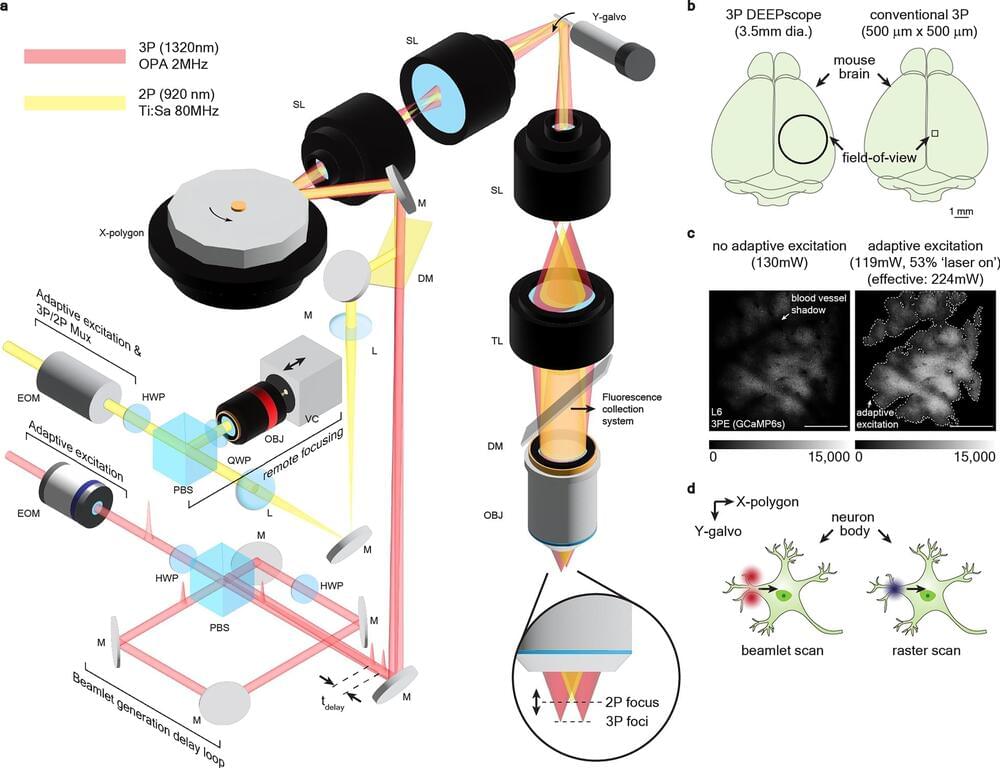
In vivo imaging of large-scale neuronal activity plays a pivotal role in unraveling the function of the brain’s circuitry. Multiphoton microscopy, a powerful tool for deep-tissue imaging, has received sustained interest in advancing its speed, field of view and imaging depth. However, to avoid thermal damage in scattering biological tissue, field of view decreases exponentially as imaging depth increases. We present a suite of innovations to optimize three-photon microscopy for large field-of-view imaging at depths unreachable by two-photon microscopy. These techniques enable us to image neuronal activities of transgenic animals expressing protein calcium sensors in a ~ 3.5-mm diameter field-of-view with single-cell resolution in the deepest cortical layer of mouse brains.