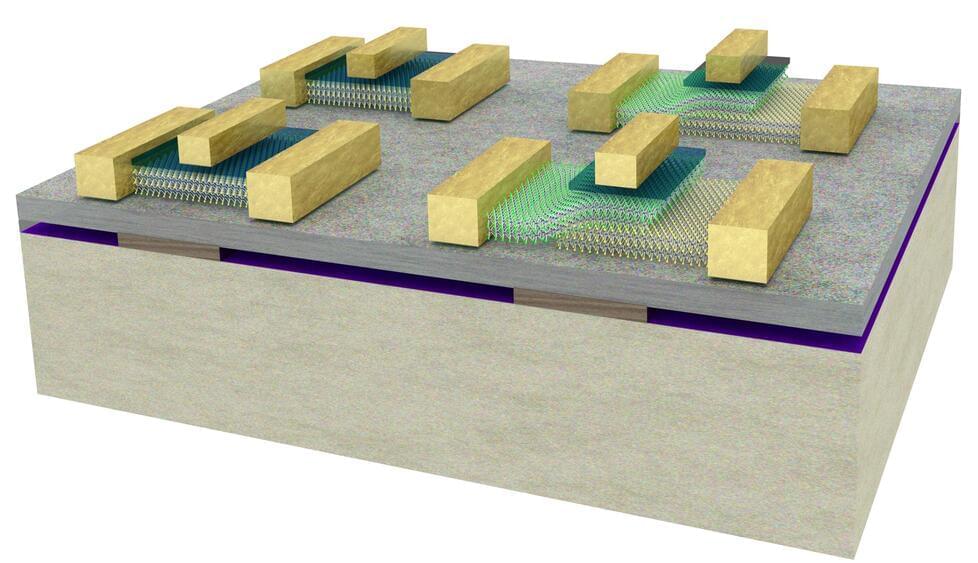
Analog and digital: The best of both worlds in one energy-efficient system
We live in an analog world of continuous information flow that is both processed and stored by our brains at the same time, but our devices process information digitally in the form of discrete binary code, breaking the information into little bits (or bites).
Researchers at EPFL have revealed a pioneering technology that combines the potential of continuous analog processing with the precision of digital devices. By seamlessly integrating ultra-thin, two-dimensional semiconductors with ferroelectric materials, the research, published in Nature Electronics, unveils a novel way to improve energy efficiency and add new functionalities in computing. The new configuration merges traditional digital logic with brain-like analog operations.
The innovation from the Nanoelectronics Device Laboratory (Nanolab), in collaboration with Microsystems Laboratory, revolves around a unique combination of materials leading to brain-inspired functions and advanced electronic switches, including the standout negative capacitance Tunnel Field-Effect Transistor (TFET).

The collective intelligence of cells during morphogenesis as a model for cognition beyond the brain
Michael Levin talk for the Mind, Technology, and Society (MTS) talk series at UC Merced on January 23, 2023. Abstract: Each of us makes the remarkable journey from the physics and chemistry of a quiescentunfertilized egg to that of a complex human being. How can we understand the continuousprocesses that scale up minds from the tiny physiological competencies of single cells to the large-scale metacognitive capacities of large brains? Here, I will describe a framework known as TAME-Technological Approach to Mind Everywhere — which enables identifying, understanding, andrelating to unconventional cognitive agents. I will use the example of the collective intelligence ofcells during morphogenesis to illustrate how we can begin to widen the lessons of multiscale neuroscience well beyond neurons. This will be essential as we head into a future that will bepopulated by a wide range of evolved, designed, and hybrid beings with novel bodies and novelminds. I will conclude with a case study of our new synthetic biorobot (Xenobots) and a discussionof the implications of these ideas for evolution, biomedicine, and ethics.
