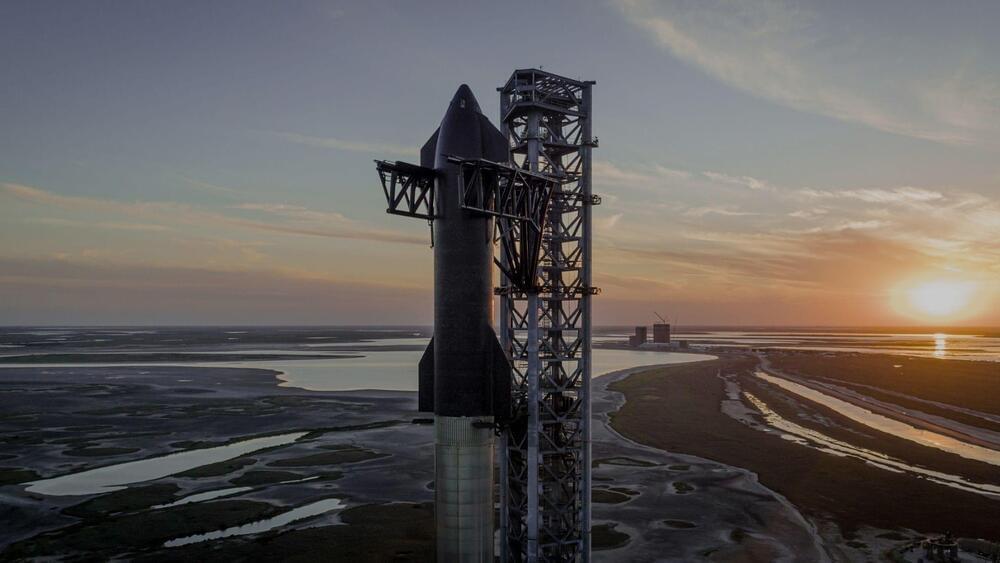
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk sets ambitious goals for Starship, including a Moon mission in 5 years, a private space station, and Pentagon interest.
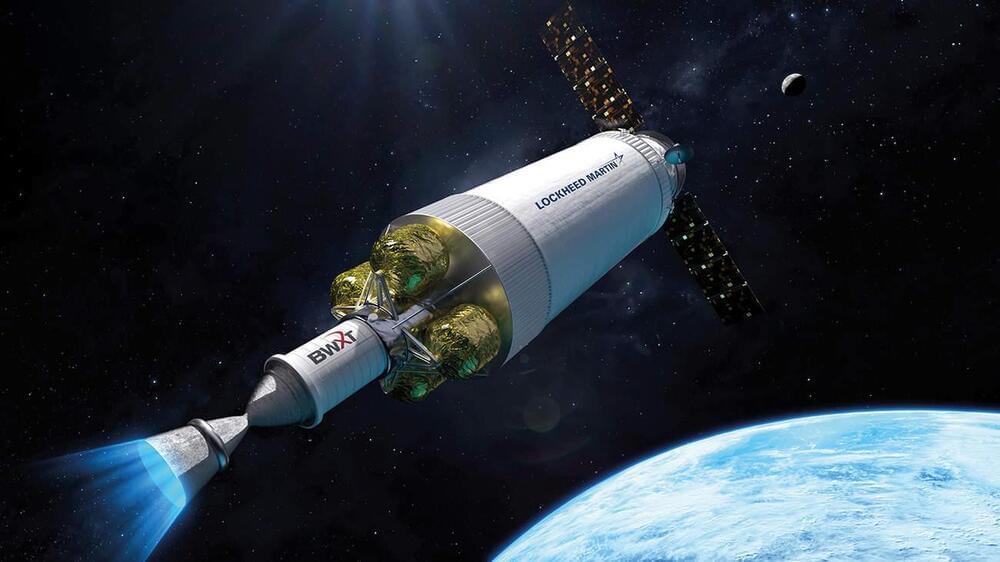



Launching rockets into space with atomic bombs is a crazy idea that was thankfully discarded many decades ago. But as Richard Corfield discovers, the potential of using the energy from nuclear-powered engines to drive space travel is back on NASA’s agenda.
