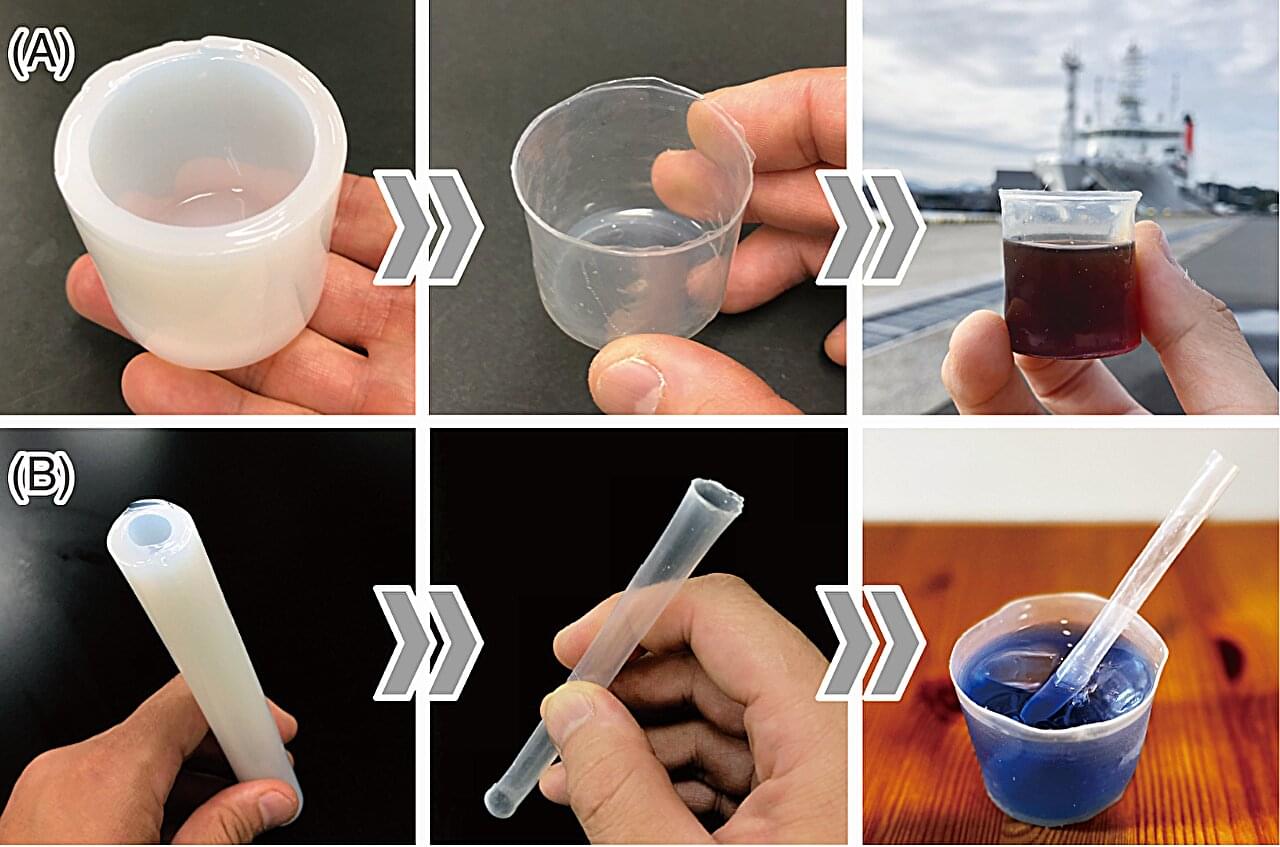
A team of biomaterial engineers, environmental resource specialists and industrial design researchers affiliated with a host of institutions across Japan has developed a biodegradable material that is clear and can hold boiling water—and it degrades in less than a year after settling on the ocean floor. Their work is published in the journal Science Advances.
Prior research has shown that millions of tons of plastics are piling up in the environment, including on the ocean floor. Because of this, scientists have been looking for better, biodegradable replacements. In this new effort, the research team has developed a paper-based, clear, biodegradable material that can stand up to liquids for several hours, even those that have been heated, allowing them to replace plastic cups, straws, and other everyday objects.
The research team made the material by starting with a standard cellulose hydrogel. After drying, the material was treated with an aqueous lithium bromide solution which forced the cellulose to solidify into desired shapes. The researchers note that end-products could be as thin as plastic cup walls, or as thick as desired. They describe the material as tPB, a transparent 3D material made solely of cellulose.