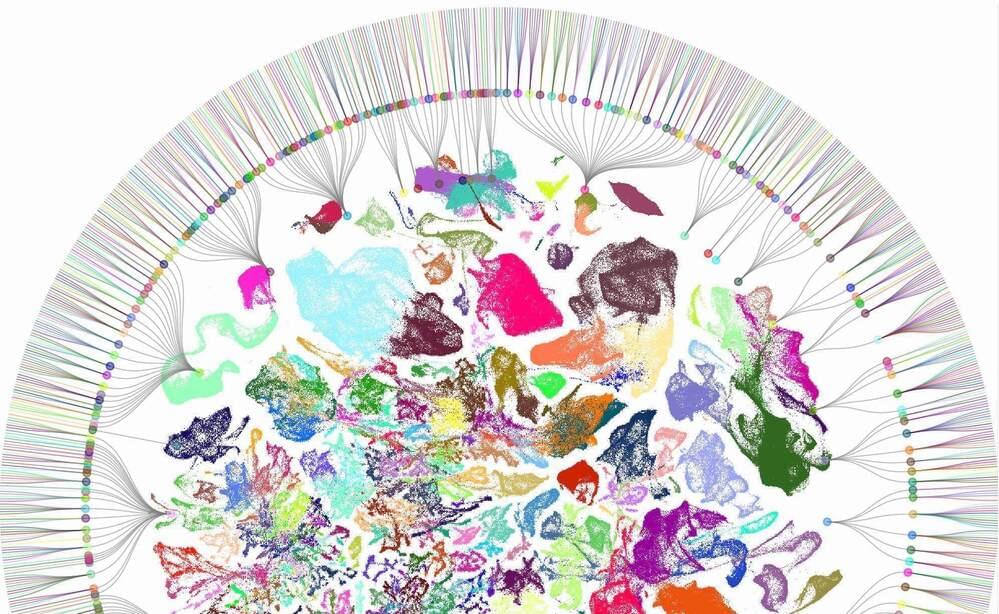
The first cellular map of a mammalian brain is here.
High-resolution atlas charts neural neighborhoods for more than 5,300 cell types.

A stroke happens when blood flow is lost to part of the brain. Your brain cells cannot get the oxygen and nutrients they need from blood, and they start to die in a few minutes. This can cause lasting brain damage, long-term disability, or even death.
A stroke can occur when an obstruction such as a blood clot travels from another part of the body and lodges inside an artery in the brain.
When an arterial wall becomes damaged, various types of emboli, or obstructions, can form. Emboli can be made up of various substances such as platelets, elements in the blood that help it clot, blood clots that form elsewhere and pass to the damaged area, cholesterol, or a combination of things.
For example, an embolism is formed in the carotid artery and breaks loose, traveling towards the brain where it will eventually lodge, blocking the blood the brain needs. The blocked artery deprives the brain of oxygen, which cause damage to the surrounding tissue. The result is a stroke.

Headquartered in Oxford, UK, MitoRx is working on orally delivered mitochondrial protective therapeutics targeting mitochondrial dysfunction linked to the progression of conditions such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy and Huntington’s disease, along with other neurodegenerative diseases. The company says the new funding will be allocated towards its preclinical work in Huntington’s disease, activating its first neurodegenerative disease program, and exploring research collaborations and partnerships.
MitoRx anticipates delivering preclinical results in Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Huntington’s disease, and COPD next year.
“Interim results in our Duchenne program demonstrate that our muscle-penetrative lead asset preserves strength in oxidative muscle, and confirms mitochondrial modulation,” said Dr Christine Charman, Chief Development Officer at MitoRx. “These results will be presented at the Muscular Dystrophy Association Clinical and Scientific Conference in Orlando during March 2024.”
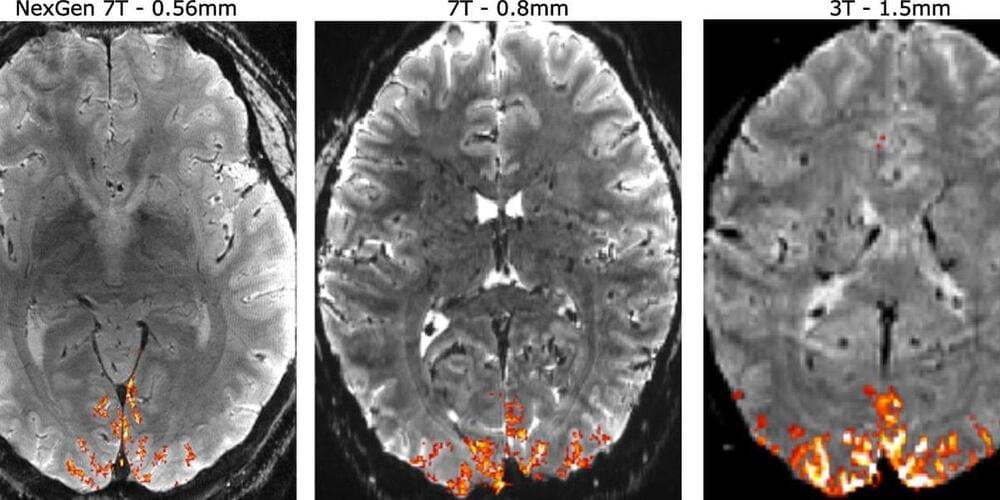