In 1914 H G Wells published The World Set Free, a novel based on the notion that radium might one day power spaceships. Wells, who was familiar with the work of physicists such as Ernest Rutherford, knew that radium could produce heat and envisaged it being used to turn a turbine. The book might have been a work of fiction, but The World Set Free correctly foresaw the potential of what one might call “atomic spaceships”
The idea of using nuclear energy for space travel took hold in the 1950s when the public – having witnessed the horrors of Hiroshima and Nagasaki – gradually became convinced of the utility of nuclear power for peaceful purposes. Thanks to programmes such as America’s Atoms for Peace, people began to see that nuclear power could be used for energy and transport. But perhaps the most radical application lay in spaceflight.
China’s People’s Liberation Army is on the market for robotic special operations robots or UAVs that can operate independently for a long period.
China’s PLA unit 78,092 has publically announced its intention to develop robotic autonomous special operations drones.
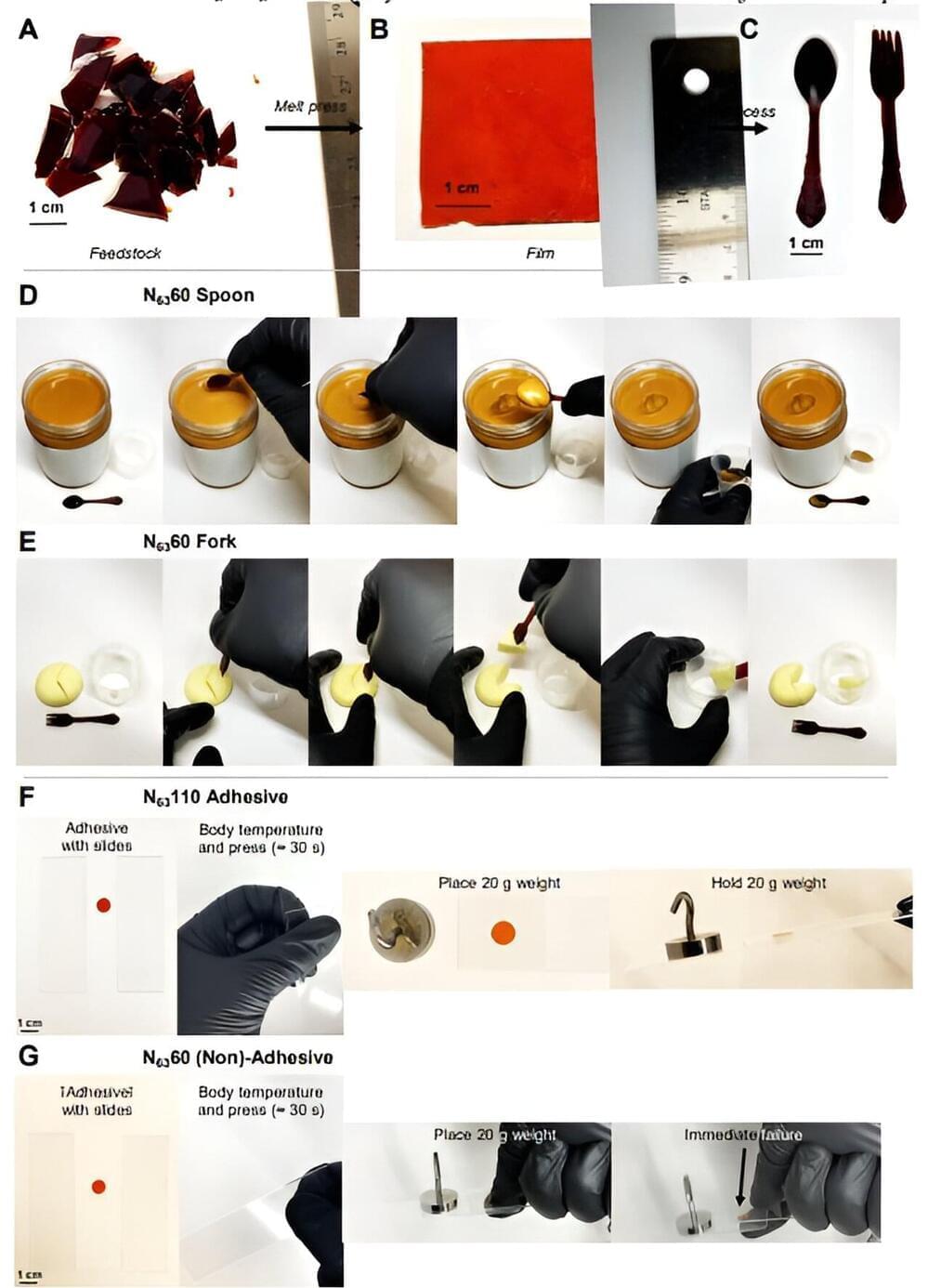

A team of molecular engineers have developed a type of plastic that can be shape-shifted using tempering. In their paper published in the journal Science the team, from the University of Chicago, with a colleagues from the US DEVCOM Army Research Laboratory, Aberdeen Proving Ground, the National Institutes of Standards and Technology and the NASA Glenn Research Center, describe how they made their plastic and how well it was able to shape shift when they applied various types of tempering.
