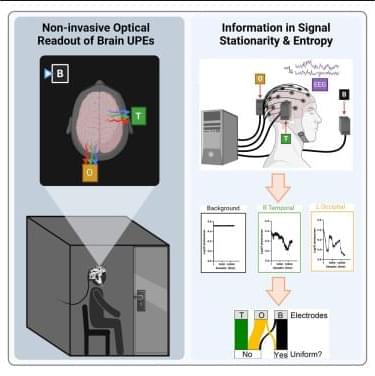
Cognitive neuroscience; Neuroscience.

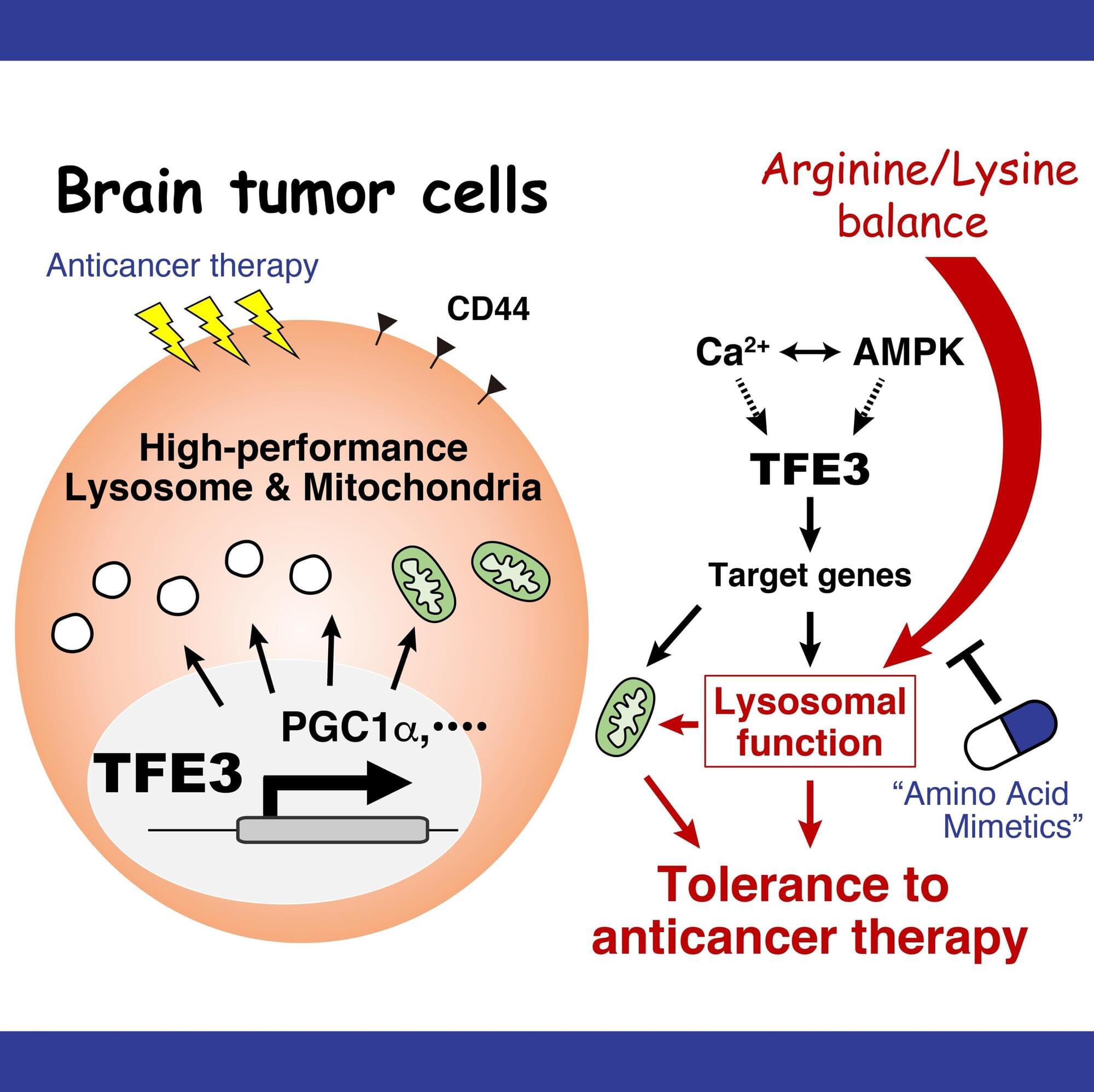
Researchers at Nano Life Science Institute (WPI-NanoLSI), Kanazawa University, report in Nature Communications on how the targeted suppression of lysosome function may lead to brain cancer therapy.
