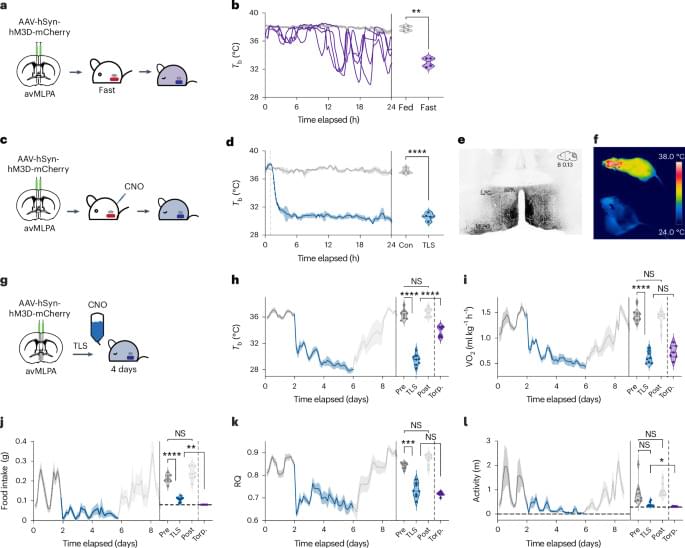
Summary: New research highlights a critical link between antibodies produced against Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and the development of multiple sclerosis (MS). Scientists discovered that these viral antibodies mistakenly target a protein called GlialCAM in the brain, triggering autoimmune responses associated with MS.
The study also revealed how combinations of genetic risk factors and elevated viral antibodies further increase the risk of developing MS. These insights may pave the way for improved diagnostics and targeted therapies, enhancing our understanding of the genetic and immunological interplay underlying this debilitating disease.