MIT scientists were surprised to discover a “chiral superconductor” — a material that conducts electricity without resistance, and also, paradoxically, is magnetic — in rhombohedral graphene.

Researchers in the U.S. have discovered a self-sustaining material that uses capillary condensation to harvest water from the air.
Magnets and superconductors go together like oil and water—or so scientists have thought. But a new finding by MIT physicists is challenging this century-old assumption.
In a paper appearing in the journal Nature, the physicists report that they have discovered a “chiral superconductor”—a material that conducts electricity without resistance, and also, paradoxically, is intrinsically magnetic. What’s more, they observed this exotic superconductivity in a surprisingly ordinary material: graphite, the primary material in pencil lead.
Graphite is made from many layers of graphene—atomically thin, lattice-like sheets of carbon atoms—that are stacked together and can easily flake off when pressure is applied, as when pressing down to write on a piece of paper. A single flake of graphite can contain several million sheets of graphene, which are normally stacked such that every other layer aligns. But every so often, graphite contains tiny pockets where graphene is stacked in a different pattern, resembling a staircase of offset layers.
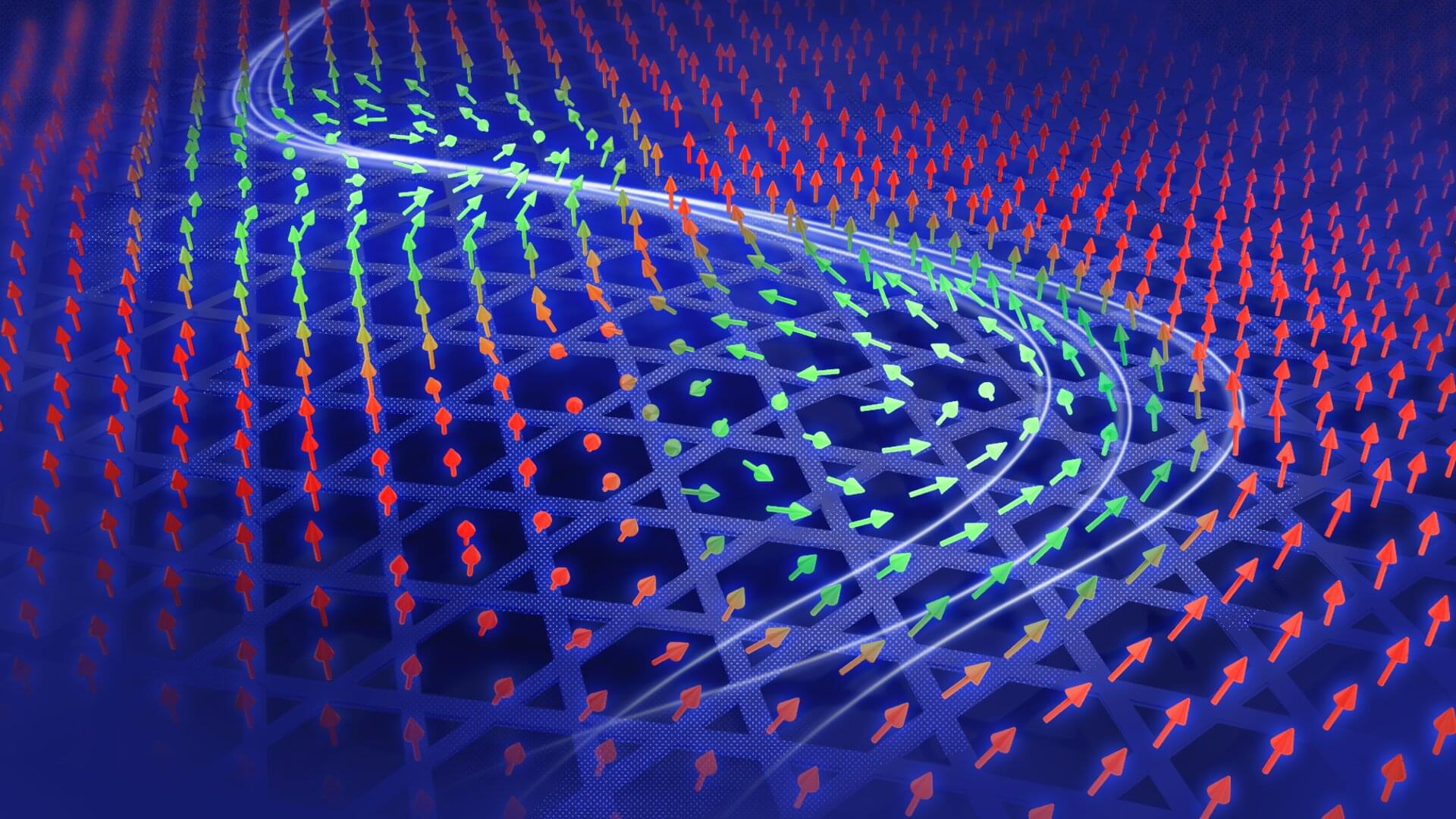
