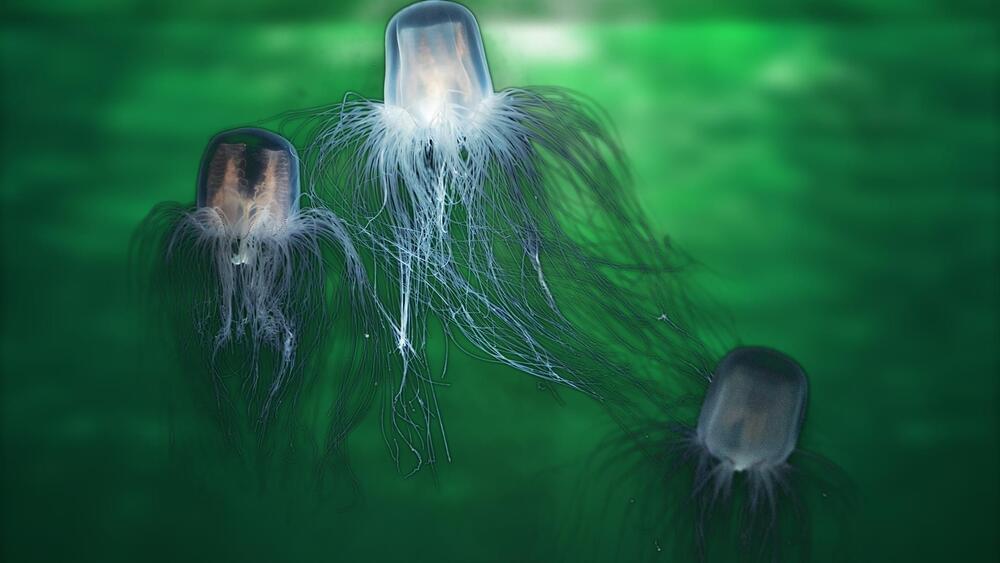
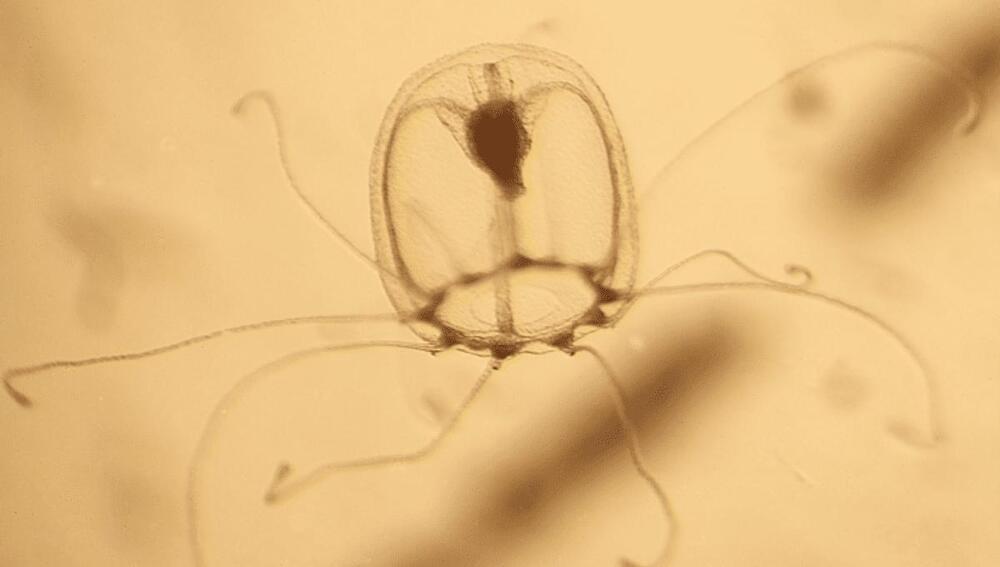
Immortality exists – but to get it, you need to be a jellyfish, not a god or a vampire. Moreover, only one species of cnidarian, Turritopsis dohrnii, is known to have found the secret of eternal life. Geneticists hope comparing T. dornii’s DNA with its close relative, T. rubra, will help us understand the aging process and how to evade it.
Turritopsis are warm water jellyfish half a centimeter (0.2 inches) long. At least three species of hydra have the capacity to age backwards like Benjamin Button, going from adult to juvenile stage, before eventually growing up again. However, two of these can only go from the hydra equivalent of adolescent to child; like the victim in some uncensored fairytale, sexual reproduction locks them into adulthood. T. dohrnii, on the other hand, appears able to go from its free-floating adult stage to bottom-living polyp, known as life cycle reversal (LCR), as many times as it wants.
A paper in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences provides a comparison of T. dorhnii and T. rubra in the hope the differences will prove enlightening, throwing in a few more distantly related types of cnidarians as well.