Worldwide, more than one billion people are obese. Obesity is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and some cancers. But permanently losing weight isn’t easy: complex interactions between body systems such as gut physiology, hormones, and the brain are known to work against it. One method for weight loss is intermittent energy restriction (IER), where days of relative fasting alternate with days of eating normally.
“Here we show that an IER diet changes the human brain-gut-microbiome axis. The observed changes in the gut microbiome and in the activity in addition-related brain regions during and after weight loss are highly dynamic and coupled over time,” said last author Dr. Qiang Zeng, a researcher at the Health Management Institute of the PLA General Hospital in Beijing. The study has been published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
The authors used metagenomics on stool samples, blood measurements, and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to study changes in the composition of the gut microbiome, physiological parameters and serum composition, and brain activity in 25 obese Chinese women and men on an IER diet. Participants were on average 27 years old, with a BMI between 28 and 45.

Progression independent of relapse activity (PIRA) has been increasingly recognized in people with multiple sclerosis (MS; NEJM JW Neurol May 24 2022 and JAMA Neurol 2022; 79:682). To learn more about PIRA, investigators used data from the Italian MS Register on 16,130 patients with relapsing-remitting MS, including 1,383 with pediatric-onset MS (POMS; median age at onset, 16), 14,113 with adult-onset MS (AOMS; median age at onset, 29), and 634 with late-onset MS (LOMS; median age at onset, 52).
Compared with patients with POMS, patients with LOMS had the highest incidence of PIRA (hazard ratio
These authors provide data supporting the notion that MS pathophysiology is different between patients with PIRA and those with relapse-associated worsening. While relapse-associated worsening seems to increase gradually and reach a plateau, PIRA begins in the 20s and continues to increase. PIRA encompasses accumulating neurodegenerative processes, supporting the concept that a subset of patients experience progression even within the relapsing-remitting phase of the disease.

People may be more than two times likelier to develop schizophrenia-related disorders if they owned cats during childhood than if they didn’t:
Living with cats as a child has once again been linked to mental health disorders, because our furry friends apparently can’t catch a break.
In a new meta-analysis published in the journal Schizophrenia Bulletin, Australian researchers identified 17 studies between 1980 and 2023 that seemed to associate cat ownership in childhood with schizophrenia-related disorders — a sample size narrowed down from a whopping 1,915 studies that dealt with cats during that 43-year time period.
As anyone who’s read anything about cats and mental health knows, there is a growing body of evidence suggesting that infection from the Toxoplasma gondii parasite, which is found in cat feces and undercooked red meat, may be linked to all sorts of surprising things. From mental illness to an interest in BDSM or a propensity for car crashes, toxoplasmosis — that’s the infection that comes from t. gondii exposure — has been thought of as a massive risk factor for decades now, which is why doctors now advise pregnant people not to clean cat litter or eat undercooked meat.
😀 Amazing breakthrough face_with_colon_three
A group of Spanish researchers have developed a brain-computer interface based on electroencephalograms that allowed a group of 22 users to play a simple multiplayer game. The interface was 94% accurate in translating players’ thoughts into game moves, with each move taking just over 5 seconds. The study was published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
A brain-computer interface is a technology that enables direct communication between the human brain and external devices, such as computers or prosthetic limbs. Brain-computer interfaces work by detecting and interpreting neural signals, typically through electrodes placed on the user’s head. These signals are then translated into actionable commands, allowing individuals to control computers, devices, or applications using their thoughts.
Brain-computer interfaces offer significant potential in medicine, from helping paralyzed individuals regain environmental control to treating neurological disorders. However, their broader adoption is hindered by challenges in accuracy and the extended time required to interpret brain signals.
Introduction and objective: Video games are crucial to the entertainment industry, nonetheless they can be challenging to access for those with severe motor disabilities. Brain-computer interfaces (BCI) systems have the potential to help these individuals by allowing them to control video games using their brain signals. Furthermore, multiplayer BCI-based video games may provide valuable insights into how competitiveness or motivation affects the control of these interfaces. Despite the recent advancement in the development of code-modulated visual evoked potentials (c-VEPs) as control signals for high-performance BCIs, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have been conducted to develop a BCI-driven video game utilizing c-VEPs. However, c-VEPs could enhance user experience as an alternative method. Thus, the main goal of this work was to design, develop, and evaluate a version of the well-known ‘Connect 4’ video game using a c-VEP-based BCI, allowing 2 users to compete by aligning 4 same-colored coins vertically, horizontally or diagonally.
Methods: The proposed application consists of a multiplayer video game controlled by a real-time BCI system processing 2 electroencephalograms (EEGs) sequentially. To detect user intention, columns in which the coin can be placed was encoded with shifted versions of a pseudorandom binary code, following a traditional circular shifting c-VEP paradigm. To analyze the usability of our application, the experimental protocol comprised an evaluation session by 22 healthy users. Firstly, each user had to perform individual tasks. Afterward, users were matched and the application was used in competitive mode. This was done to assess the accuracy and speed of selection. On the other hand, qualitative data on satisfaction and usability were collected through questionnaires.
Results: The average accuracy achieved was 93.74% ± 1.71%, using 5.25 seconds per selection. The questionnaires showed that users felt a minimal workload. Likewise, high satisfaction values were obtained, highlighting that the application was intuitive and responds quickly and smoothly.