A new study reveals a fresh way to control and track the motion of skyrmions—tiny, tornado-like magnetic swirls that could power future electronics. Using electric currents in a special magnetic material called Fe₃Sn₂, the team got these skyrmions to “vibrate” in specific ways, unlocking clues about how invisible spin currents flow through complex materials.
The discovery not only confirms what theory had predicted but also points to a powerful new method for detecting spin currents—a discovery that could one day lead to more efficient memory and sensing devices in future electronics. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications.
Led by Assistant Prof. Amir Capua and Ph.D. Candidate Nirel Bernstein from the Institute of Applied Physics and Nano Center at Hebrew University in collaboration with Prof. Wenhong Wang and Dr. Hang Li from Tiangong University, the team explored how skyrmions behave in a special magnetic material called Fe₃Sn₂ (iron tin).

A research team has developed the world’s first Pixel-Based Local Sound OLED technology. This breakthrough enables each pixel of an OLED display to simultaneously emit different sounds, essentially allowing the display to function as a multichannel speaker array. The team successfully demonstrated the technology on a 13-inch OLED panel, equivalent to those used in laptops and tablets.
The research has been published in the journal Advanced Science. The team was led by Professor Su Seok Choi of the Department of Electrical Engineering at POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) and Ph.D. candidate Inpyo Hong of the Graduate Program in Semiconductor Materials and Devices.
