Polymer-based modulation of gold-gold gap could yield new types of hologram.



Sliding ferroelectrics are a type of two-dimensional (2D) material realized by stacking nonpolar monolayers (atom-thick layers that lack an electric dipole). When these individual layers are stacked, they produce ferroelectric materials with an intrinsic polarization (i.e., in which positive and negative charges are spontaneously separated), which can be switched using an external electric field that is perpendicular to them.
Understanding the mechanisms driving the switching of this polarization in sliding ferroelectrics has been a key goal of many studies rooted in physics and materials science. This could ultimately inform the development of new advanced nanoscale electronics and quantum technologies.
Researchers at Westlake University and the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China recently uncovered a new mechanism that could drive the switching of polarization in sliding ferroelectrics. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters (PRL), suggests that polarization switching in the materials is prompted by wave-like movements of domain walls (i.e., boundaries between regions with an opposite polarization), rather than by synchronized shifts affecting entire monolayers at once, as was assumed by some earlier works.
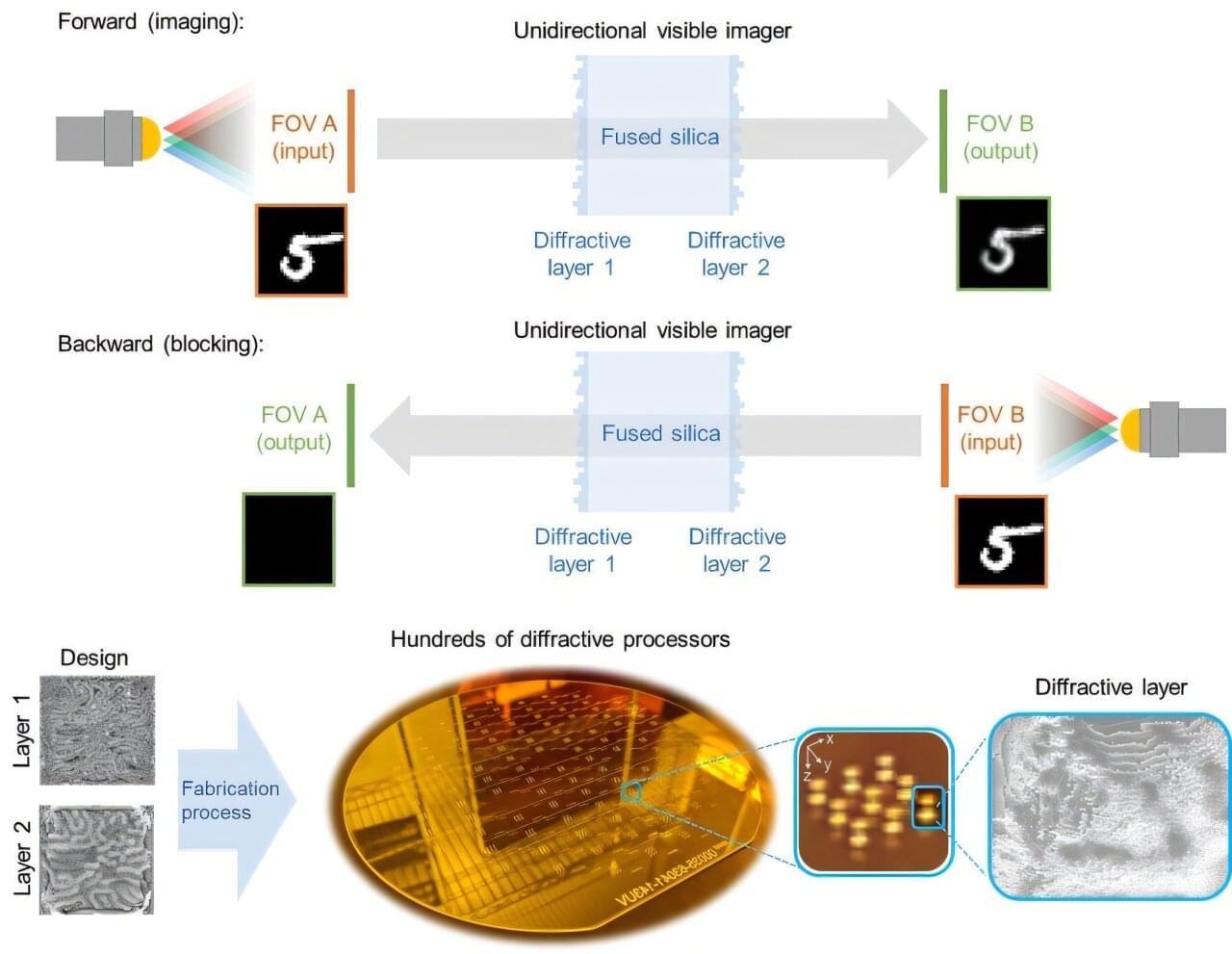
Researchers at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering, in collaboration with the Optical Systems Division at Broadcom Inc., report a broadband, polarization-insensitive unidirectional imager that operates in the visible spectrum, capable of high-efficiency image transmission in one direction while effectively suppressing image formation in the reverse direction.
