A study finds that microglia with mutant TREM2 protein reduce brain circuit connections, promote inflammation, and contribute to Alzheimer’s.


Rapid-acting antidepressants, including ketamine, scopolamine and psilocybin, have been found to have immediate and lasting positive effects on mood in patients with major depressive disorder but how these effects arise is unknown. New research led by the University of Bristol explored their neuropsychological effects and found that all three of these drugs can modulate affective biases associated with learning and memory.
The paper, published in Science Translational Medicine was carried out in collaboration with researchers at Compass Pathways, Boehringer Ingelheim, and the University of Cambridge.
Negative affective biases are a core feature of major depressive disorder. Affective biases occur when emotions alter how the brain processes information and negative affective biases are thought to contribute to the development and continuation of depressed mood.
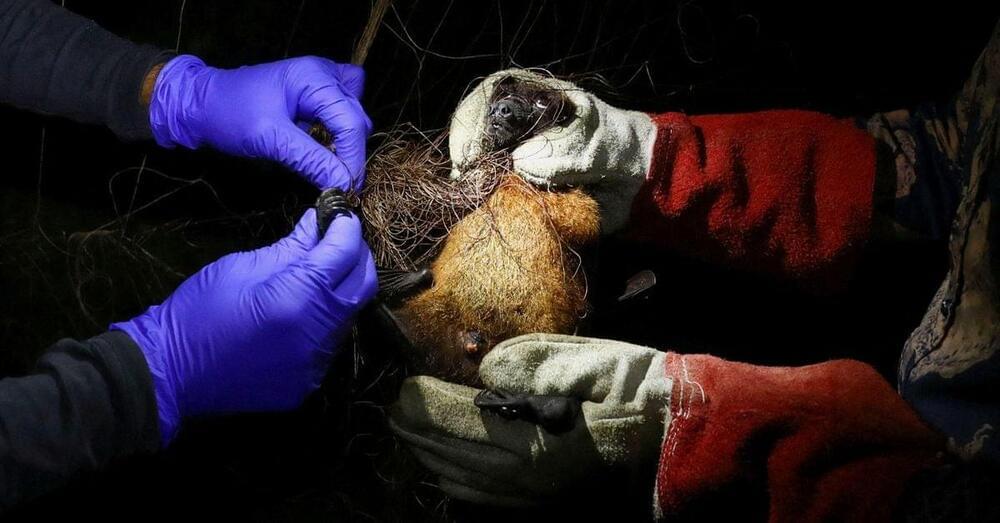

Jan 11 (Reuters) — The University of Oxford said on Thursday it had begun human testing of an experimental vaccine against the brain-swelling Nipah virus that led to outbreaks in India’s Kerala state and other parts of Asia.
There is no vaccine yet for the deadly virus. Nipah was first identified about 25 years ago in Malaysia and has led to outbreaks in Bangladesh, India and Singapore.
The first participants in the Oxford trial received doses of the vaccine over the last week. The shot is based on the same technology as the one used in AstraZeneca (AZN.L) and Serum Institute of India’s COVID-19 shots.

Ancient DNA helps explain why northern Europeans have a higher risk of multiple sclerosis than other ancestries: It’s a genetic legacy of horseback-riding cattle herders who swept into the region about 5,000 years ago.
The findings come from a huge project to compare modern DNA with that culled from ancient humans’ teeth and bones — allowing scientists to trace both prehistoric migration and disease-linked genes that tagged along.
When a Bronze Age people called the Yamnaya moved from the steppes of what are now Ukraine and Russia into northwestern Europe, they carried gene variants that today are known to increase people’s risk of multiple sclerosis, researchers reported Wednesday.
In my paper, “A Case for Physicalism about the Human Mind,” I didn’t attempt to defend physicalism about human mentality (henceforth, just physicalism) against the many objections that philosophers, and others, have made to it. Instead, I tried to assemble positive evidence that physicalism is true, while insisting that no aspect of human behavior, including human linguistic behavior, makes it necessary to adopt any kind of dualism about human mentality. In their reply to my paper, Professors Taliaferro and Goetz (henceforth, TG) don’t engage in any detail with my positive case for physicalism[1], and they offer no examples of human behavior that can’t be explained unless some kind of dualism is assumed. Their main objection to my paper is, rather, that, because it only takes account of evidence “from the third-person point of view,” it entirely overlooks “the first-person point of view,” which, they hold, shows us that human mentality has certain features incompatible with physicalism. Examples of such features would be that “a choice is an uncaused mental event,” and that “a reason is a purpose that provides an ultimate and irreducible teleological explanation of that choice.” In my reply to TG, I’ll respond to this objection only; I won’t take up every disagreement I have with TG’s reply.
Before I can respond to TG’s main objection, however, I must clarify it. Since “the first-person point of view” is presumably just the point of view provided by introspection, TG’s main objection must be that introspection of one’s mental states somehow shows one that human mentality has certain features incompatible with physicalism. However, it’s important to distinguish between the following two claims:
(TG1) By introspecting one’s own (say) choices, one acquires some reason to think that they are uncaused mental events.