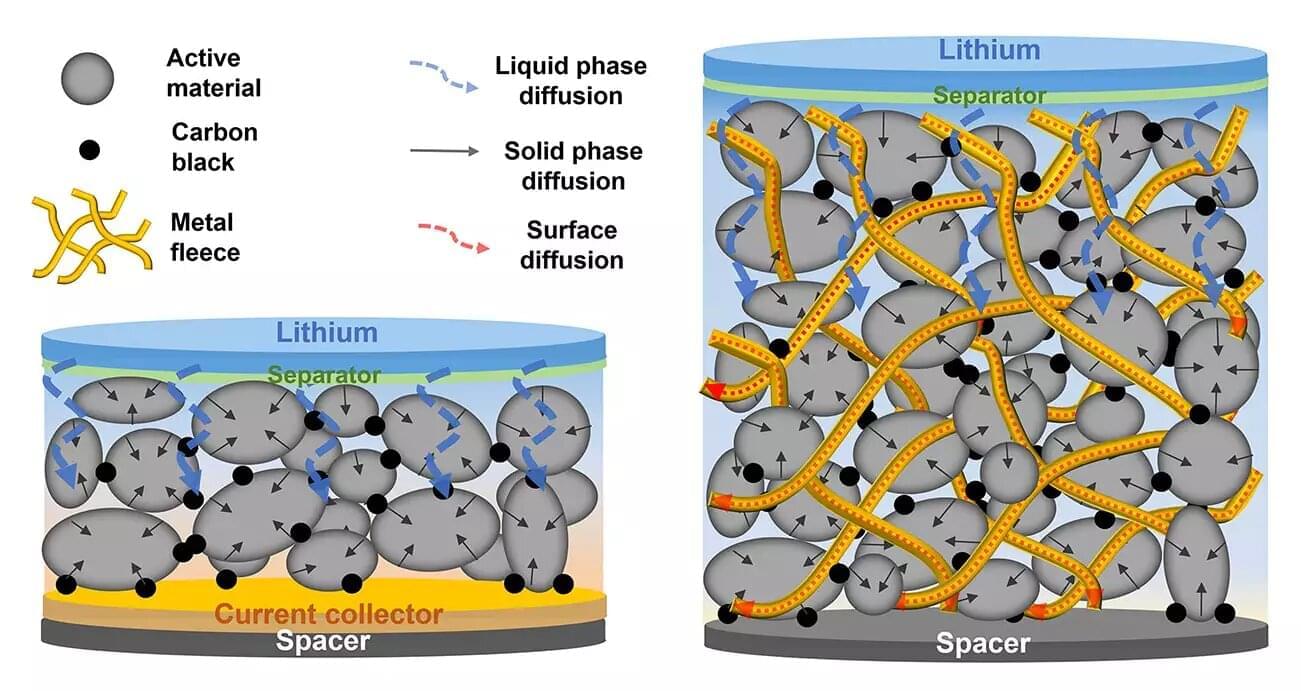
Batteries are becoming more and more powerful. A discovery by researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg could now give them a significant energy boost.
A team led by Max Planck Director Joachim Spatz has discovered that metal fleeces used as contact material in battery electrodes significantly accelerate the charge transport of metal ions, in particular. This makes it possible to build significantly thicker electrodes than is standard today. It means that roughly half of the contact metal and other materials that do not contribute to energy storage can be saved, and makes it possible for researchers to significantly increase the energy density in batteries.
The findings are published in the journal ACS Nano.
With the declared aim of measuring matter under extreme pressure, an international research collaboration headed by the University of Rostock and the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) used the high-performance laser DIPOLE 100-X at the European XFEL for the first time in 2023. With spectacular results: In this initial experiment they managed to study liquid carbon—an unprecedented achievement as the researchers report in the journal Nature.