This device incorporates diffractive structures fabricated through wafer-scale lithography on high-purity fused silica, offering high optical transparency, thermal stability and ultra-low loss.
The work appears in Light: Science & Applications.
A photonics research group co-led by Gregor Weihs of the University of Innsbruck has developed a new technique for generating multi-photon states from quantum dots that overcomes the limitations of conventional approaches. This has immediate applications in secure quantum key distribution protocols, where it can enable simultaneous secure communication with different parties.
Quantum dots—semiconductor nanostructures that can emit single photons on demand—are considered among the most promising sources for photonic quantum computing. However, every quantum dot is slightly different and may emit a slightly different color. This means that to produce multi-photon states, we cannot use multiple quantum dots.
Usually, researchers use a single quantum dot and multiplex the emission into different spatial and temporal modes, using a fast electro-optic modulator. The technological challenge is that faster electro-optic modulators are expensive and often require very customized engineering. To add to that, they may not be very efficient, which introduces unwanted losses into the system.
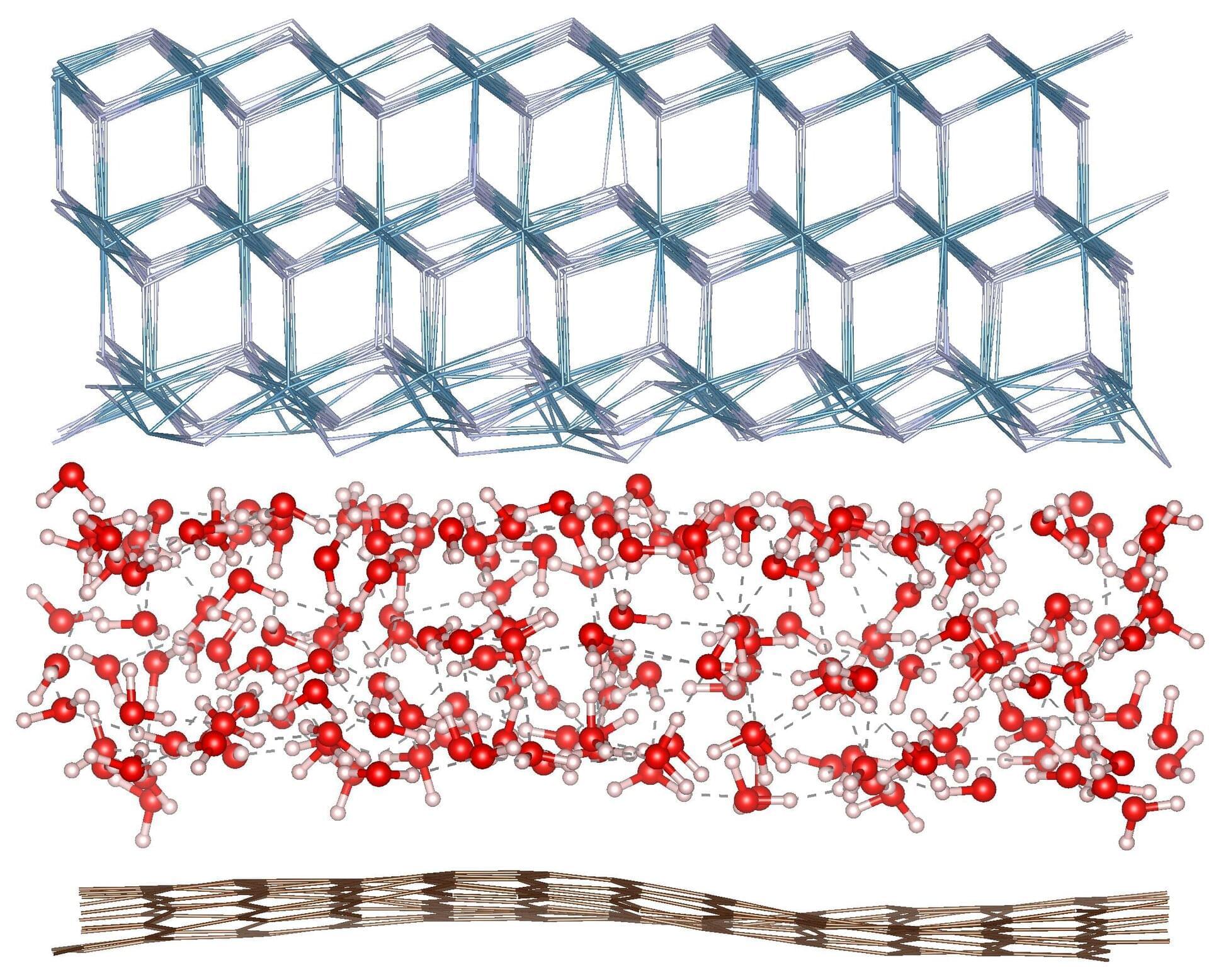
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research have upended assumptions about how water behaves when squeezed into atom-scale spaces. By applying spectroscopic tools together with the machine learning simulation technique to water confined in a space of only a few molecules thick, the team, led by Mischa Bonn, found that water’s structure remains strikingly “normal” until confined to below a nanometer, far thinner than previously believed.
