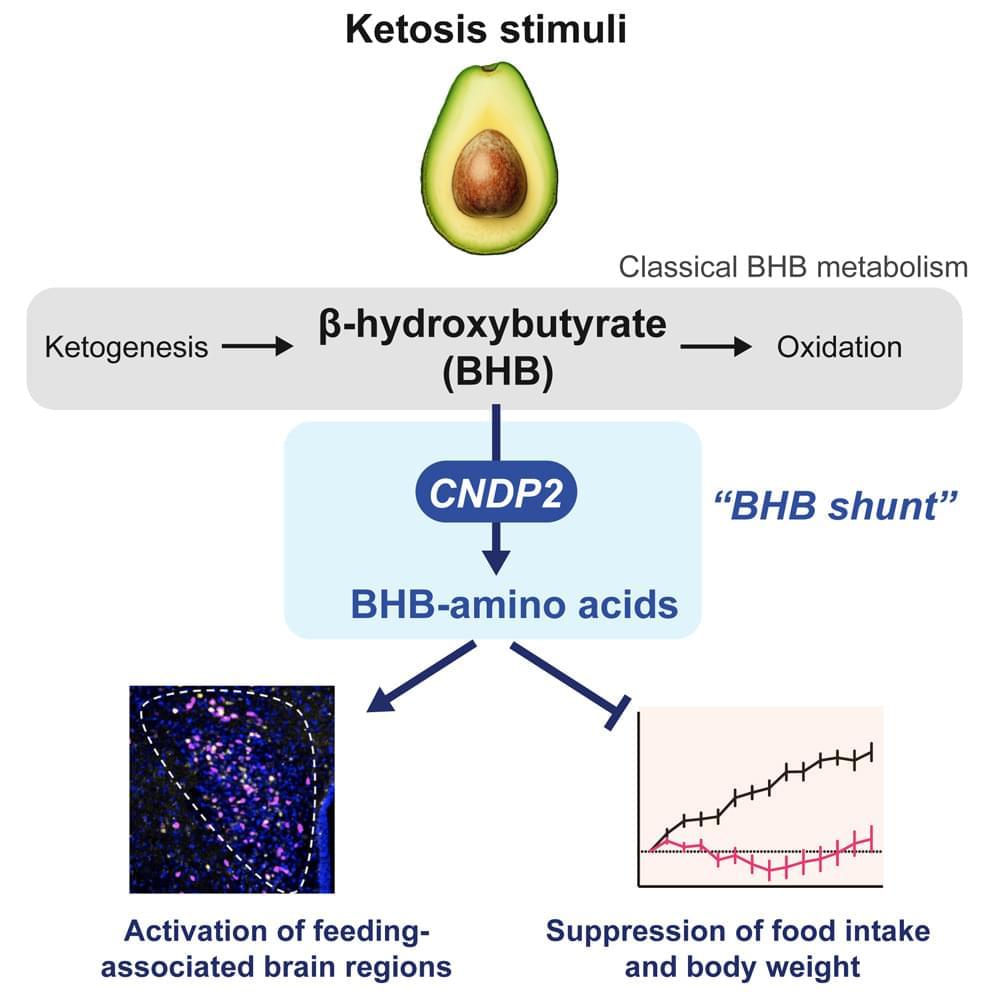
Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by difficulties in communication and social behavior. Approximately 20% of cases are linked to a specific genetic mutation, but the origin of the remaining 80%, known as idiopathic autism, remains a mystery.
A team of scientists led by Drs. Raúl Méndez and Xavier Salvatella at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) has identified a molecular mechanism that explains why certain alternations of the neuronal protein CPEB4 are associated with idiopathic autism.
The study is based on previous work published in 2018 that identified CPEB4 as a key protein in the regulation of neuronal proteins related to autism.