Biograph, a company co-founded by longevity guru Peter Attia and a prominent Silicon Valley VC, has emerged from stealth.

The progress of a human being through life might be thought of as a mostly gradual succession of changes from the ovum to the grave.
But if you wake up one morning, look in the mirror, and wonder when you suddenly grew so much older, you may not be imagining things.
According to recent research into the molecular changes associated with aging, humans experience two drastic lurches forward, one at the average age of 44 and the other at the average age of 60.
Peggy Hoyt is a Florida-based estate planner and co-author, with Rudi Hoffman, of The Cryonics Estate Planning Handbook. We discuss dynastic trusts, the Rule Against Perpetuities and why it isn’t a problem in the USA, reasons to have a living will, how to build in financial incentives to revive you, the components of a cryonics/biostasis estate plan, the role of the trust protector, financing the preservation of pets, and more.
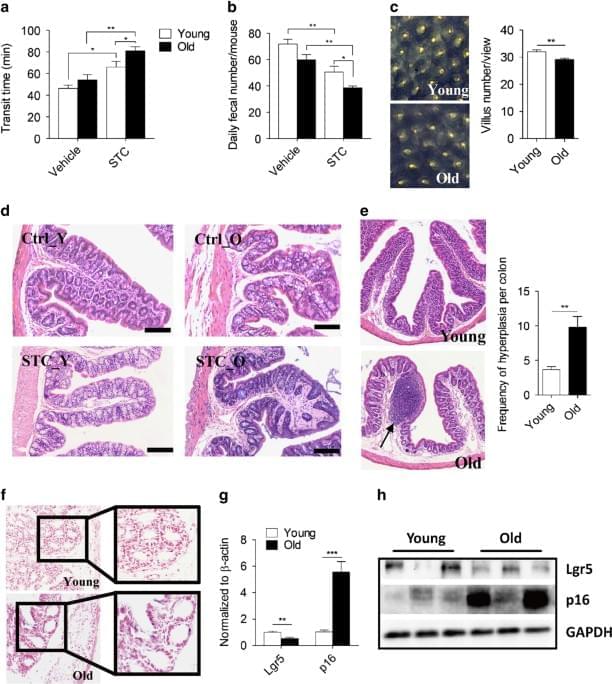
face_with_colon_three Year 2017 nad plus is essentially immortality of the colon which can reduce colon aging.
Boosting the level of a coenzyme regulating metabolism could help treat constipation and other aging-related intestinal problems. Researchers in Hangzhou, China, led by Qinsong Sheng from the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University and Zhenyu Ju from Hangzhou Normal University studied differences in colon function between young and old mice. They showed that older animals had more difficulty in defecation through the gastrointestinal tract and that this was associated with a lower level of the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). Treatment with an NAD precursor improved defecation ability, whereas administering a drug that blocks NAD synthesis led to worsened colon function in mice. These findings point to NAD as a key regulator of colon motility and suggest a therapeutic strategy for older individuals with bowel-movement problems.

face_with_colon_three year 2024.
Genes from regenerative organisms rejuvenate intestinal stem cells in fruit flies.
In a groundbreaking experiment, Japanese researchers transferred regenerative genes to fruit flies, leading to improved intestinal health and enhanced stem cell activity. This discovery opens new possibilities for anti-aging strategies in higher organisms, including humans, through targeted gene therapy.
Researchers including those from the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences transferred genes from simple organisms capable of regenerating their bodies into common fruit flies, more complex animals that cannot. They found the transferred gene suppressed an age-related intestinal issue in the flies. Their results suggest studying genes specific to animals with high regenerative capability may uncover new mechanisms for rejuvenating stem cell function and extending the healthy lifespan of unrelated organisms.
“Of these children, 85% are going to beat their cancer, but it’s a win at a cost,” says Armstrong. “We know that these kids will have shortened lifespans. They often die young of chronic diseases like heart disease, stroke or secondary cancers which present much earlier. And we discovered about a decade ago that this is because they’re ageing much faster than their chronological age.”
In particular, this is reflected not just in their biology, but in physical frailty. When Kirsten Ness, a physical therapist and clinical epidemiologist at St Jude, assessed a group of childhood cancer survivors aged 24–41, she noted that when it came to heart function, flexibility, respiratory capacity and range of motion, they resembled people decades older. “We showed that at 30, they have physiological frailty that resembles people in their 70s and 80s, and it’s getting worse over time,” says Ness.
The underlying cause of this is senescence, a state in which cells cease to continue dividing as normal, but instead simply linger, refusing to die. Because of this quality, senescent cells have sometimes been described as “zombie cells” and they are now regarded as a driving force and a reflection of ageing. Over the course of a lifetime, our bodies incur increasing amounts of damage which in turn makes many of our cells, distributed throughout our body, more likely to become senescent.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
At the very start Aubrey claims, so long as he has the funding, he can finish the RMR in 3 years and then things take off from there. He seems to hint that the LEV prediction of 12–15 years could be thrown out and come sooner.
In this in-depth conversation, Dr. Aubrey de Grey discusses his Robust Mouse Rejuvenation (RMR) studies at the LEV Foundation and why he believes we’re close to achieving the crucial RMR milestone within just three years — a breakthrough that could transform aging research forever.
You’ll also hear about:
His predictions for reaching Longevity Escape Velocity by the late 2030s.
What he would change about Bryan Johnson’s longevity algorithm.
How reaching RMR could trigger a global \.