The research, “Interfaces Govern the Structure of Angstrom-Scale Confined Water Solutions,” was published in Nature Communications.
Peering into the structure of a layer of water molecules that is only a few molecules thick is a formidable scientific challenge. The team fabricated a nanoscale capillary device by trapping water between a single layer of graphene and a calcium fluoride (CaF₂) substrate. They then wielded cutting-edge vibrational surface-specific spectroscopy—capable of detecting the microscopic structure of confined water, including the orientation and hydrogen-bonding of water molecules—to “see” the elusive few layers of water.
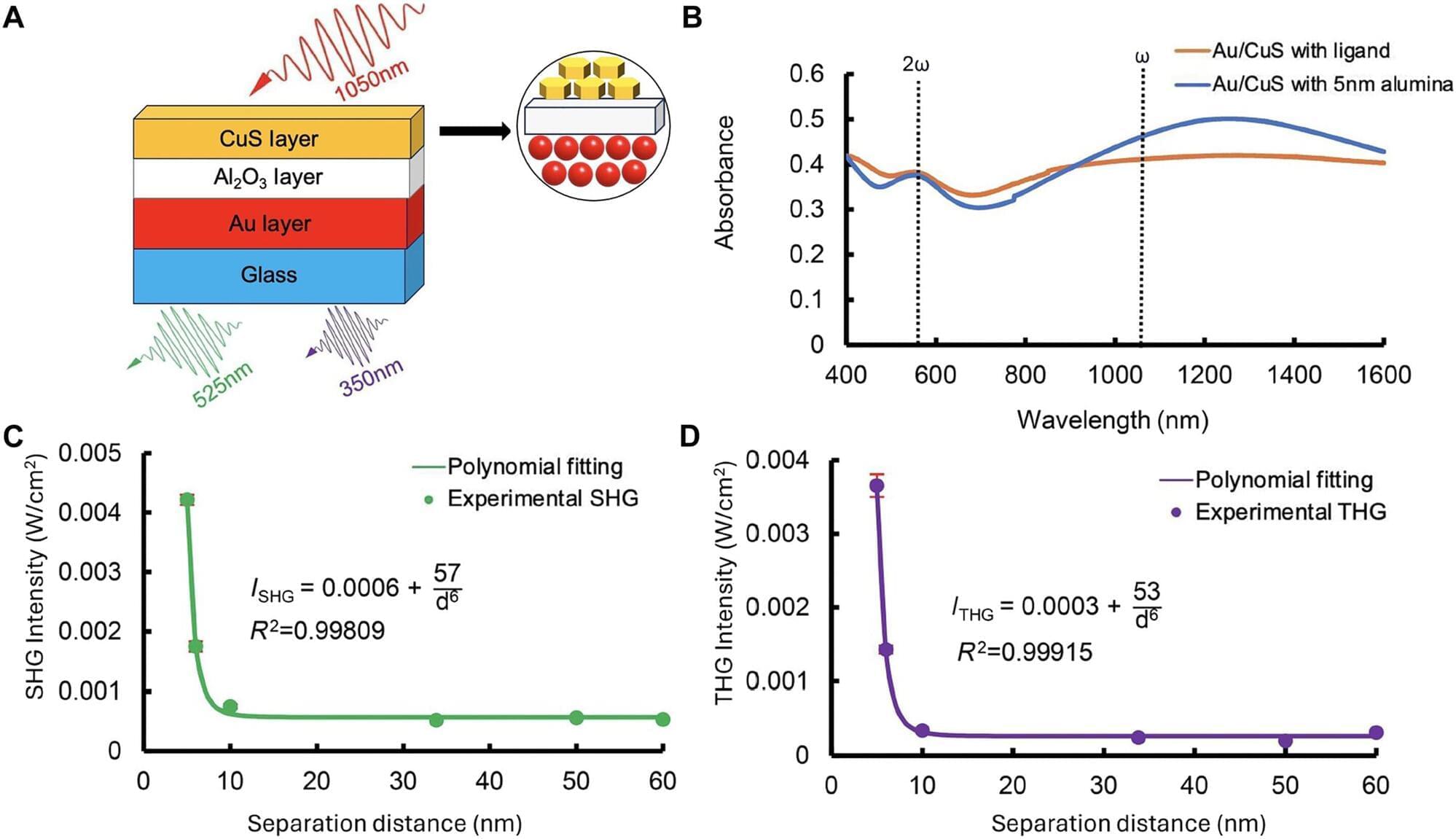
A new breakthrough in the field of physics led by doctoral student Yueming Yan could allow for the creation of small, thin, low-power optical devices to be used in both medical imaging and environmental sensing.
In a study published in Science Advances, Yan and his colleagues, including Associate Professor of Chemistry Janet Macdonald and Stevenson Professor of Physics Richard Haglund, examined tiny nanoparticles of metals and semiconductors, specifically gold and copper.
The team laid down two ultrathin layers of gold and semiconducting copper sulfide nanoparticles, creating a “sandwich” 100 times thinner than a human hair. They then zapped this sandwich with a flash of light shorter than a trillionth of a second. Doing so caused the particles to “chat” back and forth, exchanging energy so efficiently that they re-emitted light in multiple different colors.