Glioblastoma is a type of brain cancer with a very poor prognosis of survival. Causes of glioblastoma are not known, and there is no method for preventing the cancer. Traditional treatment includes the drug temozolomide (TMZ). In many cases, TMZ kills glioblastoma cells, but a significant portion of patients show resistance to the drug.
Changes in the levels of metabolites—small molecules playing key roles in metabolic processes in living organisms—have been observed in TMZ-resistant glioblastoma cells, pointing to the importance of understanding and targeting metabolic pathways in the context of cancer therapy.
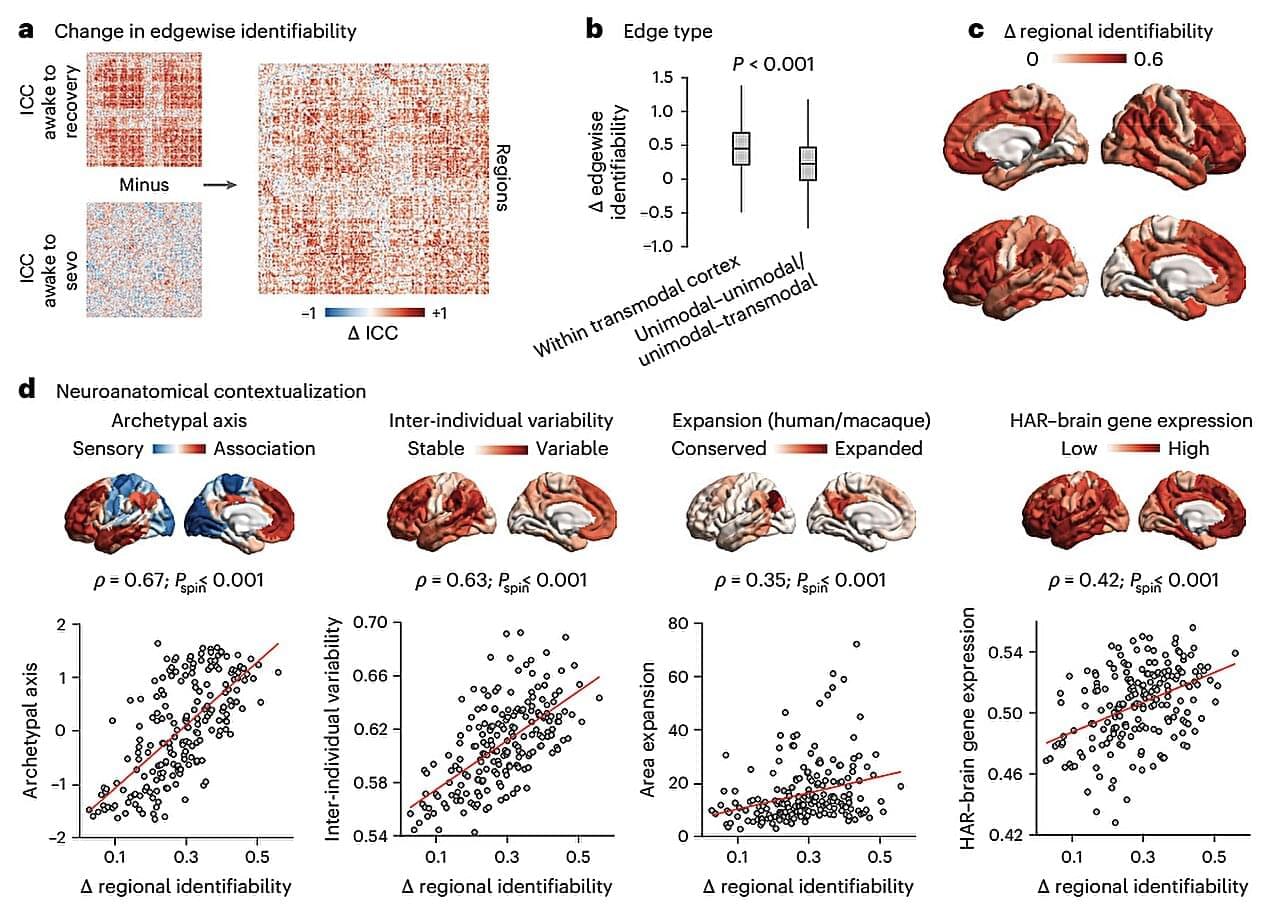
Past psychology research suggests that different people display characteristic patterns of spontaneous thought, emotions and behaviors. These patterns make the brains of distinct individuals unique, to the point that neuroscientists can often tell them apart based on their neural activity.
Researchers at McGill University, University of Cambridge and other institutes recently carried out a study aimed at investigating how general anesthesia influences the unique neural activity signatures that characterize the brains of different people and animals.
Their findings, published in Nature Human Behavior, show that general anesthesia suppresses each brain’s unique functional connectivity patterns (i.e., the connections and communication patterns between different regions of the brain), both in humans and other species.
