Interesting articles on theranostic iron nanowires. I’m interested in watching all aspects of development of nanobots, because I think it may lead to new forms of treatments for superlongevity and superintelligence.
Phys.org: Iron nanorobots go undercover to do surveillance on living cells in real time:
https://phys.org/…/2020–05-iron-nanorobots-undercover-surve…
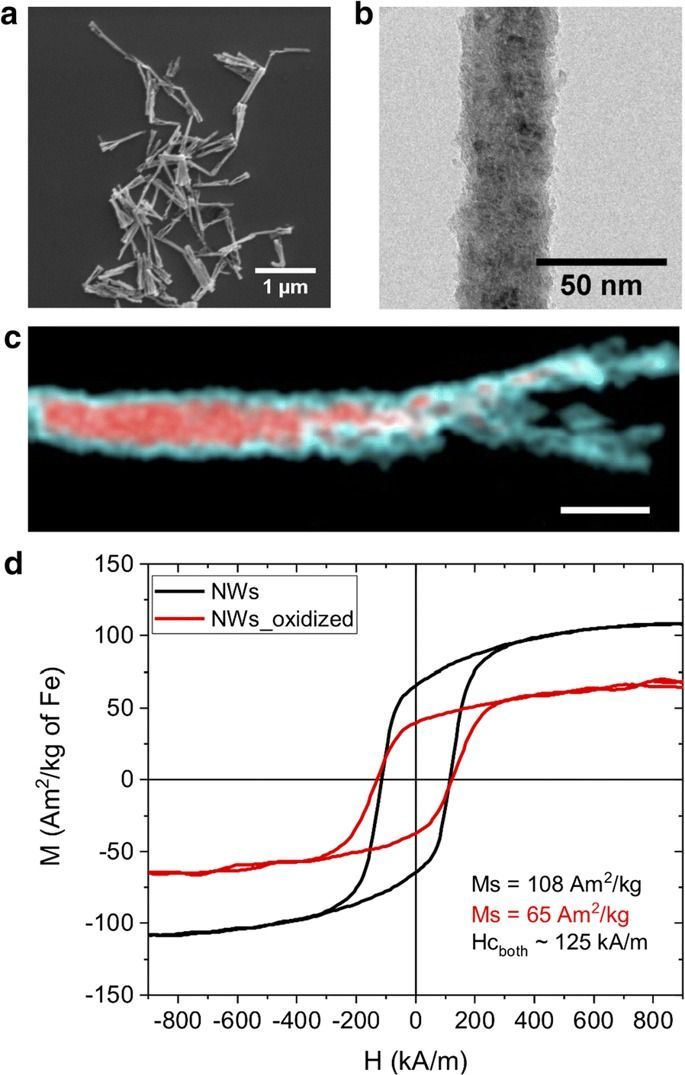
Identifying the precise location of cells and their migration dynamics is of utmost importance for achieving the therapeutic potential of cells after implantation into a host. Magnetic resonance imaging is a suitable, non-invasive technique for cell monitoring when used in combination with contrast agents.
This work shows that nanowires with an iron core and an iron oxide shell are excellent materials for this application, due to their customizable magnetic properties and biocompatibility. The longitudinal and transverse magnetic relaxivities of the core–shell nanowires were evaluated at 1.5 T, revealing a high performance as T2 contrast agents. Different levels of oxidation and various surface coatings were tested at 7 T. Their effects on the T2 contrast were reflected in the tailored transverse relaxivities. Finally, the detection of nanowire-labeled breast cancer cells was demonstrated in T2-weighted images of cells implanted in both, in vitro in tissue-mimicking phantoms and in vivo in mouse brain. Labeling the cells with a nanowire concentration of 0.8 μg of Fe/mL allowed the detection of 25 cells/µL in vitro, diminishing the possibility of side effects.