Become a member of the Science Fiction community to continue the discussionWebsite — https://damiengwalter.comYouTube — https://www.youtube.com/c/DamienWalte…
Category: military – Page 42

Neural Decoding Unveils Secrets of Navigation
Summary: A new study combines deep learning with neural activity data from mice to unlock the mystery of how they navigate their environment.
By analyzing the firing patterns of “head direction” neurons and “grid cells,” researchers can now accurately predict a mouse’s location and orientation, shedding light on the complex brain functions involved in navigation. This method, developed in collaboration with the US Army Research Laboratory, represents a significant leap forward in understanding spatial awareness and could revolutionize autonomous navigation in AI systems.
The findings highlight the potential for integrating biological insights into artificial intelligence to enhance machine navigation without relying on GPS technology.


We Need a Far Better Plan for Dealing With Existential Threat
Here’s my latest Opinion piece just out for Newsweek. Check it out! Lifeboat Foundation mentioned.
We need to remember that universal distress we all had when the world started to shut down in March 2020: when not enough ventilators and hospital beds could be found; when food shelves and supplies were scarce; when no COVID-19 vaccines existed. We need to remember because COVID is just one of many different existential risks that can appear out of nowhere, and halt our lives as we know it.
Naturally, I’m glad that the world has carried on with its head high after the pandemic, but I’m also worried that more people didn’t take to heart a longer-term philosophical view that human and earthly life is highly tentative. The best, most practical way to protect ourselves from more existential risks is to try to protect ourselves ahead of time.
That means creating vaccines for diseases even when no dire need is imminent. That means trying to continue to denuclearize the military regardless of social conflicts. That means granting astronomers billions of dollars to scan the skies for planet-killer asteroids. That means spending time to build safeguards into AI, and keeping it far from military munitions.
If we don’t take these steps now, either via government or private action, it could be far too late when a global threat emerges. We must treat existential risk as the threat it is: a human species and planet killer—the potential end of everything we know.

NASA seeks volunteers for a paid, yearlong simulated Mars mission
The agency says applicants must have a master’s degree with STEM qualifications and experience in the field, or a minimum of 1,000 hours piloting an aircraft or the requisite military experience. A bachelor of science degree in a STEM field also may be considered, NASA said.
“What we are looking for in this call is everyday civilians who are very astronaut-like to be research participants for us,” Bell said.
Compensation for participating in the mission is available, according to NASA, but an exact salary will be provided during the candidate screening process.
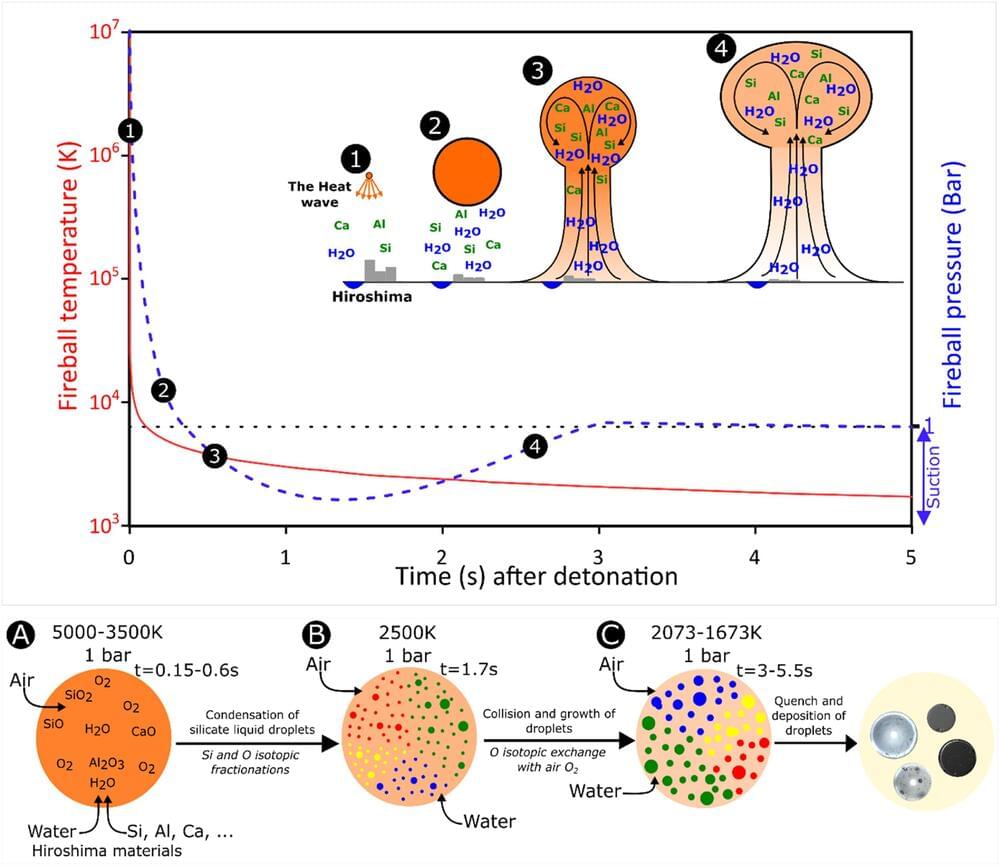
Hiroshima fallout debris linked to first solar system condensates
The atomic bombing of Hiroshima, Japan, by the United States in August 1945 was not only devastating at the time, resulting in the deaths of hundreds of thousands of people, but it has had long-standing impacts to the present day, particularly the elevated incidence of cancer from radiation.
Continued research of Hiroshima Bay has uncovered a new kind of debris from the fallout, known as Hiroshima glasses. These formed from vaporized materials of the bomb and the surrounding landscape and infrastructure being targeted.
New research published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters has analyzed the chemical and isotopic compositions of these glasses to ascertain their formation process during the nuclear event.