Michael Levin: Cognition and diverse intelligence in non-neural cellular collectives
Consciousness is usually ascribed to a specific set of mechanisms and functional capabilities of the complex brain. Importantly, those mechanisms (ion channels, electrical networks, neurotransmitter machinery) long pre-date the evolutionary innovation of nervous systems. Moreover, the algorithms and competencies such as memory, decision-making, and information integration likewise have an ancient evolutionary origin: before they controlled moving the body through 3D space, electrical networks moved body configurations through anatomical morphospace. In this talk, I will describe how we view the morphogenesis during embryonic development and regeneration as the behavior of a collective intelligence, which has many problem-solving capacities. I will describe the tools we have developed, paralleling neuroscientists’ attempts to read and write mental content by control of electrophysiology, to decode and re-write the pattern memories of the body. This has significant implications not only for biomedicine and evolutionary biology, but also for questions about consciousness and the scaling of coherent Selves from agential materials. I will conclude with some conjectures about what this new field offers the science of consciousness, in the form of new embodied living creatures that are outside the natural evolutionary stream of Earth, and the quest for theories of consciousness.-https://www.drmichaellevin.org/ Participate in our online research survey-Survey on Diverse intelligence-https://tufts.qualtrics.com/jfe/form/SV_eE51vKE34q3hexo (takes 9 minutes). Thank you.
Edited by Emilio Manzotti.
https://github.com/emilim/

Virtual Reality for Supporting the Treatment of Depression and Anxiety: Scoping Review
Conclusions: Most studies demonstrated the use of VR to be effective for supporting the treatment of anxiety or depression in a range of settings and recommended its potential as a tool for use in a clinical environment. Even though standalone headsets are much easier to work with and more suitable for home use, the shift from tethered VR headsets to standalone headsets in the mental health environment was not observed. All studies that looked at the use of CBT either in vivo or in a virtual environment found it to be effective in supporting the treatment of anxiety or depression.
Keywords: CBT; anxiety; depression; mental health; virtual reality.
©Nilufar Baghaei, Vibhav Chitale, Andrej Hlasnik, Lehan Stemmet, Hai-Ning Liang, Richard Porter. Originally published in JMIR Mental Health (https://mental.jmir.org), 23.09.2021.
VR Trips Help Treat Depression in the Elderly
Like this video about how Viva Vita addresses loneliness and depression in the elderly using VR. Subscribe here: https://freeth.ink/youtube-subscribe-depressionintheelderly.
Watch the next video in our series on virtual reality therapy: https://youtu.be/IZE41KejIBw.
In the United States, about six million people over the age of 65 experience late life depression and about one-third of seniors feel lonely.
Viva Vita is taking a novel approach to addressing both loneliness and depression in the elderly population.
The organization provides virtual reality excursions for seniors to help them break through personal limitations and find enjoyment exploring new settings.
At first glance, virtual reality for seniors might seem like a gimmick, but early studies of VR for depression, chronic pain, and other ailments are quite promising.
The biological switch that could turn neuroplasticity on and off in the brain
The Conversation Weekly podcast is taking a short break in August. In the meantime, we’re bringing you extended versions of some of our favourite interviews from the past few months.
This week, how researchers discovered a biological switch that could turn on and off neuroplasticity in the brain – the ability of neurons to change their structure. We speak to Sarah Ackerman, a postdoctoral fellow at the Institute of Neuroscience and Howard Hughes Medical Institute at the University of Oregon, about what she and her team have found and why it matters.
This episode of The Conversation Weekly features an extended version of an interview first published on April 29. The Conversation Weekly is produced by Mend Mariwany and Gemma Ware, with sound design by Eloise Stevens. Our theme music is by Neeta Sarl. You can sign up to The Conversation’s free daily email here. Full credits for this episode available here.
Further reading: Astrocyte cells in the fruit fly brain are an on-off switch that controls when neurons can change and grow, by Sarah DeGenova Ackerman, University of OregonSwimming gives your brain a boost – but scientists don’t know yet why it’s better than other aerobic activities, by Seena Mathew, University of Mary Hardin-BaylorWhat is brain plasticity and why is it so important?, by Duncan Banks, The Open University.