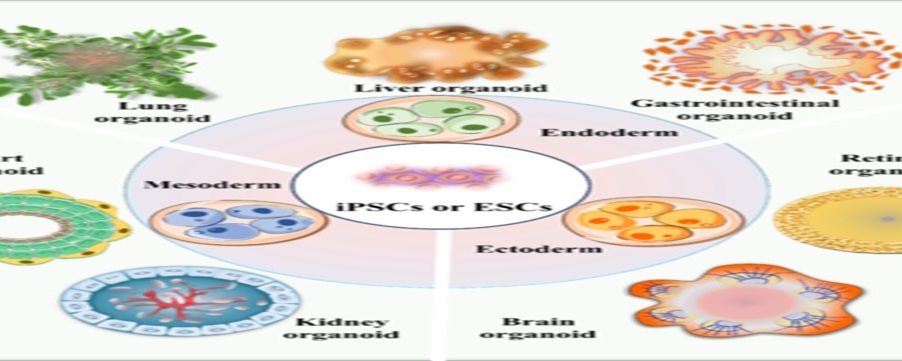
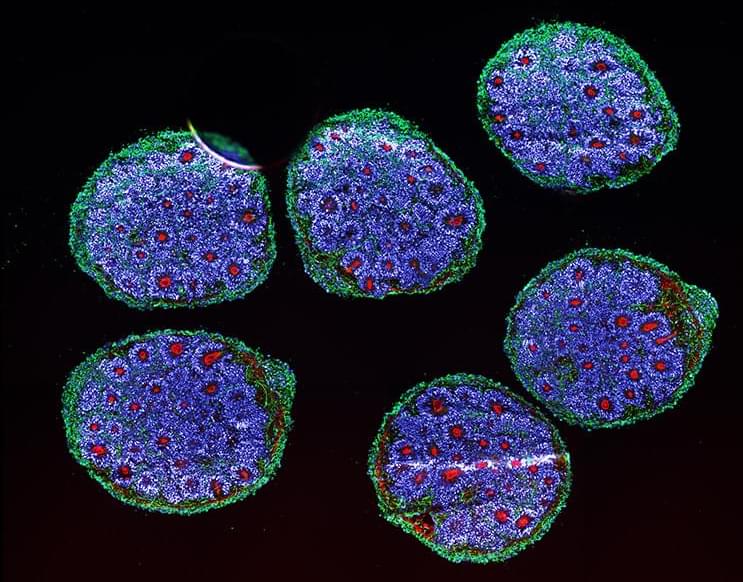
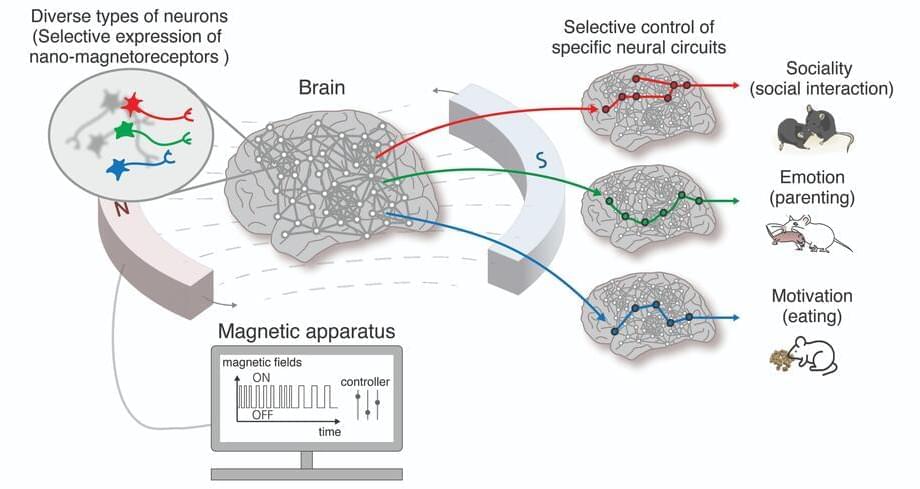
The idea of the brain as a computer is everywhere. So much so we have forgotten it is a model and not the reality. It’s a metaphor that has lead some to believe that in the future they’ll be uploaded to the digital ether and thereby achieve immortality. It’s also a metaphor that garners billions of dollars in research funding every year. Yet researchers argue that when we dig down into our grey matter our biology is anything but algorithmic. And increasingly, critics contend that the model of the brain as computer is sending scientists (and their resources) nowhere fast. Is our attraction to the idea of the brain as computer an accident of current human technology? Can we find a better metaphor that might lead to a new paradigm?