Bioweapons Designed by AI: a ‘Very Near-Term Concern,’ Schmidt Says
Artificial intelligence could bring about “biological conflict,” said former Google chief executive Eric Schmidt, who co-chaired the National Security Commission on Artificial Intelligence.
Schmidt spoke with defense reporters Sept. 12 as he helped release a new paper from his tech-oriented nonprofit think tank, the Special Competitive Studies Project. Schmidt launched the think tank with staff from the commission in order to continue the commission’s work.
AI’s applicability to biological warfare is “something which we don’t talk about very much,” Schmidt said, but it poses grave risks. “It’s going to be possible for bad actors to take the large databases of how biology works and use it to generate things which hurt human beings,” Schmidt said, calling that risk “a very near-term concern.”
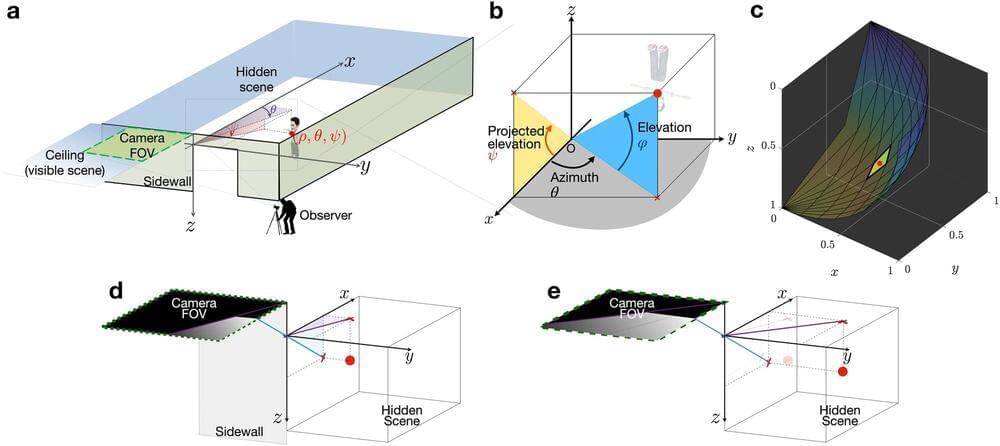
Science fiction meets reality as researchers develop techniques to overcome obstructed views
After a recent car crash, John Murray-Bruce wished he could have seen the other car coming. The crash reaffirmed the USF assistant professor of computer science and engineering’s mission to create a technology that could do just that: See around obstacles and ultimately expand one’s line of vision.
Using a single photograph, Murray-Bruce and his doctoral student, Robinson Czajkowski, created an algorithm that computes highly accurate, full-color three-dimensional reconstructions of areas behind obstacles—a concept that can not only help prevent car crashes but help law enforcement experts in hostage situations search-and-rescue and strategic military efforts.
“We’re turning ordinary surfaces into mirrors to reveal regions, objects, and rooms that are outside our line of vision,” Murray-Bruce said. “We live in a 3D world, so obtaining a more complete 3D picture of a scenario can be critical in a number of situations and applications.”
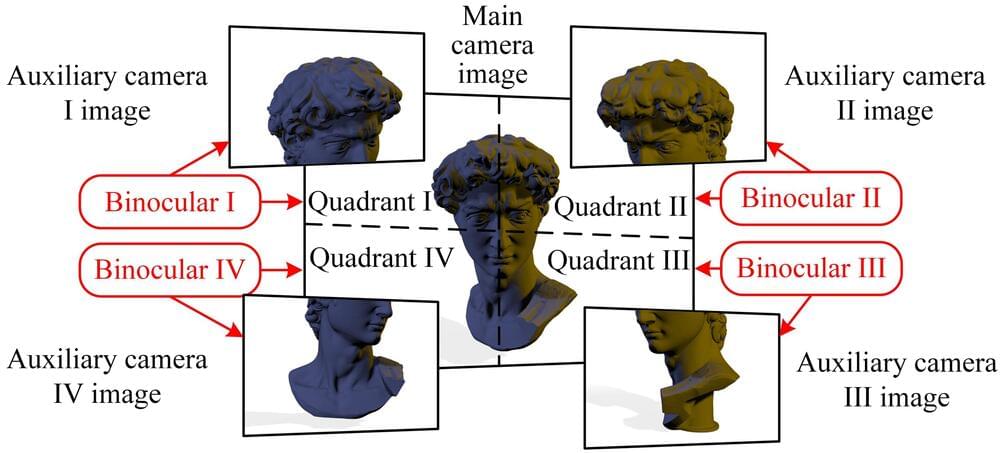
A multi-camera differential binocular vision sensor for robots and autonomous systems
Recent technological advances have enabled the development of increasingly sophisticated sensors, which can help to advance the sensing capabilities of robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, and other smart systems. Many of these sensors, however, rely on individual cameras, thus the accuracy of the measurements they collect is limited by the cameras’ field of view (FOV).
Researchers at Beihang University in China recently developed a new multi-camera differential binocular vision sensor with a wider FOV that could collect more accurate measurements. This sensor, introduced in a paper published in Optics & Laser Technology, could be integrated into a wide range of devices and smart robotic systems.
“Aiming at the high-precision requirements of environment perception for unmanned aerial vehicle detection, robot navigation, and autonomous driving, inspired by the multi-camera module of mobile phones, we introduced a visual perception mode based on the principle of high-precision binocular vision measurement,” Fuqiang Zhou, co-author of the paper, told Tech Xplore. “This principle involves a central high-resolution camera and peripheral auxiliary cameras that work together.”