Scientists have turned brain cells into tiny light sources, revealing the brain at work like never before.
Category: neuroscience – Page 32
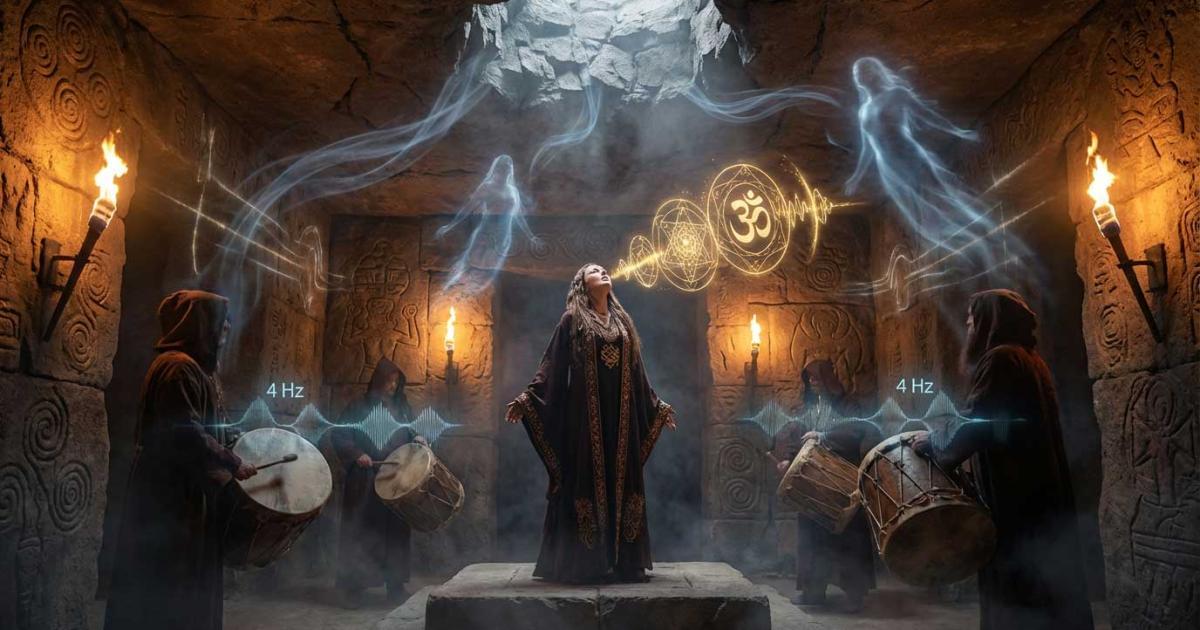

Ancient Priests Hacked Consciousness With Sound
Let’s travel back in time. We are in Malta, deep beneath the earth, inside a chamber, where the only light is that of torches. We hear a low hum that reverberates through the stone walls. A priestess enters, chanting a mantra, resonating within the walls, and her voice echoes with unparallel precision, while rhythmic drumbeats pulse like a heartbeat. The participants are entranced, they feel their minds slip from this mundane world into realms of heightened awareness. Suddenly, visions of spirits, out-of-body journeys, and profound insights interfere with the very nature of reality. Do you think this is fantasy? Absolutely not. This is the essence of the ancient rituals where sound and vibration served as gateways to altered states of consciousness. As we go deep into the mysteries of sacred sounds, we will uncover how mantras and drums were instruments of rebellion against the illusions of the material world, where mystics challenged the tyrannical grip of false gods through transcendent practices.
In this fascinating exploration, we will travel through time and cultures, and we will examine the scientific and spiritual foundations of these auditory phenomena. We will move from the shamanic drums of indigenous tribes to the mantras of the Vedic sages and the hymnic invocations of ancient Greece. And we will find a common thread: the “sound”. The universal key to unlocking the mind’s hidden potentials. We’ll also venture into archaeoacoustics, the study of sound in ancient sites, and connect these old practices to modern research on binaural beats, revealing how vibration continues to bridge the ancient and the contemporary in our quest for cosmic liberation. And as usual, we keep reinventing ancient knowledge of thousands of years before us.

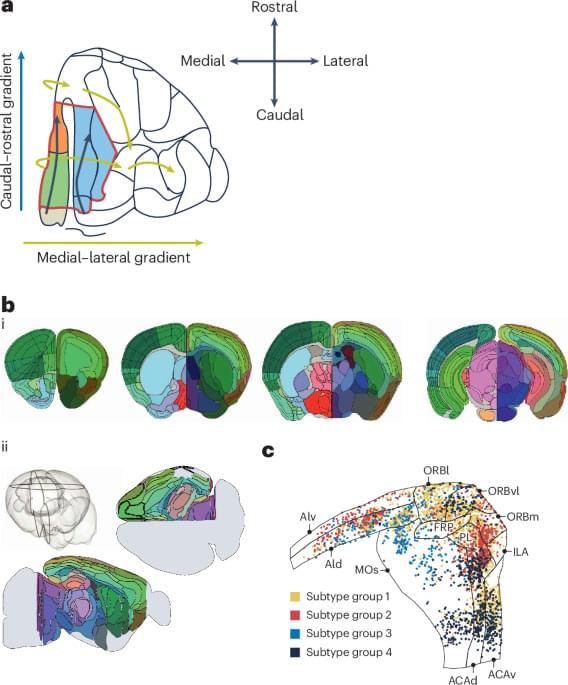
Rethinking the centrality of brain areas in understanding functional organization
For decades, neuroscience textbooks have taught us that the brain is organized into discrete areas — like Broca’s area for language or V1 for early vision, each with a well-defined role. This kind of areal parcellation has shaped how we interpret brain imaging, neural recordings, and even theories of cognition.
