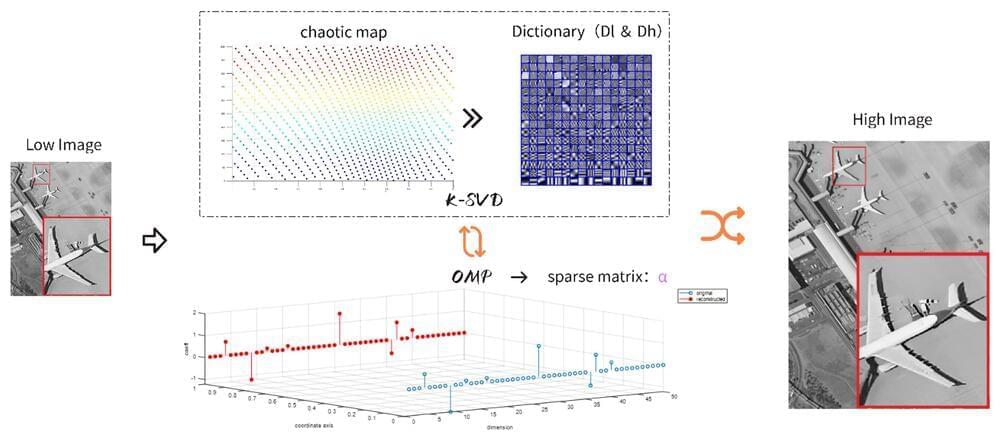
Super-resolution (SR) technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing the quality of images. SR reconstruction aims to generate high-resolution images from low-resolution ones. Traditional methods often result in blurred or distorted images. Advanced techniques such as sparse representation and deep learning-based methods have shown promising results but still face limitations in terms of noise robustness and computational complexity.
In a recent study published in Sensors, researchers from the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed innovative solutions that integrate chaotic mapping into SR image reconstruction process, significantly enhancing the image quality across various fields.
Researchers innovatively introduced circle chaotic mapping into the dictionary sequence solving process of the K-singular value decomposition (K-SVD) dictionary update algorithm. This integration facilitated balanced traversal and simplified the search for global optimal solutions, thereby enhancing the noise robustness of the SR reconstruction.