📝 — Bertran, et al.
Full text is available 👇
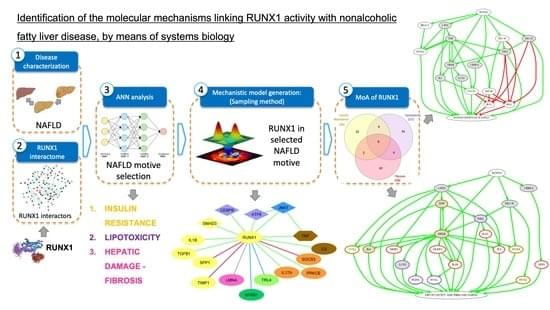
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most prevalent chronic hepatic disease; nevertheless, no definitive diagnostic method exists yet, apart from invasive liver biopsy, and nor is there a specific approved treatment. Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) plays a major role in angiogenesis and inflammation; however, its link with NAFLD is unclear as controversial results have been reported. Thus, the objective of this work was to determine the proteins involved in the molecular mechanisms between RUNX1 and NAFLD, by means of systems biology. First, a mathematical model that simulates NAFLD pathophysiology was generated by analyzing Anaxomics databases and reviewing available scientific literature.