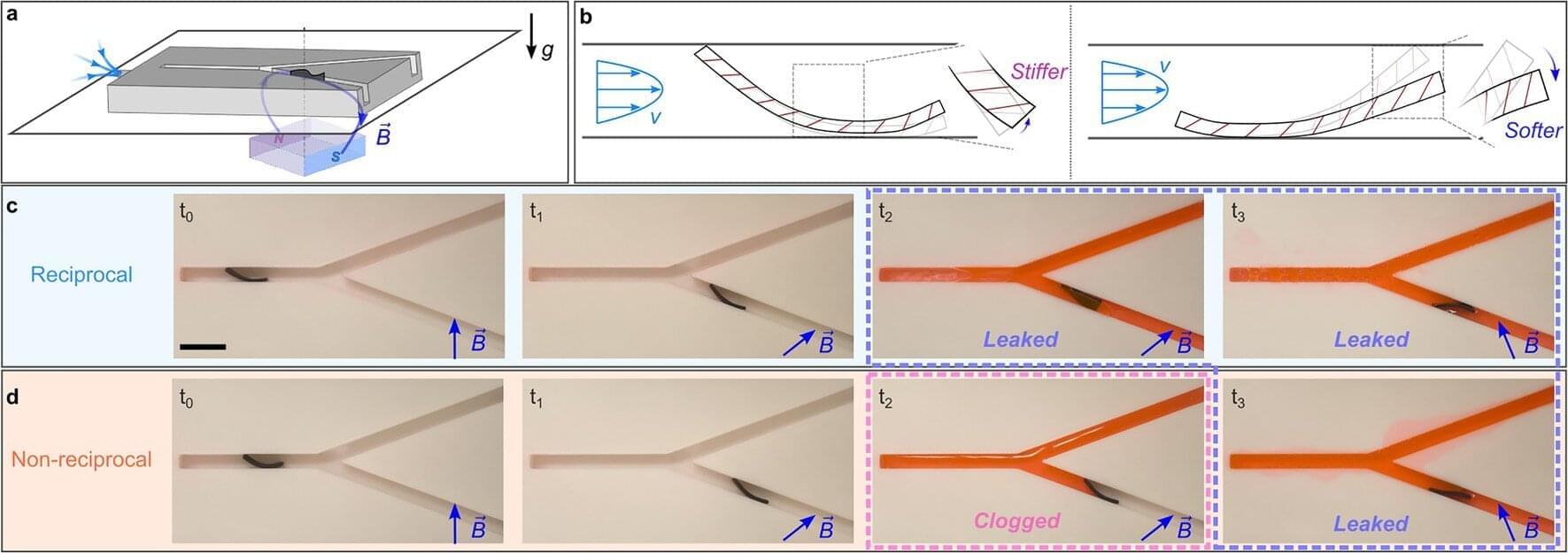
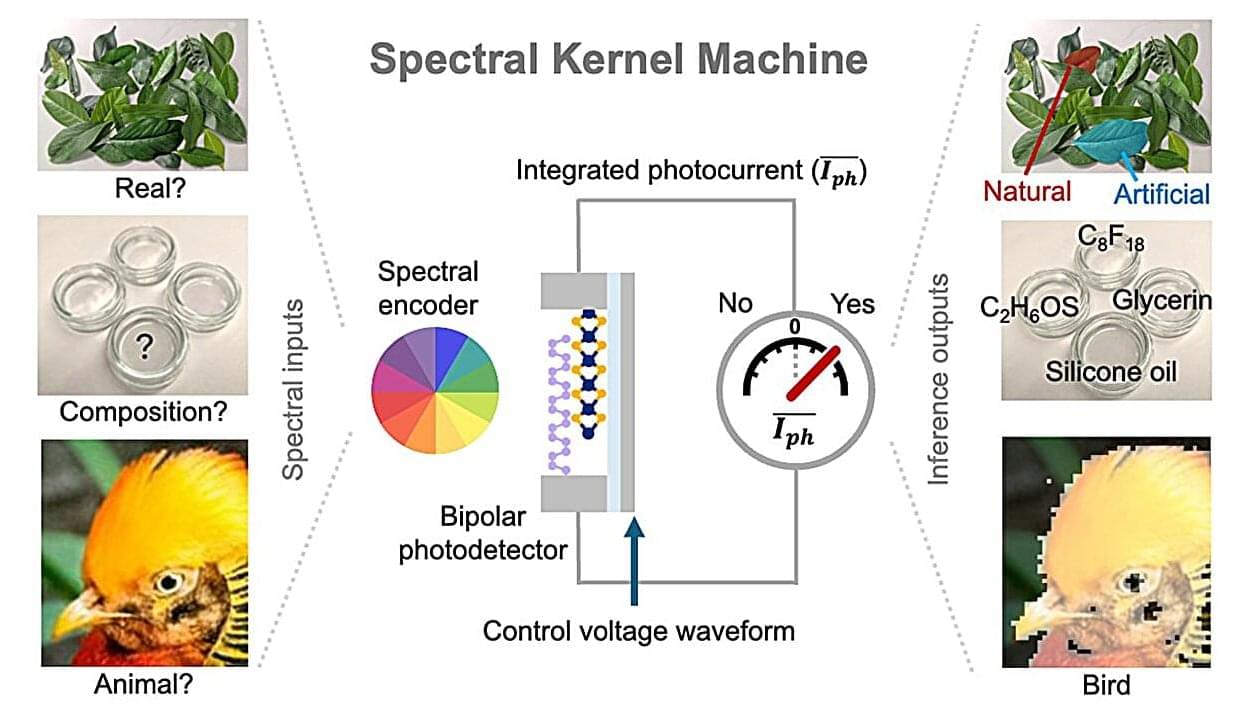
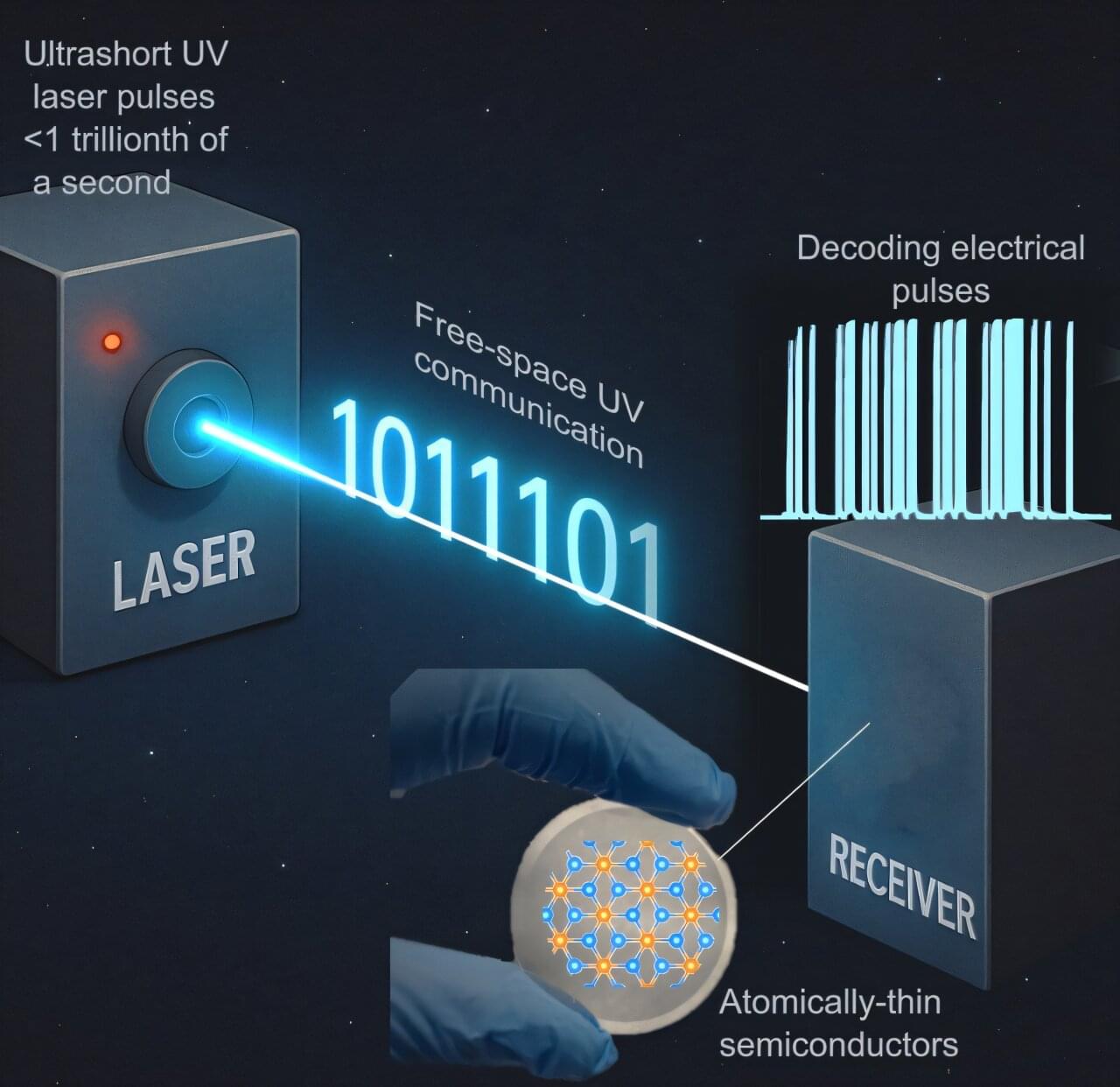
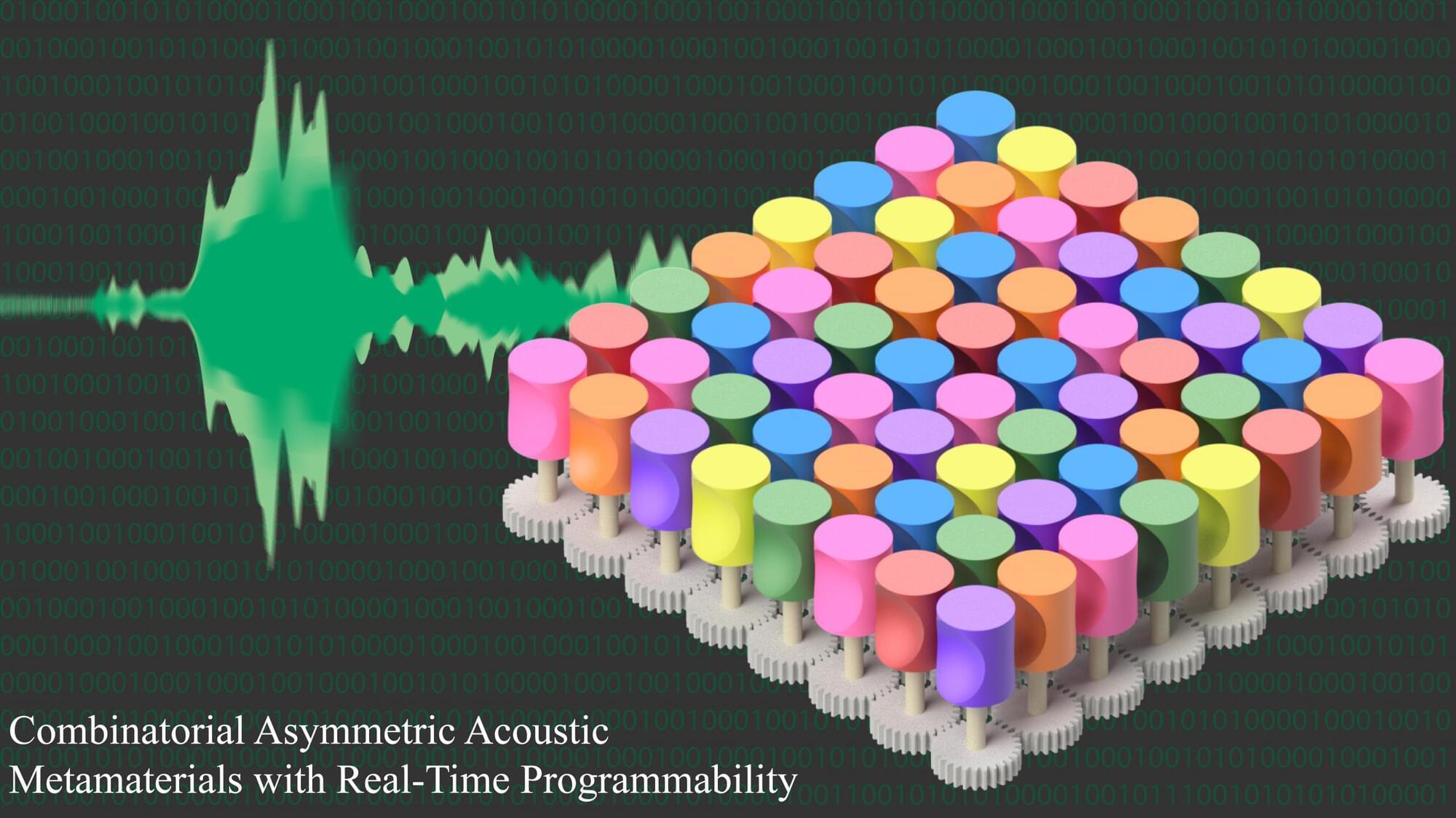
Researchers have created gyromorphs, a new material that controls light more effectively than any structure used so far in photonic chips.
These hybrid patterns combine order and disorder in a way that stops light from entering from any angle. The discovery solves major limitations found in quasicrystals and other engineered materials. It may open the door to faster, more efficient light-powered computers.
Light-based computers and the need for better materials.