“We included 151 adults ages 21 to 70 years old with chronic back pain. We found that 66% of participants reported being pain-free or nearly pain-free after pain reprocessing therapy, compared with 20% of people who received a placebo.”
Understanding that chronic back pain originates from within the brain could lead to quicker recovery, a new study finds.
New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience has found an association between a reduction in gray matter in the brain and early onset psychosis (EOP).
The study, published in Molecular Psychiatry, is the largest ever brain imaging study in EOP and has provided unprecedented levels of detail about the illness. It shows that in contrast to other mental health disorders, people with EOP have a reduced volume of gray matter across nearly all regions of their brain. Researchers hope that this detailed mapping could be used to assist in future diagnosis, as well as to track the effects of treatment in patients with EOP.
EOP occurs before the age of 18 during a critical period of development in the brain. Individuals diagnosed with the illness are likely to experience severe and long-lasting symptoms that respond less well to treatment. Despite this, research into EOP has been limited in sample size and statistical power.
Adults with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) have smaller cerebellums, according to new research from a Duke-led brain imaging study.
The cerebellum, a part of the brain well-known for helping to coordinate movement and balance, can influence emotion and memory, which are impacted by PTSD. What isn’t known yet is whether a smaller cerebellum predisposes a person to PTSD or PTSD shrinks the brain region.
“The differences were largely within the posterior lobe, where a lot of the more cognitive functions attributed to the cerebellum seem to localize, as well as the vermis, which is linked to a lot of emotional processing functions,” said Ashley Huggins, Ph.D., the lead author of the report who helped carry out the work as a postdoctoral researcher at Duke in the lab of psychiatrist Raj Morey, M.D.
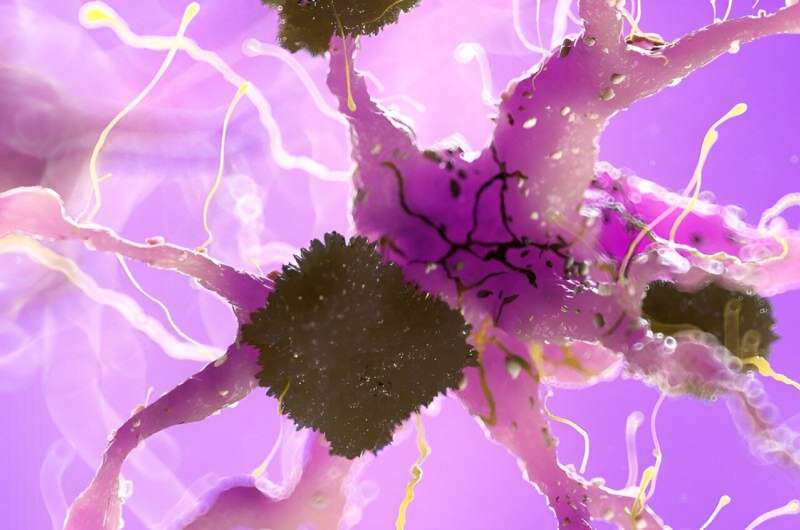
The therapy—developed at the University of Nebraska Medical Center (UNMC)—relies on both the immune system to fight key aspects of Alzheimer’s, plus modified cells that zero in on the brain protein plaques that are a hallmark of the disease.
In patients with Alzheimer’s, amyloid-beta protein forms plaques that prevent nerve cells from signaling each other. One theory is that this might cause irreversible memory loss and behavior changes characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease.
The new study was recently published in the journal Molecular Neurodegeneration. Researchers used genetically modified immune-controlling cells called Tregs to target amyloid-beta.