After nine years of painstaking work, an international team of researchers on Wednesday published a precise map of the vision centers of a mouse brain, revealing the exquisite structures and functional systems of mammalian perception.
To date, it is the largest and most detailed such rendering of neural circuits in a mammalian brain.
The map promises to accelerate the study of normal brain function: seeing, storing and processing memories, navigating complex environments. As importantly, it will deepen the study of brain diseases in anatomical and physiological terms—that is, in terms of the wiring and the relationships between circuits and signals. That’s especially promising for diseases that may arise from atypical wiring, such as autism and schizophrenia.
Stanford Medicine scientists have rebuilt, in laboratory glassware, the neural pathway that sends information from the body’s periphery to the brain, promising to aid research on pain disorders.
Immune evasion of human stem-cell-derived neural graft in rodent models.
Transplantation rejection is the main challenge in human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC)-derived therapies.
The researchers used hPSC line (termed H1-FS-8IM), engineered to overexpress 8 immunomodulatory transgenes, to enable transplant immune evasion.
They show in co-cultures, H1-FS-8IM PSC-derived midbrain neurons evaded rejection by T lymphocytes, natural killer cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
The authors also provide preclinical evidence of pluripotent stem cell line evading immune detection after neural engraftment in a humanized immune system mouse model and reversal of motor symptoms in Parkinsonian rats.