Haley McAllister and Julia Kalow, with Northwestern University, have published a Perspective piece in the same issue of Science outlining the work.
Over the past several years, it has become evident that the use of plastics in products is harmful to not only the environment but also human health —bits of plastic have been found in the soil, the atmosphere, the oceans, and the human body.
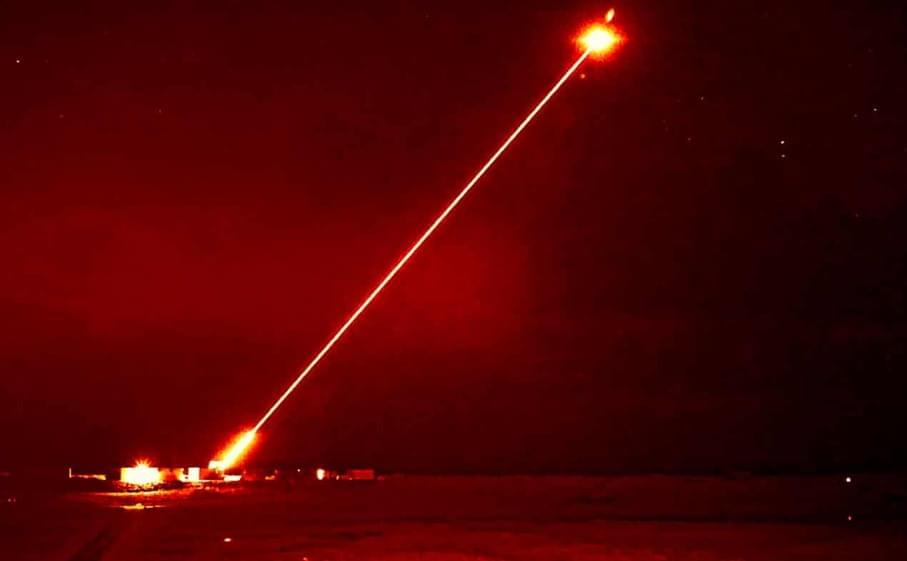



The DragonFire laser-directed energy weapon (LDEW) system has achieved the UK’s first high-power firing of a laser weapon against aerial targets during a trial at the MOD’s Hebrides Range.
The DragonFire is a line-of-sight weapon and can engage with any visible target, and its range is classified. The system is able to deliver a high-power laser over long ranges and requires precision equivalent to hitting a £1 coin from a kilometer away.
Laser-directed energy weapons are incredibly powerful and can engage targets at lightning-fast speeds. They use a concentrated beam of light to cut through their target, resulting in structural failure or other devastating outcomes if the warhead is targeted.

Walmart-backed EV startup Canoo has announced that deliveries of its all-electric commercial van have officially begun – and the first production Canoo LDV 130 vans are already hard at work.
