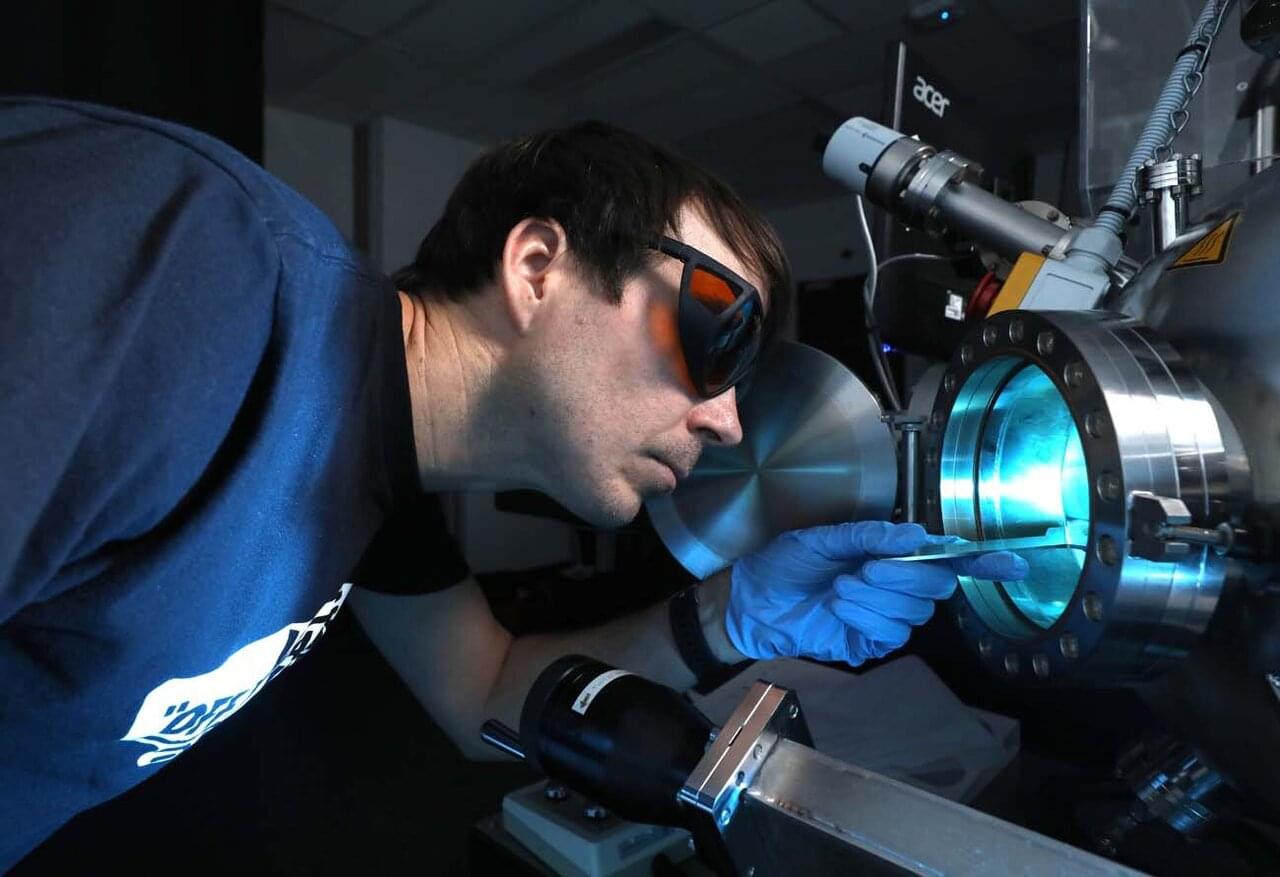
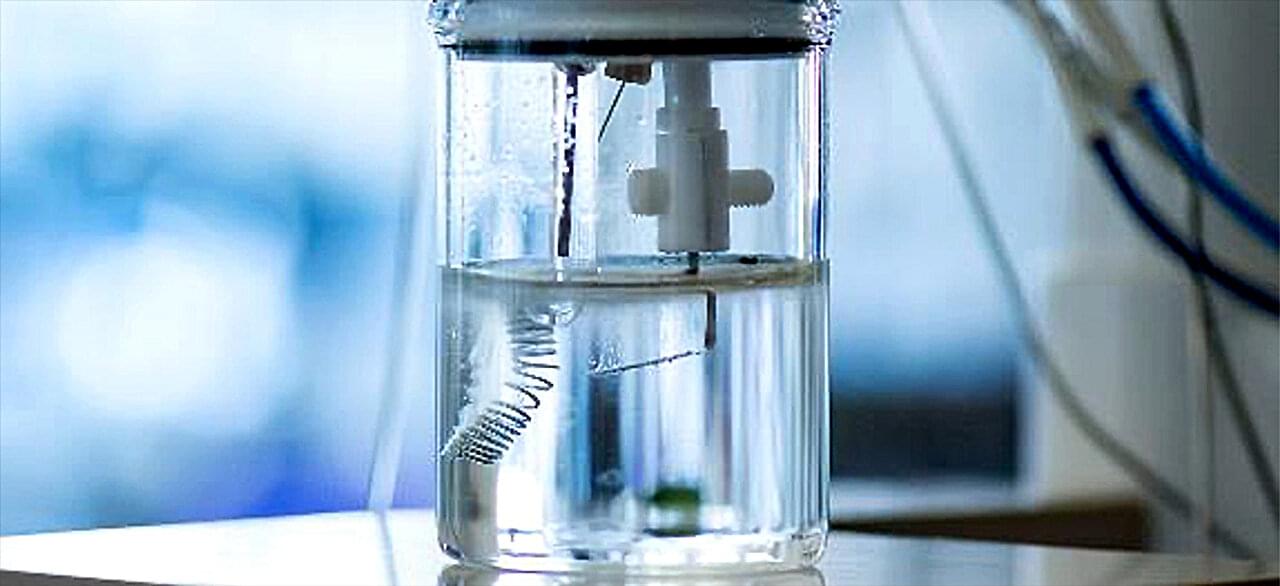
A multidisciplinary team at the University of California, Berkeley, the Georgia Institute of Technology and the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology has developed a stretchable, self-healing lithium battery that remains stable after 500 charge/discharge cycles. In their paper published in the journal Science Advances, the group describes how they developed the battery and possible uses for it.
Over the past several years, scientists have been developing batteries for different types of applications. One such type is the stretchable battery, which could be used in wearable electronics. Recently, a team at Linköping University announced that they had developed a fluid battery that can take any shape, allowing for its use in a wide variety of applications. In this new study, the team at UC Berkeley has developed a stretchable battery that also heals itself.
To make the new battery, the research team started with a zwitterionic polymer that had both a positive and negative charge. With such polymers, water molecules bond with the charged parts while the lithium ions are attracted by the negative parts of plastic. The arrangement allows water to be tightly bound in the battery, reducing the risk of it splitting when voltage is applied, while still allowing lithium ions to be released when desired.