This article was originally published by Christopher Carey on Cities Today, the leading news platform on urban mobility and innovation, reaching an international audience of city leaders. For the latest updates, follow Cities Today on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram, and YouTube, or sign up for Cities Today News.
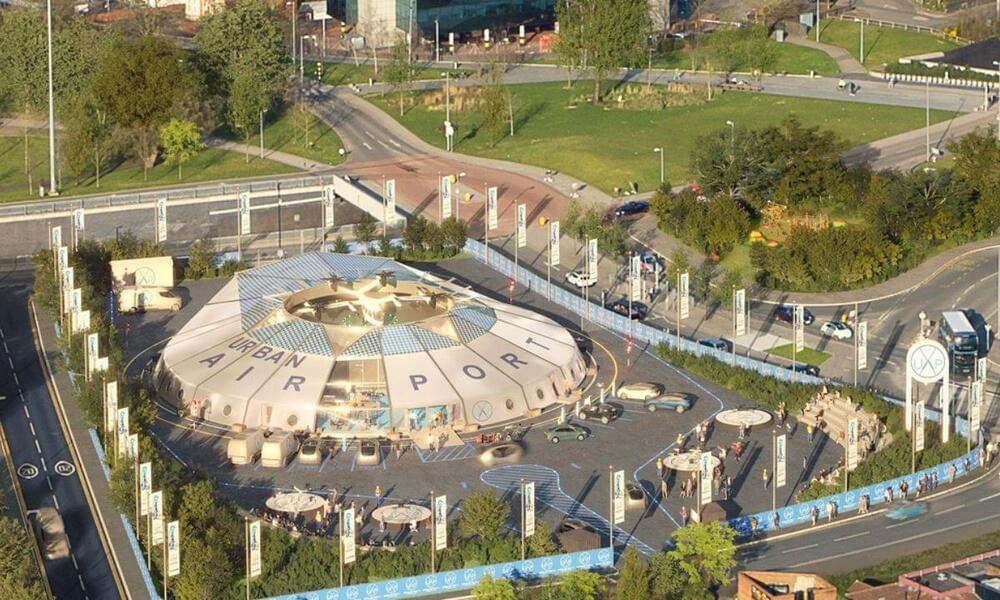
UK start-up Urban-Air Port (UAP) has announced plans to establish 200 hubs for flying taxis and cargo drones across 65 cities globally over the next five years.
The firm is set to launch its first ‘vertiport’, dubbed the “worlds smallest airport”, in Coventry in April, and says a “significant investment” from Hyundai Motor Group’s urban air division Supernal will enable expansion to further sites.