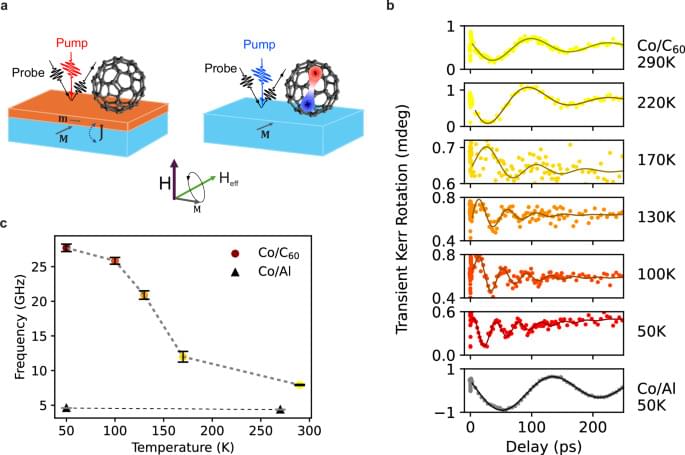
Advancing quantum information and communication technology requires smaller and faster components with actively controllable functionalities. This work presents an all-optical strategy for dynamically modulating magnetic properties via proximity effects controlled by light. We demonstrate this concept using hybrid nanoscale systems composed of C₆₀ molecules proximitized to a cobalt metallic ferromagnetic surface, where proximity interactions are particularly strong. Our findings show that by inducing excitons in the C60 molecules with resonant ultrashort light pulses, we can significantly modify the interaction at the Cobalt/C60 interface, leading to a remarkable 60% transient shift in the frequency of the Co dipolar ferromagnetic resonance mode. This effect, detected via a specifically designed time-resolved Magneto-Optical Kerr Effect (tr-MOKE) experiment, persists on a timescale of hundreds of picoseconds. Since this frequency shift directly correlates with a transient change in the anisotropy field—an essential parameter for technological applications—our findings establish a new material platform for ultrafast optical control of magnetism at the nanoscale.
Proximity effects in molecule/metal heterostructures offer a promising route to control magnetic properties. Here, the authors report a light-controlled proximity effect at a Co/C₆₀ interface, where laser-induced excitons in C₆₀ alter interfacial interactions, leading to a 60% quenching of the ferromagnetic resonance frequency of Co.