But this new article challenges that foundational idea. Instead of treating brain areas as the central units of brain function, the authors argue that brain organization is more complex, multi-layered, and distributed than traditional area-based frameworks suggest.
The authors begin with a simple observation: the ways in which neuroscientists define cortical areas, based on cell structure (cytoarchitecture), connectivity, or response properties — don’t always point to the same boundaries. In other words, different methods of dividing the cortex produce different “maps,” and there’s surprisingly little convergence on a single, definitive set of brain areas.
This inconsistency raises a big question: If areas aren’t consistently defined by structure or connectivity, can we really treat them as the fundamental units of brain function.
Parcellation of the cortex into functionally modular brain areas is foundational to neuroscience. Here, Hayden, Heilbronner and Yoo question the central status of brain areas in neuroscience from the perspectives of neuroanatomy and electrophysiology and propose an alternative approach.
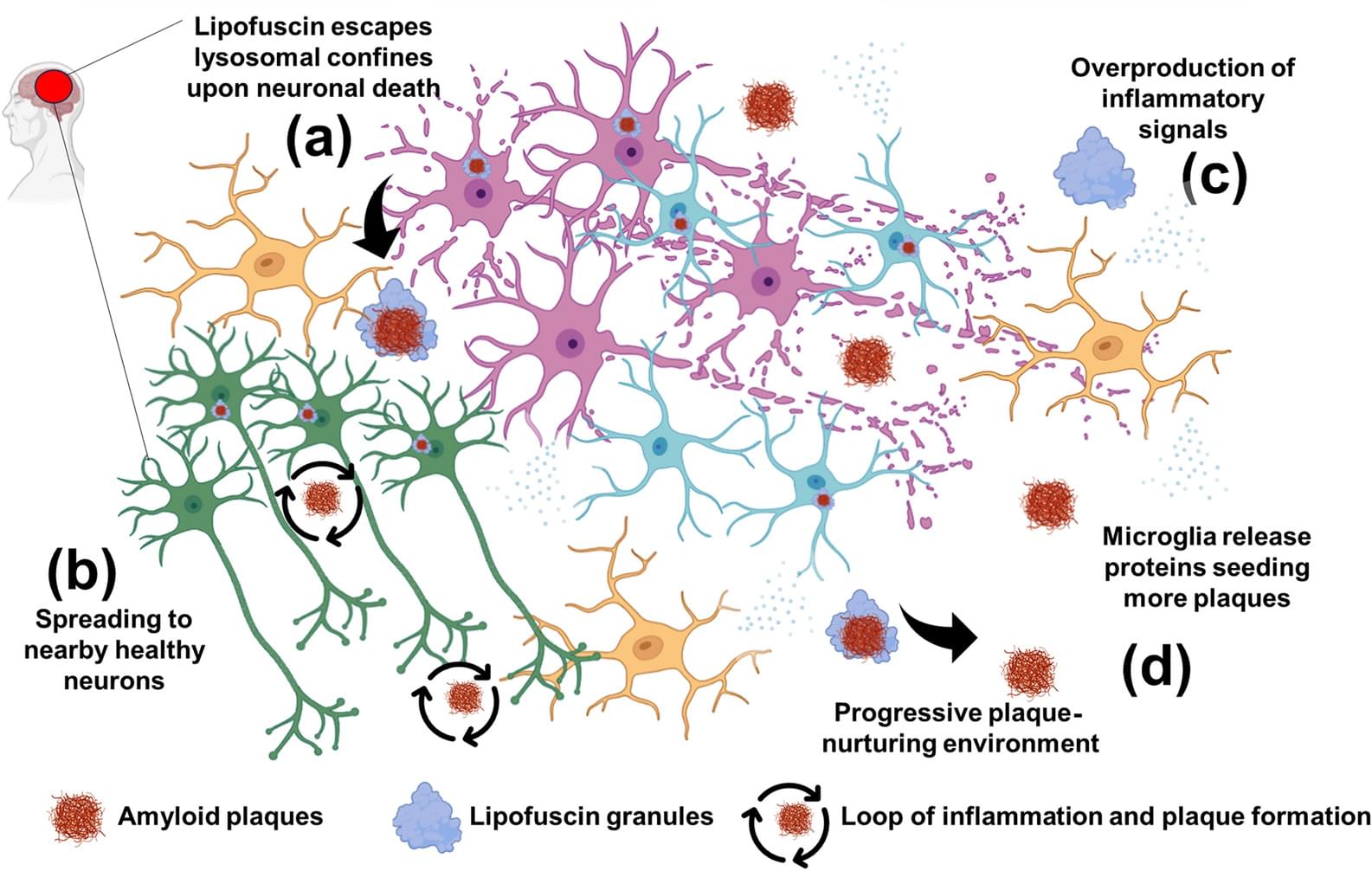
Lipofuscin accumulation in aging and neurodegeneration: a potential “timebomb” overlooked in Alzheimer’s disease
Lipofuscin, a marker of aging, is the accumulation of autofluorescent granules within microglia and postmitotic cells such as neurons. Lipofuscin has traditionally been regarded as an inert byproduct of cellular degradation. However, recent findings suggest that lipofuscin may play a role in modulating age-related neurodegenerative processes, and several questions remain unanswered. For instance, why do lipofuscin granules accumulate preferentially in aged neurons and microglia? What happens to these pigments upon neuronal demise? Particularly in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease (AD), why does amyloid β (Aβ) deposition usually begin in late adulthood or during aging? Why do lipofuscin and amyloid plaques appear preferentially in grey matter and rarely in white matter? In this review, we argue that lipofuscin should be revisited not as a simple biomarker of aging, but as a potential modulator of neurodegenerative diseases. We synthesize emerging evidence linking lipofuscin to lysosomal dysfunction, oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and disease onset—mechanisms critically implicated in neurodegeneration. We also explore the potential interactions of lipofuscin with Aβ and their spatial location, and summarize evidence showing that lipofuscin may influence disease progression via feedback loops affecting cellular clearance and inflammation. Finally, we propose future research directions toward better understanding of the mechanisms of lipofuscin accumulation and improved lysosomal waste clearance in aging.