Liquid carbon can be found, for example, in the interior of planets and plays an important role in future technologies like nuclear fusion. To date, however, only very little was known about carbon in its liquid form because in this state it was practically impossible to study in the lab: Under normal pressure, carbon does not melt but immediately changes into a gaseous state.
Only under extreme pressure and at temperatures of approximately 4,500 degrees Celsius—the highest melting point of any material—does carbon become liquid. No container would withstand that.
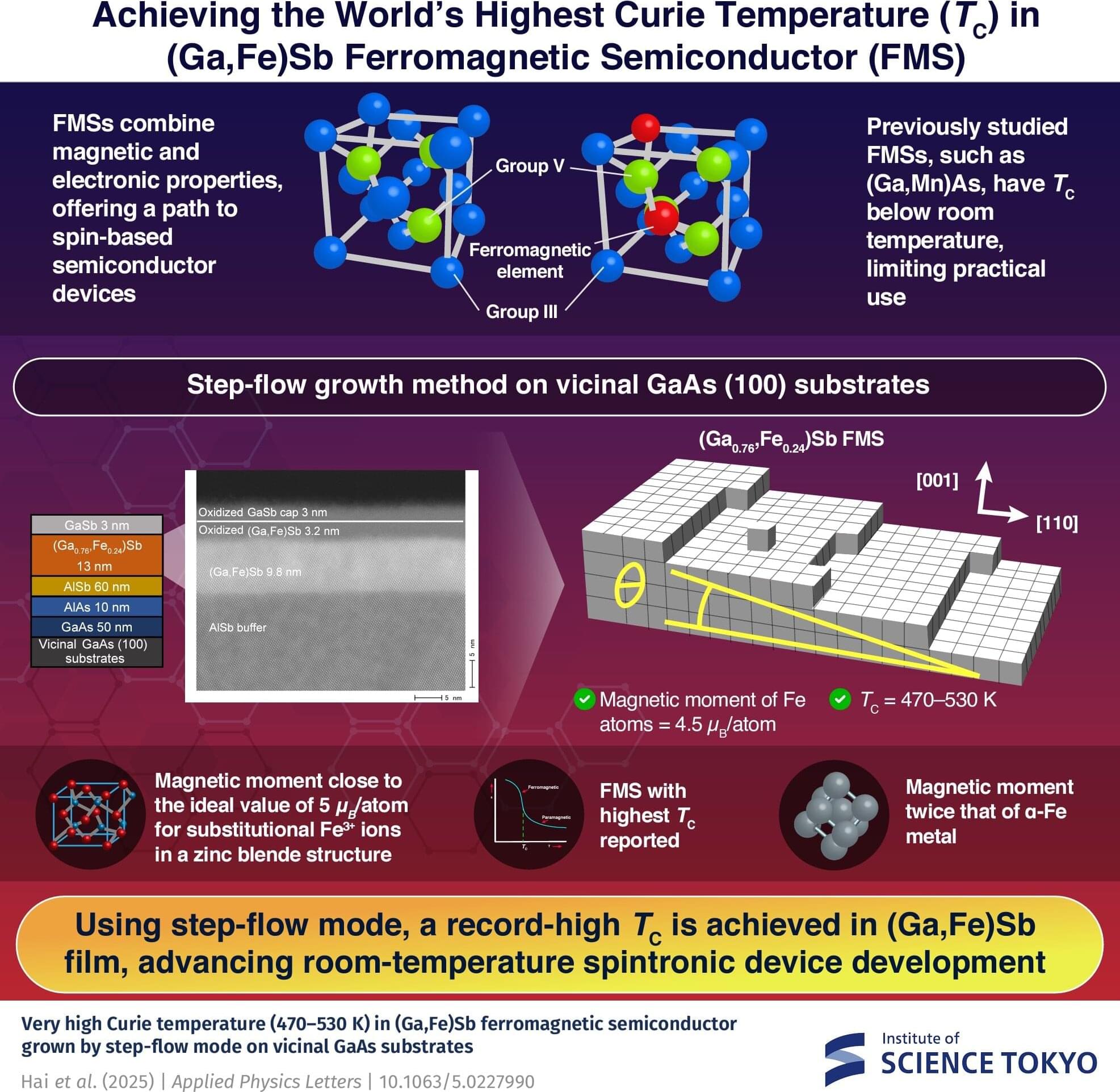
Ferromagnetic semiconductors (FMSs) combine the unique properties of semiconductors and magnetism, making them ideal candidates for developing spintronic devices that integrate both semiconductor and magnetic functionalities. However, one of the key challenges in FMSs has been achieving high Curie temperatures (TC) that enable their stable operation at room temperature.
Though previous studies achieved a TC of 420 K, which is higher than room temperature, it was insufficient for effectively operating the spin functional materials, highlighting the demand for an increase in TC among FMSs. This challenge has been featured among the 125 unsolved questions selected by the journal Science in 2005.
Materials such as (Ga, Mn)As exhibit low TC, limiting their practical use in spintronic devices. While adding Fe to narrow bandgap semiconductors like GaSb seemed promising, incorporating high concentrations of Fe while maintaining crystallinity proved difficult, restricting the attainable TC.
