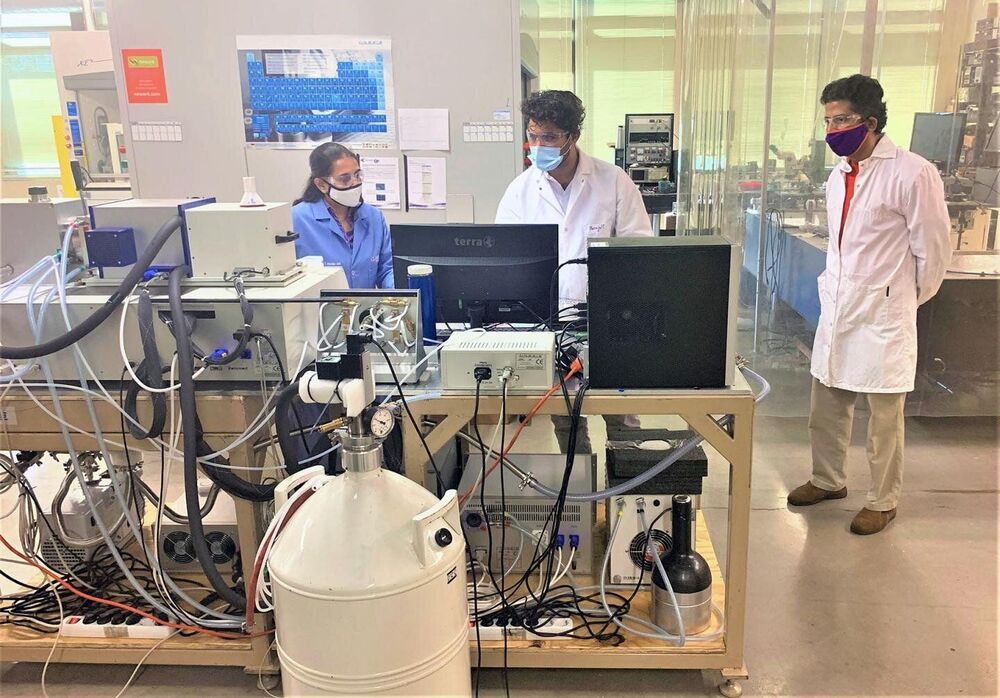
Groundbreaking science is often the result of true collaboration, with researchers in a variety of fields, viewpoints and experiences coming together in a unique way. One such effort by Clemson University researchers has led to a discovery that could change the way the science of thermoelectrics moves forward.
Graduate research assistant Prakash Parajuli; research assistant professor Sriparna Bhattacharya; and Clemson Nanomaterials Institute (CNI) Founding Director Apparao Rao (all members of CNI in the College of Science’s Department of Physics and Astronomy) worked with an international team of scientists to examine a highly efficient thermoelectric material in a new way—by using light.
Their research has been published in the journal Advanced Science and is titled “High zT and its origin in Sb-doped GeTe single crystals.”