For millennia, dreams have been a source of fascination, but their systematic study is a modern endeavor with significant scientific applications. Investigating subjective experiences during sleep can inform research into consciousness itself, aid in understanding memory consolidation, and provide insights into sleep disorders like sleepwalking. Despite this importance, progress has been hampered by a persistent challenge: dream studies are resource-intensive, often resulting in small sample sizes that are difficult to compare across different laboratories.
To address this limitation, a consortium of 53 researchers from 37 institutions across 13 countries came together to build the Dream EEG and Mentation database, known as DREAM. Coordinated by Monash University in Australia and supported by organizations including the Bial Foundation, the project aimed to centralize and standardize decades of dream research.
The goal was to create a large-scale, publicly accessible resource that would allow scientists to conduct more robust and comprehensive analyses of the dreaming brain. Giulio Bernardi of the IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca in Italy, a contributor to the project, noted that the effort represents a decisive step in the scientific exploration of human consciousness by gathering vast amounts of research into a single place.
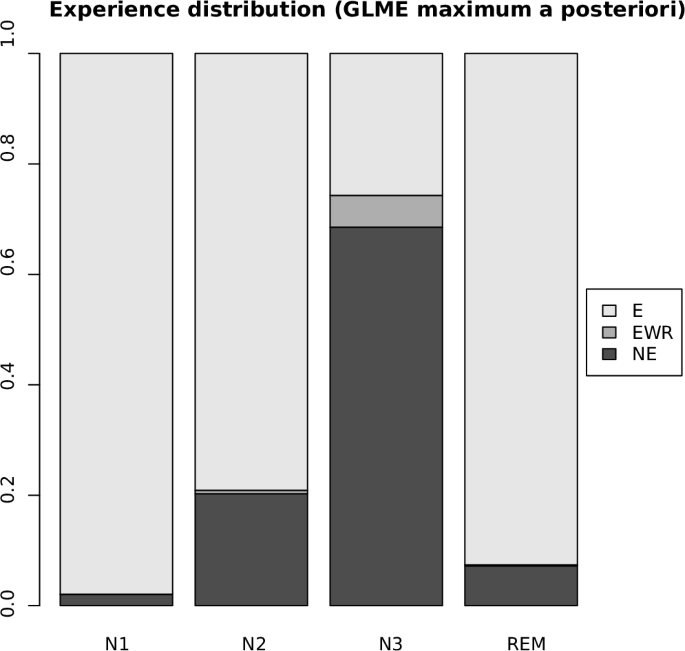
The team assembled data from 20 different studies, resulting in a collection of more than 2,600 records of awakenings from 505 participants. For each record, the database contains electroencephalography, or EEG, recordings, which measure the brain’s electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp. Some records also include magnetoencephalography, a related technique that measures magnetic fields produced by the brain’s electrical currents. These neurophysiological recordings are paired with a report from the participant upon waking.
A dream EEG and mentation database.