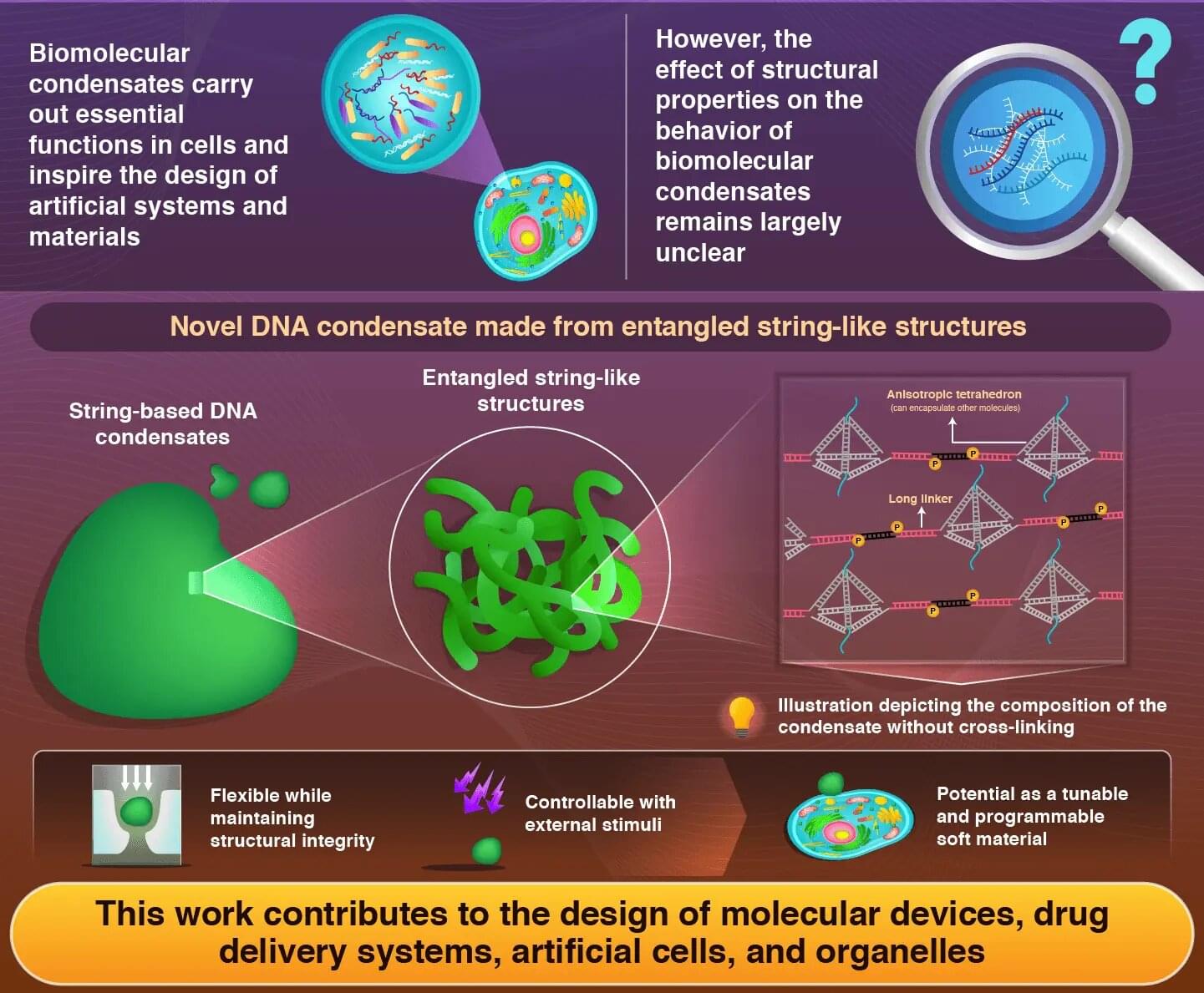
Newly developed DNA nanostructures can form flexible, fluid, and stimuli-responsive condensates without relying on chemical cross-linking, report researchers from the Institute of Science Tokyo and Chuo University, in the journal JACS Au.
Owing to a rigid tetrahedral motif that binds the linkers in a specific direction, the resulting string-like structures form condensates with exceptional fluidity and stability. These findings pave the way for adaptive soft materials with potential applications in drug delivery, artificial organelles, and bioengineering platforms.
Within living cells, certain biomolecules can organize themselves into specialized compartments called biomolecular condensates. These droplet-like structures play crucial roles in cellular functions, such as regulating gene expression and biochemical reactions; they essentially represent nature’s clever way of organizing cellular activity without the need for rigid membranes.