The first batch of Canoo’s electric vans are reportedly in service now at Kingbee, a national work-ready van rental provider. The company says the delivery of vans to Kingbee is consistent with its previously announced “phased ramp-up manufacturing approach,” and asserts that additional customer deliveries will continue throughout 2024.
Canoo had previously delivered vehicles to NASA, the US military, and the State of Oklahoma (its home state) for testing. The vans delivered to Kingbee, however, seem to be the first that will be accessible to “the public.”
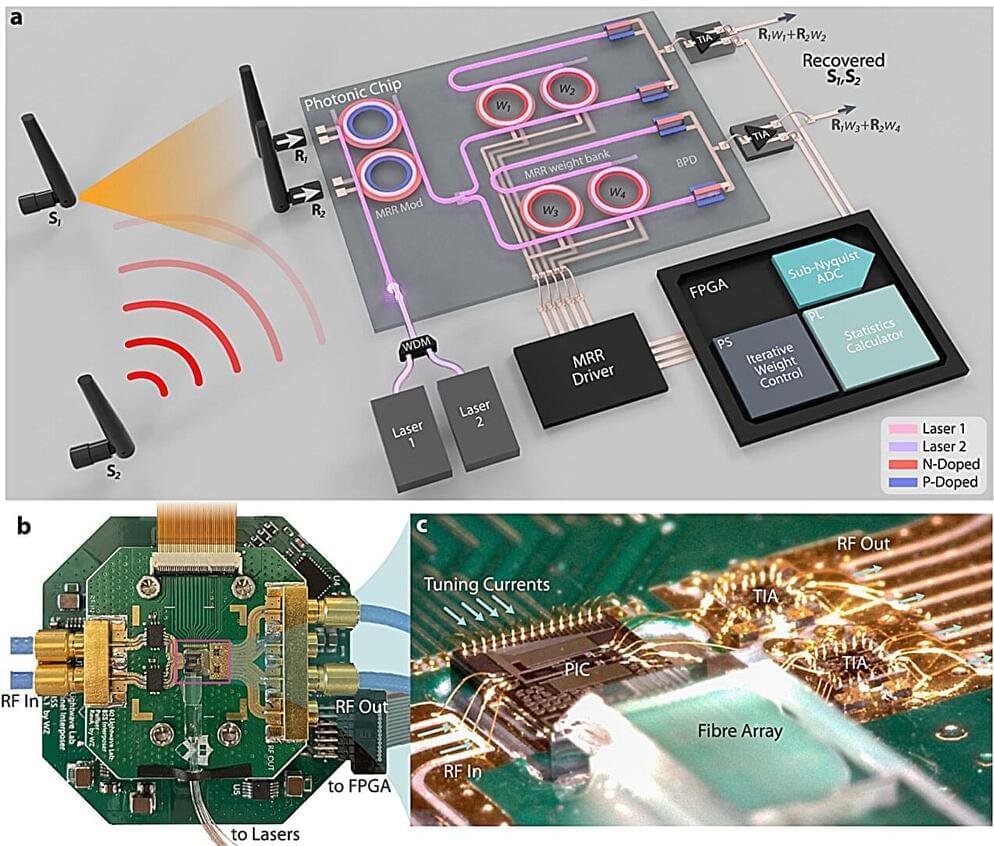
Radar altimeters are the sole indicators of altitude above a terrain. Spectrally adjacent 5G cellular bands pose significant risks of jamming altimeters and impacting flight landing and takeoff. As wireless technology expands in frequency coverage and utilizes spatial multiplexing, similar detrimental radio-frequency (RF) interference becomes a pressing issue.
To address this interference, RF front ends with exceptionally low latency are crucial for industries like transportation, health care, and the military, where the timeliness of transmitted messages is critical. Future generations of wireless technologies will impose even more stringent latency requirements on RF front-ends due to increased data rate, carrier frequency, and user count.
Additionally, challenges arise from the physical movement of transceivers, resulting in time-variant mixing ratios between interference and signal-of-interest (SOI). This necessitates real-time adaptability in mobile wireless receivers to handle fluctuating interference, particularly when it carries safety-to-life critical information for navigation and autonomous driving, such as aircraft and ground vehicles.