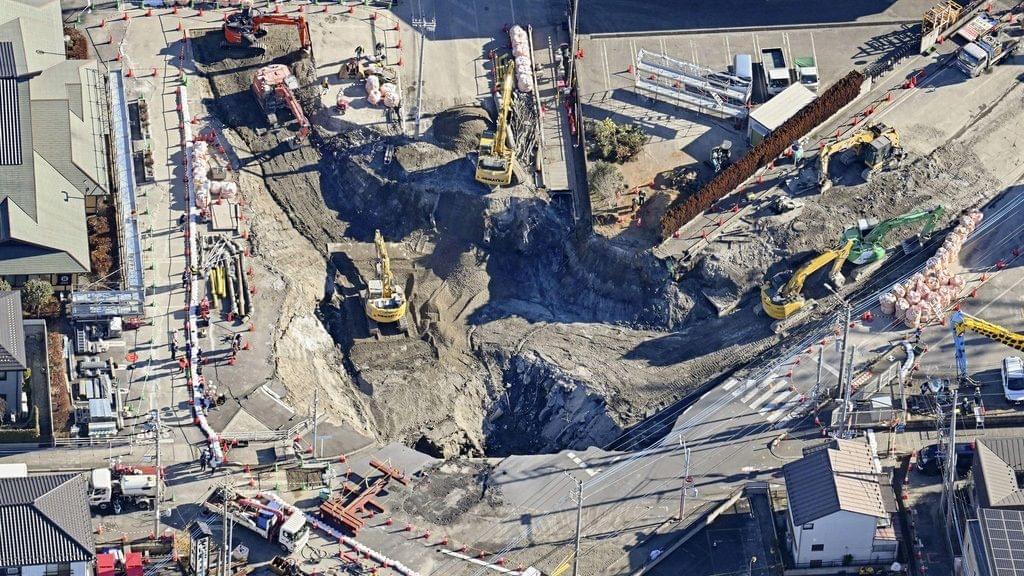
The impact of the collapse extended far beyond the immediate disruption to traffic and businesses in the area, affecting wastewater services for 1.2 million residents in the prefecture. Authorities called on inhabitants of surrounding cities to reduce their water usage, pressing them to curtail activities like bathing and washing clothing. In addition, wastewater was collected to reduce the flow to the damaged pipe, with the effluent then chlorinated and released into a nearby river, potentially damaging the environment.
The wide scale of service disruption is linked to Japan’s approach to wastewater management. Wastewater operations are overseen by public sewage systems operated by a single municipality or regional sewage systems operated jointly by multiple municipalities. The pipeline in Yashio was in the latter category and carried wastewater collected from 12 municipalities. While such regional management systems provide significant advantages to cities in terms of efficiency and cost savings, the failed pipe and resulting sinkhole illustrates the risk of widespread disruption of services when anything goes wrong.
Moreover, the incident laid bare the fragile state of Japan’s sewage infrastructure. Morita Hiroaki, who heads the prefectural panel studying the gargantuan task of repairing the damaged pipe, highlighted the direness of the situation when he warned that reconstruction could take at least two or three years to complete.