Keith wiley stream of consciousness and identity.
Shared with Dropbox.

Get alerts for new articles, or get an alert when an article is cited.
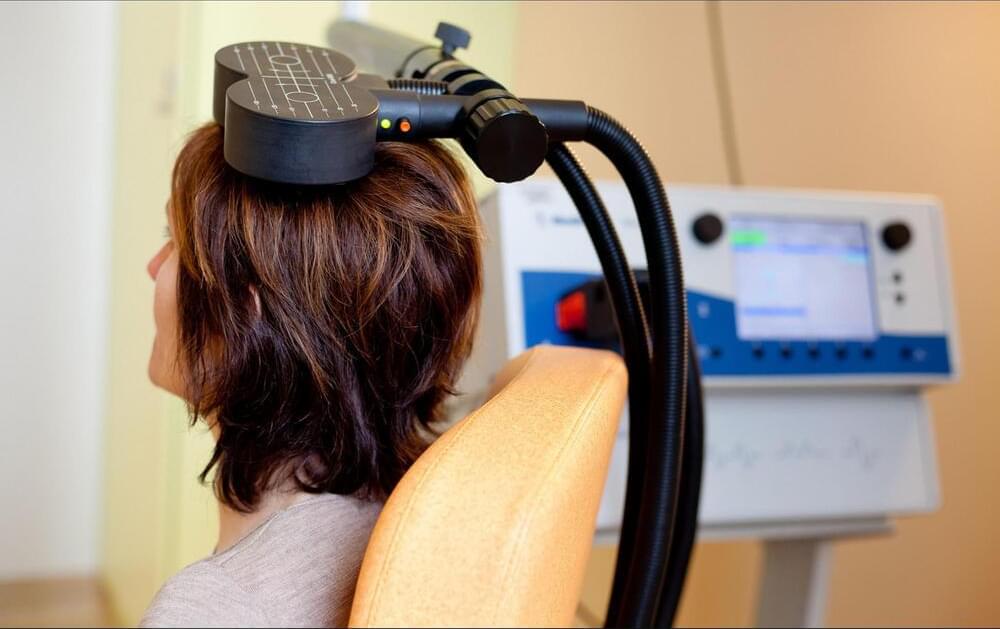
Even so, proponents say that TMS and other noninvasive brain-stimulation methods—which include updated forms of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) and transcranial direct-current stimulation—have yet to achieve their full potential, both as research tools and as clinical treatments for a range of neurological conditions. To get there, researchers want to fully understand the biological mechanisms behind these techniques, along with finding more rigorous ways to test them in the lab, all with a view toward making treatments more tailored and reliably successful. With its demonstrated benefits and lack of serious side effects, Colleen Loo, a neurostimulation pioneer at the University of New South Wales, says, “there’s no reason TMS can’t be used as a frontline treatment” for major depression.


Aging reversed in dogs face_with_colon_three
Age-related decline in mobility and cognition are associated with cellular senescence and NAD+ depletion in dogs and people. A combination of a novel NAD+ precursor and senolytic, LY-D6/2 was examined in this randomized controlled trial. Seventy dogs were enrolled and allocated into placebo, low or full dose groups. Primary outcomes were change in cognitive impairment measured with the owner-reported Canine Cognitive Dysfunction Rating (CCDR) scale and change in activity measured with physical activity monitors. Fifty-nine dogs completed evaluations at the three-month primary endpoint, and 51 reached the six-month secondary endpoint. There was a significant difference in CCDR score across treatment groups from baseline to the primary endpoint (p=0.02) with the largest decrease in the full dose group. There were no significant differences between groups in changes in measured activity. However, the proportion of dogs that improved in frailty and owner-reported activity levels and happiness was higher in the full dose group than other groups. Adverse events occurred equally across groups. All groups showed improvement in cognition, frailty, and activity suggesting placebo effect and benefits of trial participation. We conclude that LY-D6/2 significantly improves owner-assessed cognitive function and may have broader effects on frailty, activity and happiness as reported by owners.
The authors have declared no competing interest.
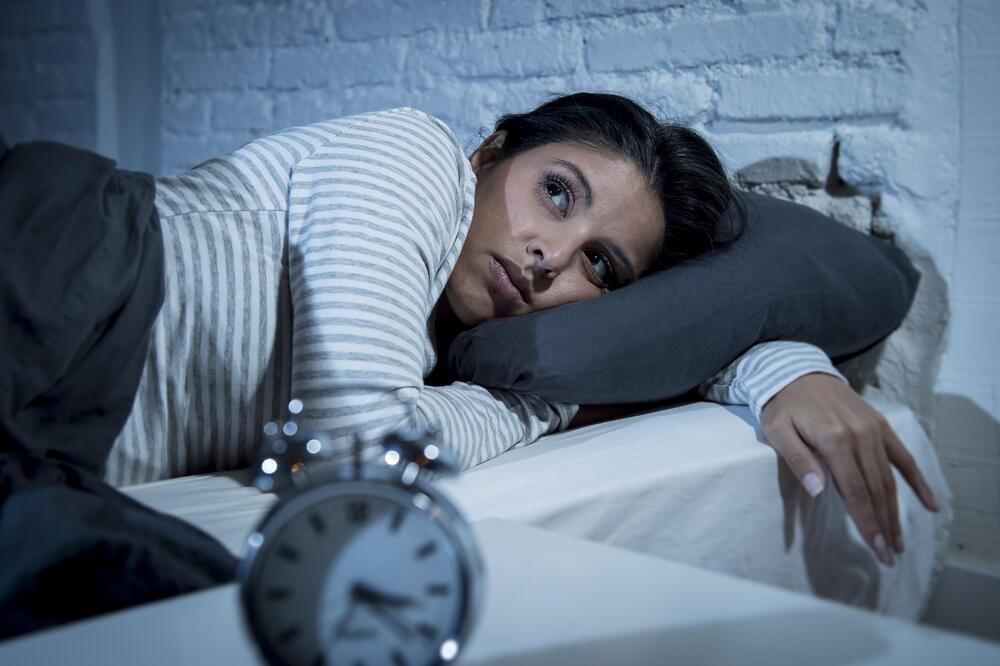

Insomnia is a common sleep disorder. If you have it, you may have trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. As a result, you may get too little sleep or have poor-quality sleep. You may not feel refreshed when you wake up.
What are the types of insomnia?
Insomnia can be acute (short-term) or chronic (ongoing). Acute insomnia is common. Common causes include stress at work, family pressures, or a traumatic event. It usually lasts for days or weeks.