Why consciousness can’t be reduced to code
The familiar fight between “mind as software” and “mind as biology” may be a false choice. This work proposes biological computationalism: the idea that brains compute, but not in the abstract, symbol-shuffling way we usually imagine. Instead, computation is inseparable from the brain’s physical structure, energy constraints, and continuous dynamics. That reframes consciousness as something that emerges from a special kind of computing matter, not from running the right program.



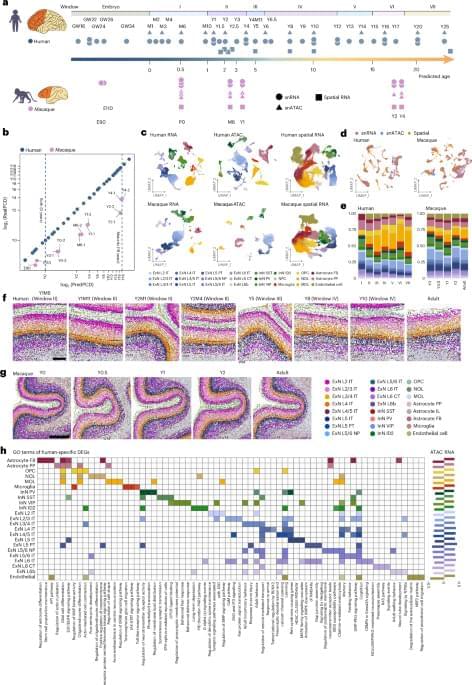
Single-cell spatiotemporal transcriptomic and chromatin accessibility profiling in developing postnatal human and macaque prefrontal cortex
The human brain is a fascinating and complex organ that supports numerous sophisticated behaviors and abilities that are observed in no other animal species. For centuries, scientists have been trying to understand what is so unique about the human brain and how it develops over the human lifespan.
Recent technological and experimental advances have opened new avenues for neuroscience research, which in turn has led to the creation of increasingly detailed descriptions of the brain and its underlying processes. Collectively, these efforts are helping to shed new light on the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders.
Researchers at Beijing Normal University, the Changping Laboratory and other institutes have recently set out to study both the human and macaque brain, comparing their development over time using various genetic and molecular analysis tools. Their paper, published in Nature Neuroscience, highlights some key differences between the two species, with the human pre-frontal cortex (PFC) developing slower than the macaque PFC.
“Unraveling the cellular and molecular characteristics of human prefrontal cortex (PFC) development is crucial for understanding human cognitive abilities and vulnerability to neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders,” wrote Jiyao Zhang, Mayuqing Li, and their colleagues in their paper. “We created a comparative repository for gene expression, chromatin accessibility and spatial transcriptomics of human and macaque postnatal PFC development at single-cell resolution.”
Human-specific molecular and cellular regulatory programs prolong prefrontal cortical maturation by orchestrating postnatal development of neurons and glia, with implications for cognitive function and susceptibility to neurodevelopmental disorders.