Dear Colleagues.
In the context of an ageing world population, certain pathologies that are exacerbated in this process of ageing, such as osteoarthritis (OA), will become more prevalent in the coming years. Moreover, OA is one of the main causes of chronic pain and physical disability in the elderly. It is therefore of great relevance to gain a deep understanding on the pathophysiology of this disease, and also to identify potential prognostic and diagnostic tools along with novel promising therapeutic targets for OA.
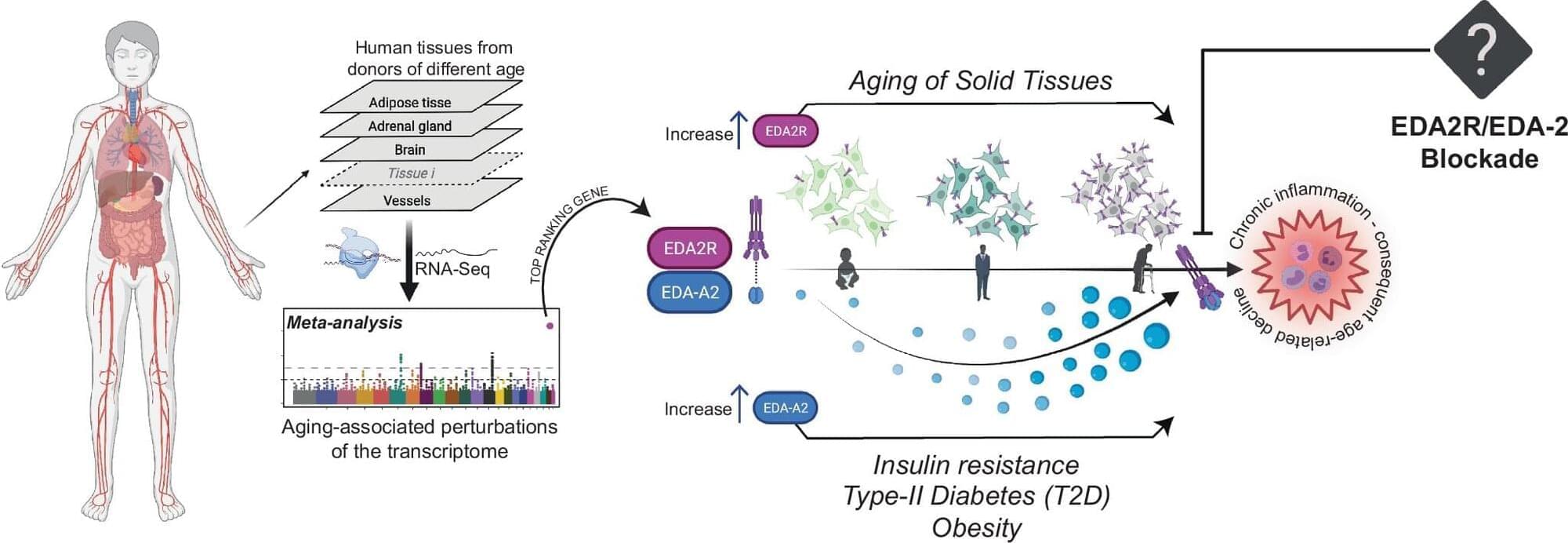
New therapies for managing aging could emerge from research into a new gene, which scientists have identified as a key driver of degeneration.
Age-related diseases are strongly linked to inflammation which, when chronic, albeit low-grade, contributes to conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, neurodegeneration, and sarcopenia, significantly impacting health and longevity.
In a study published in Nature Communications, Dr. Ildus Akhmetov, a geneticist at Liverpool John Moores University’s School of Sport and Exercise Sciences, along with colleagues from Italy, Switzerland, and the Netherlands, uncovered groundbreaking insights into the role of the Ectodysplasin A2 Receptor (EDA2R) in this process.