Incorporation of a suicide gene within the universal donor cell ensures safety for cell-based therapies. https://sciencemission.com/A-cloaked-human-stem-cell-derived-neural-graft

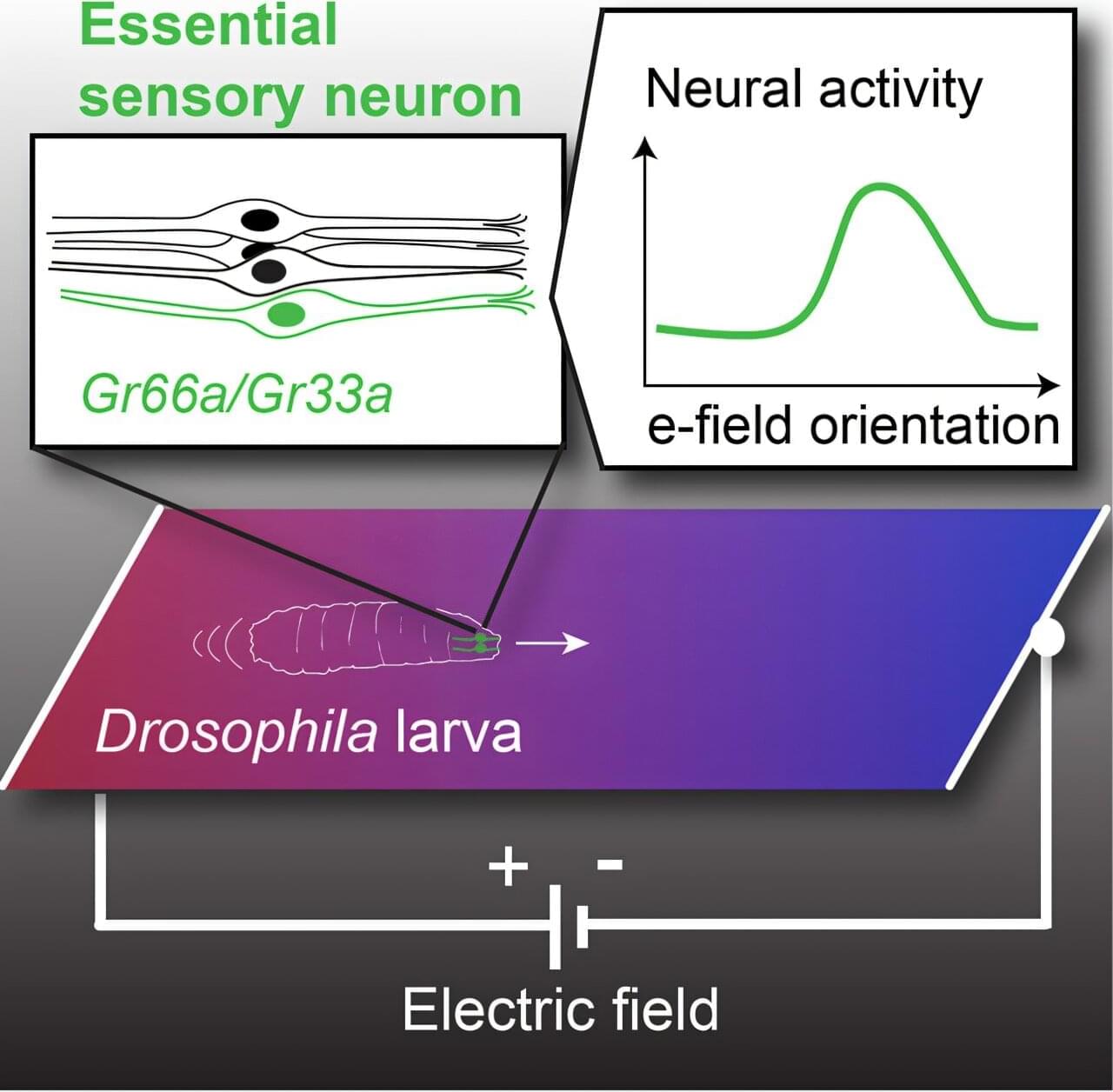
While it may be an unfamiliar sensation to humans, electroreception is relatively commonplace in the animal kingdom. Sharks, bees and even the platypus all share this ability to detect electric fields in their environment.
Scientists at UC Santa Barbara have just added fruit flies to that list. A team of researchers led by Matthieu Louis found that fruit fly larvae can sense electric fields and navigate toward the negative electric potential using a small set of sensory neurons in their head.
The findings, published in Current Biology, present an immense opportunity. Fruit flies are arguably the most commonly used experimental animals, the basis for studies in fields as disparate as genetics, neurobiology and aging. Uncovering electroreception in fruit flies opens new avenues of research into the basis of this sense and could even lead to new techniques in bioengineering.