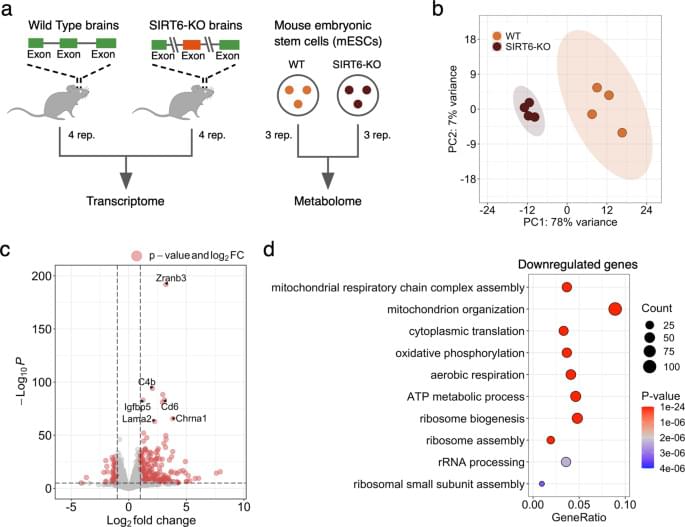
Though mitochondrial dysfunction is a known marker of aging and neurodegenerative diseases, the exact mechanism behind it remains unknown. Our study suggests that the decay of SIRT6 levels during aging [18] and in Alzheimer’s disease [18, 23, 46] could be a key mechanism causing the deterioration of mitochondrial functions. The changes induced by the SIRT6 knockout that we observe at the metabolite level support this claim: metabolites related to mitochondrial energy system pathways (in particular, OXPHOS and TCA cycle) are significantly overrepresented among differentially abundant metabolites. In line with the discussed mitochondrial dysfunction in aging, all these metabolites are downregulated in the SIRT6-KO samples. Importantly, the dramatic decline of one of them, NAD+, was also associated with pro-senescence mechanisms in various species [47, 48], as well as with limited neuroprotective activity of sirtuins [49].
Accordingly, the vast majority of differentially expressed mitochondria-related genes were downregulated in our gene expression analysis. As they were strongly enriched with mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes, we measured the mitochondrial membrane potential and mitochondrial content in SIRT6-KO cells because reduced gene expression might indicate the loss of mitochondria. Both measured characteristics were significantly decreased, validating the suggested impairment of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and mitochondrial biogenesis in SIRT6-deficient brains. Interestingly, the average decrease of mtDNA gene expression (~19.7%) in SIRT6-KO was in good agreement with the corresponding reduction of mitochondrial content (21.8%), suggesting impaired mitochondrial biogenesis as a primary cause of the observed transcriptional dysregulation in mitochondria upon SIRT6 knockout.
Concordantly, the impaired membrane potential upon SIRT6-KO can be partially rescued by restoring SIRT3 and SIRT4 levels, which were significantly downregulated in SIRT6-deficient brains. Both of them are localized in mitochondria and impact mitochondrial pathways related to redox homeostasis and cellular metabolism [38] and have important roles in mitochondria metabolism ROS balance and lifespan [50,51,52]. The analysis of our and publicly available gene expression data [39] confirms that SIRT6 transcriptionally regulates SIRT3 and SIRT4. Our analysis further indicates that SIRT6 regulates mitochondrial gene expression through the transcription factor YY1. We have previously shown that SIRT6 and YY1 form a complex that regulates many shared target genes [24]. Our analysis of YY1 ChIP-seq data [53] suggests that SIRT6 and YY1 regulate mitochondrial processes coordinately.