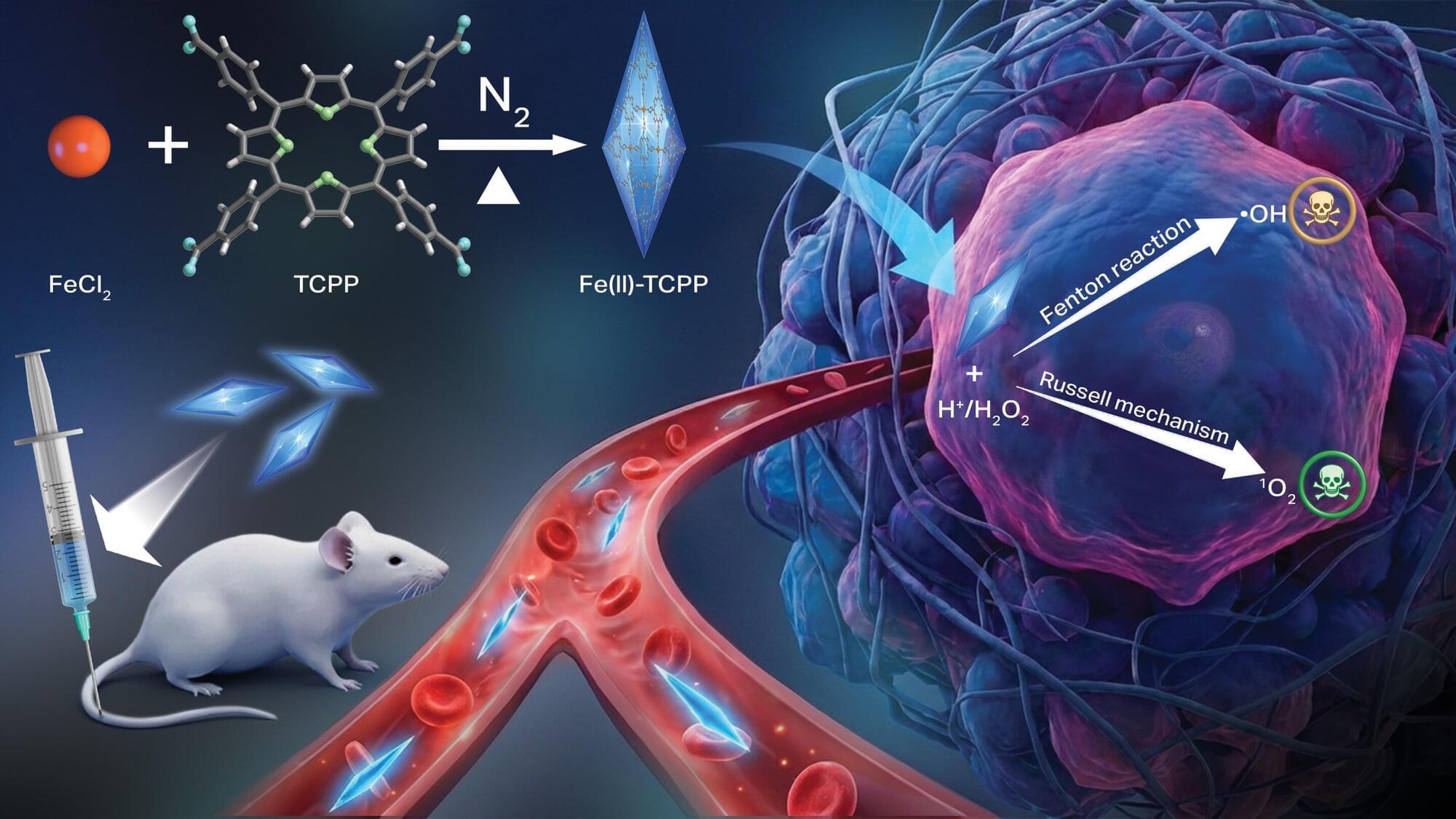
Scientists at Oregon State University have developed a new nanomaterial that triggers a pair of chemical reactions inside cancer cells, killing the cells via oxidative stress while leaving healthy tissues alone. The study led by Oleh and Olena Taratula and Chao Wang of the OSU College of Pharmacy appears in Advanced Functional Materials.
The findings advance the field of chemodynamic therapy (CDT), an emerging treatment approach based on the distinctive biochemical environment found in cancer cells. Compared to healthy tissues, malignant tumors are more acidic and have elevated concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, the scientists explain.
Conventional CDT works by using the tumor microenvironment to trigger the chemical production of hydroxyl radicals—molecules, made up of oxygen and hydrogen—with an unpaired electron. These reactive oxygen species are able to damage cells through oxidation by stealing electrons from molecules like lipids, proteins, and DNA.