Here’s my latest Opinion piece just out for Newsweek. Check it out! Lifeboat Foundation mentioned.
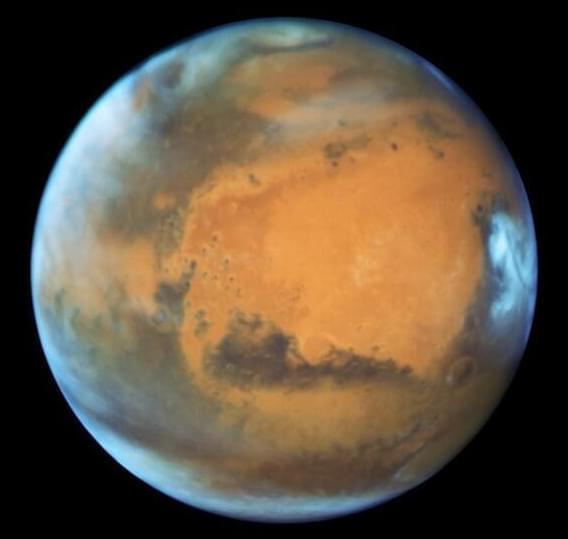
We need to remember that universal distress we all had when the world started to shut down in March 2020: when not enough ventilators and hospital beds could be found; when food shelves and supplies were scarce; when no COVID-19 vaccines existed. We need to remember because COVID is just one of many different existential risks that can appear out of nowhere, and halt our lives as we know it.
Naturally, I’m glad that the world has carried on with its head high after the pandemic, but I’m also worried that more people didn’t take to heart a longer-term philosophical view that human and earthly life is highly tentative. The best, most practical way to protect ourselves from more existential risks is to try to protect ourselves ahead of time.
That means creating vaccines for diseases even when no dire need is imminent. That means trying to continue to denuclearize the military regardless of social conflicts. That means granting astronomers billions of dollars to scan the skies for planet-killer asteroids. That means spending time to build safeguards into AI, and keeping it far from military munitions.
If we don’t take these steps now, either via government or private action, it could be far too late when a global threat emerges. We must treat existential risk as the threat it is: a human species and planet killer—the potential end of everything we know.