New in JNeurosci from Wang et al: Impaired ATP release in the dorsal hippocampus of male mice may lead to depressive-and anxiety-like behavior. Connexin 43 may be a key molecular player in this mechanism.
▶️
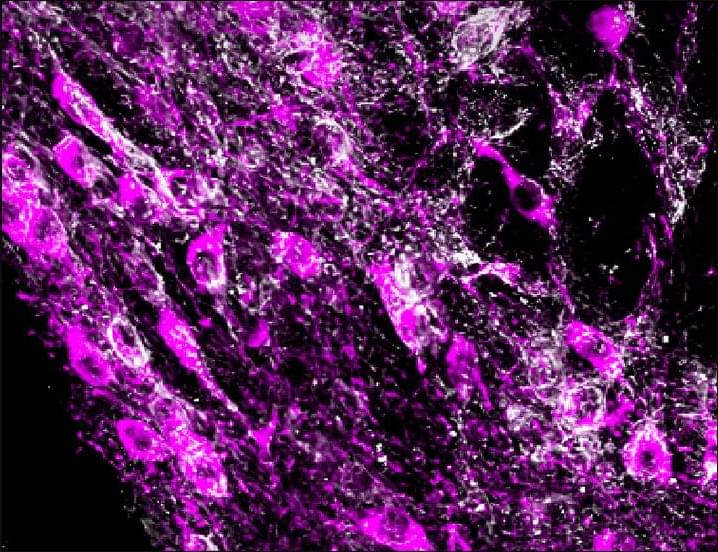
Depression is a common psychiatric disorder, and increasing evidence implicates the dysregulation of extracellular ATP and hippocampal dysfunction in its pathophysiology. However, whether ATP release is involved in depression and mechanisms underlying this involvement remain unclear. Moreover, the basis for the comorbidity of depression and anxiety disorders remains unclear. In our study, we observed reduced connexin 43 (Cx43) and extracellular ATP levels in the dorsal hippocampus but not ventral hippocampus of susceptible adult male mice exposed to chronic social defeat stress. Conditional knockout of astrocytic Cx43 or its specific knockdown in dorsal hippocampal astrocytes led to depressive-and anxiety-like behaviors, whereas neuronal knockout of Cx43 had no effect on these behaviors. These deficits were accompanied by decreased extracellular ATP levels, while supplementation with exogenous ATPγS reversed these behavioral deficits. We further identified Cx43 as a critical regulator of ATP release and a modulator of astrocytic network connectivity and morphology. Notably, overexpression of Cx43 combined with the inhibition of ATP-degrading enzymes in the dorsal hippocampus restored ATP levels and ameliorated behavioral deficits. Taken together, our results demonstrate that deficiency of ATP release from dorsal hippocampal astrocytes leads to depressive-and anxiety-like behaviors, primarily through Cx43. These findings shed new light on the mechanisms by which ATP regulates depression and anxiety pathogenesis and the role of dorsal hippocampus in depression and anxiety, providing potential therapeutic targets for treating these comorbid disorders.
Significance statement This study provides the first direct evidence of a causal relationship between astrocytic Cx43 in the dorsal hippocampus and depressive-like behaviors. It highlights the crucial role of ATP release in the comorbidity of depression and anxiety. Astrocyte-specific knockout or knockdown of Cx43 in the dorsal hippocampus resulted in reduced extracellular ATP levels and emotional disturbances. Conversely, restoring Cx43 expression combined with inhibition of ATP degradation rescued both ATP levels and behavioral deficits in susceptible mice. These findings underscore the central role of astrocytic Cx43-mediated ATP release in the pathophysiology of depression and highlight promising therapeutic strategies for the treatment of comorbid depression and anxiety.