Anyone can give you a brainwave menu and say “Go wild.”
Because it’s not about the tech. It’s about changing your life.
#EngineeringMindset #DIYSuccess #ImpactfulChange #EfficiencyMatters #WellnessJourney
Anyone can give you a brainwave menu and say “Go wild.”
Because it’s not about the tech. It’s about changing your life.
#EngineeringMindset #DIYSuccess #ImpactfulChange #EfficiencyMatters #WellnessJourney
A new USC study suggests that gut imbalances in children with autism may create an imbalance of metabolites in the digestive system—ultimately disrupting neurotransmitter production and influencing behavioral symptoms.
The research, published in Nature Communications, adds to a growing body of science implicating the “gut-brain” axis in autism. The discovery raises the possibility of new treatment avenues. It’s an example of how research at USC, and other universities, drives innovation and leads to discoveries that improve lives.
“We demonstrated that gut metabolites impact the brain, and the brain, in turn, affects behavior. Essentially, the brain acts as the intermediary between gut health and autism-related behaviors,” said first author Lisa Aziz-Zadeh, a professor at the Brain and Creativity Institute at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences.

Our brain’s ability to absorb fresh information — whether that means mastering a new task at work, memorizing the refrain of a song, or navigating unfamiliar streets — depends on a remarkable talent for neural self‑reinvention.
Every time we practice something novel, millions of tiny contacts between nerve cells subtly adjust their strength and neurons use multiple mechanisms to store knowledge.
Some connections, called synapses, amplify their signals to stamp in crucial details; others turn down the volume to clear away noise. Collectively these shifts are known as synaptic plasticity and for decades neuroscientists have cataloged dozens of molecular pathways that can nudge a synapse up or down.
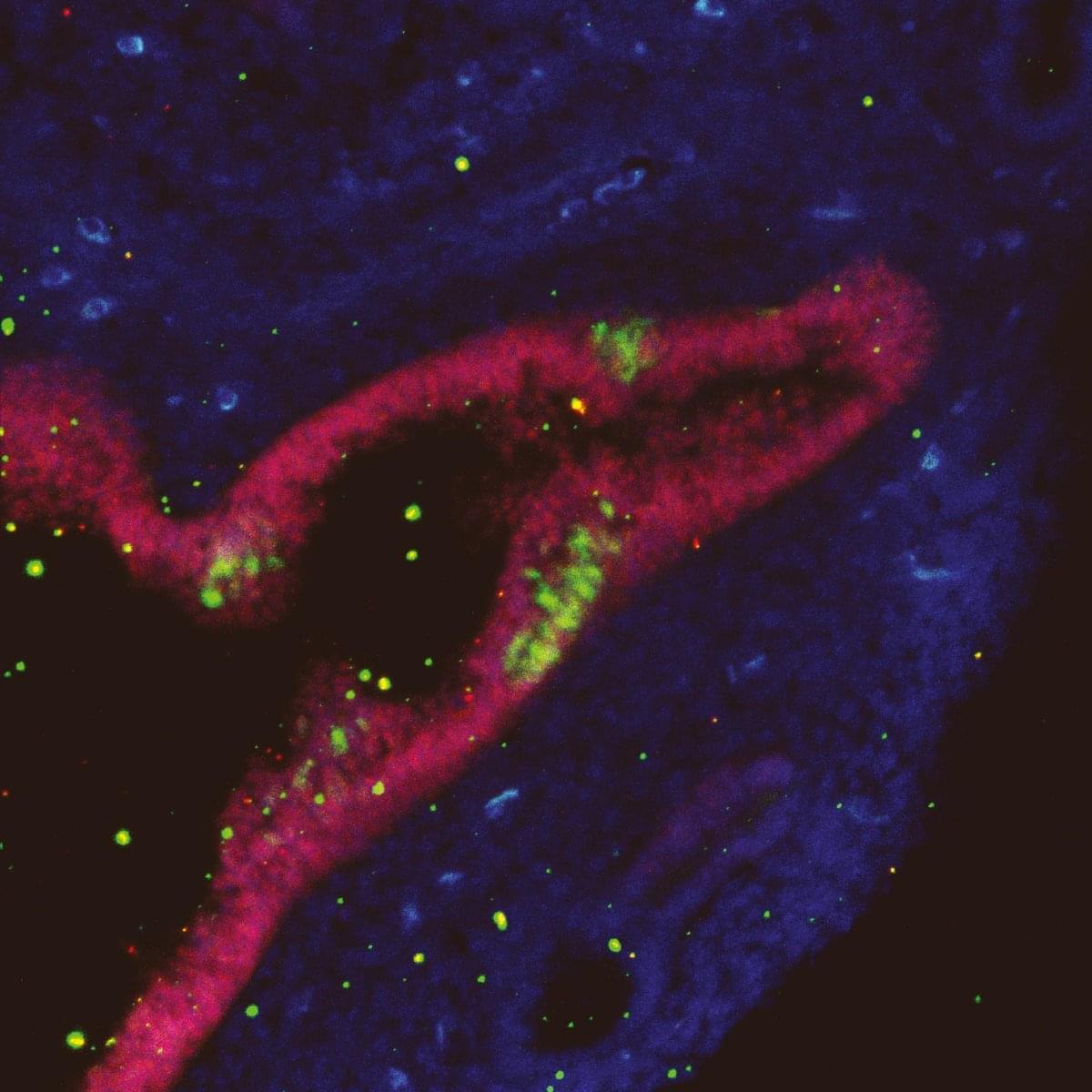
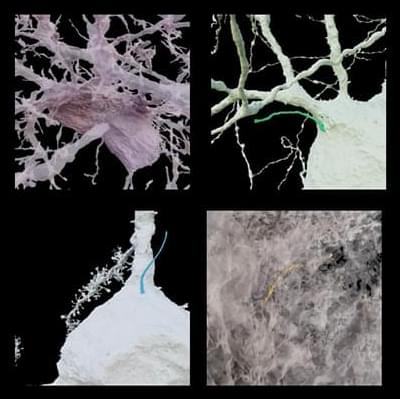
Many cells in our body have a single primary cilium, a micrometer-long, hair-like organelle protruding from the cell surface that transmits cellular signals. Cilia are important for regulating cellular processes, but because of their small size and number, it has been difficult for scientists to explore cilia in brain cells with traditional techniques, leaving their organization and function unclear.
In a new series of work, researchers at HHMI’s Janelia Research Campus, the Allen Institute, the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, and Harvard Medical School used super high-resolution 3D electron microscopy images of mouse brain tissue generated for creating connectomes to get the best look yet at primary cilia.


Every day, people are constantly learning and forming new memories. When you pick up a new hobby, try a recipe a friend recommended or read the latest world news, your brain stores many of these memories for years or decades.
But how does your brain achieve this incredible feat?
In our newly published research in the journal Science, we have identified some of the “rules” the brain uses to learn.

Compared to other animal species, humans can plan and execute highly sophisticated motor tasks, including the ability to write complex characters using their hands. While many past studies have tried to better understand the neural underpinnings of handwriting and other complex human motor capabilities, these have not yet been fully elucidated.
Past studies showed that the motor cortex plays a crucial role in the human ability to translate intentions into actions. Yet the processes via which it enables the execution of precise and sequential movements, such as those associated with handwriting, are poorly understood.
Researchers at Zhejiang University in China recently carried out a study aimed at further exploring the role of the human motor cortex in the encoding of intricate handwriting, such as Chinese characters. Their findings, published in Nature Human Behavior, suggest that this encoding unfolds via a sequence of stable neural states.