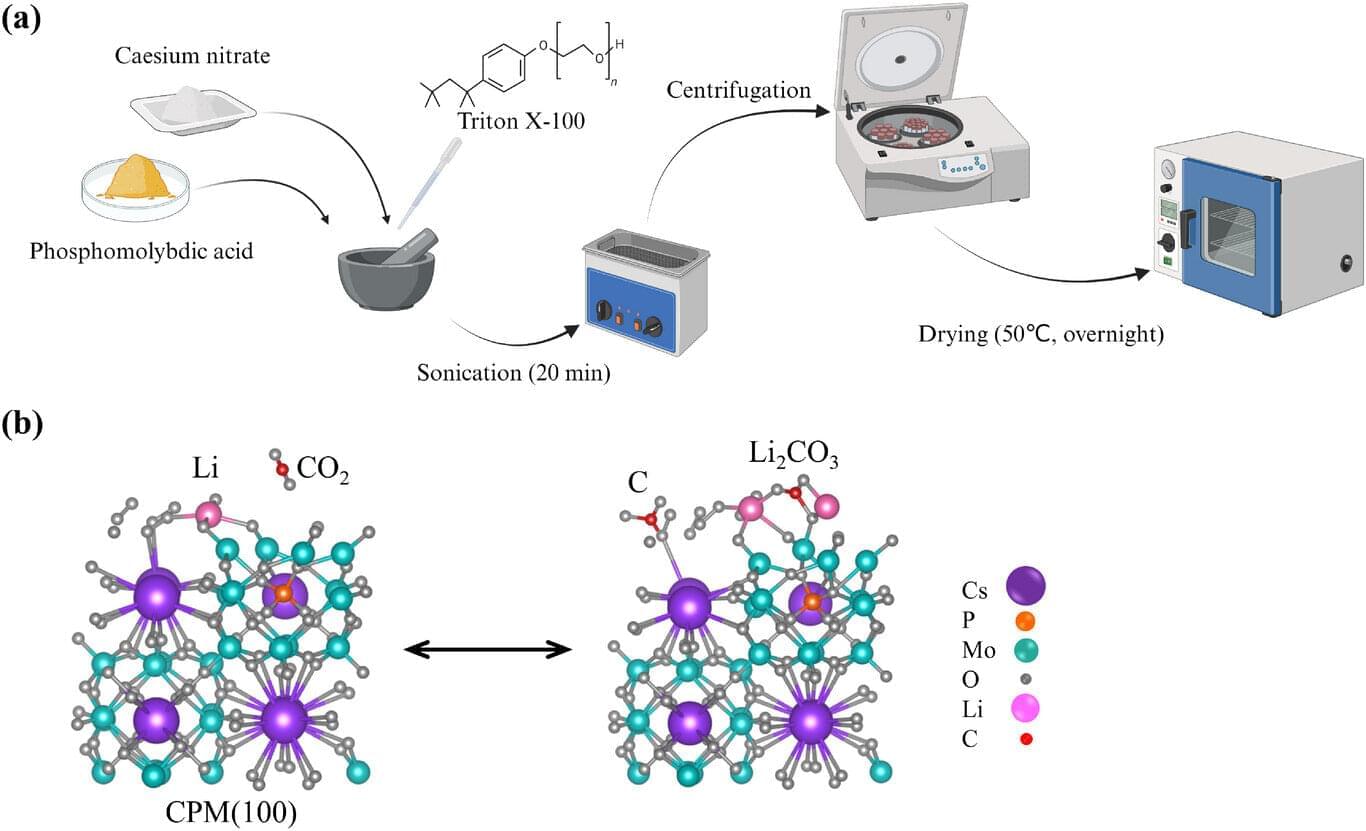
Scientists at the University of Surrey have made a breakthrough in eco-friendly batteries that not only store more energy but could also help tackle greenhouse gas emissions. Lithium–CO2 “breathing” batteries release power while capturing carbon dioxide, offering a greener alternative that may one day outperform today’s lithium-ion batteries.
Until now, lithium-CO2 batteries have faced setbacks in efficiency—wearing out quickly, failing to recharge and relying on expensive rare materials such as platinum.
However, researchers from Surrey have found a way to overcome these issues by using a low-cost catalyst called cesium phosphomolybdate (CPM). Using computer modeling and lab experiments, tests showed this simple change allowed the battery to store significantly more energy, charge with far less power and run for over 100 cycles.