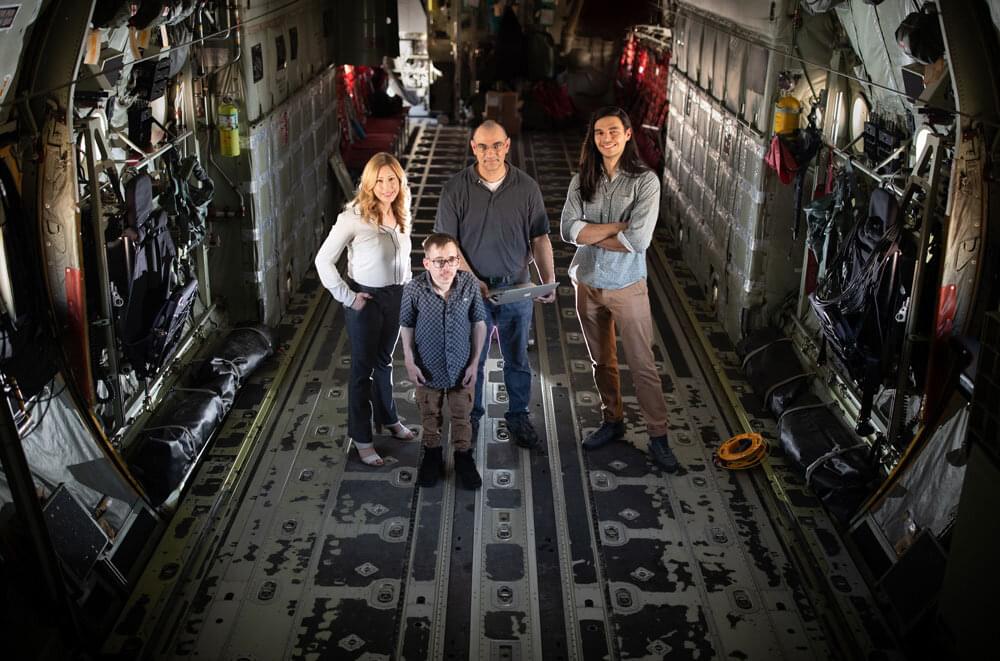
A cybersecurity technique that shuffles network addresses like a blackjack dealer shuffles playing cards could effectively befuddle hackers gambling for control of a military jet, commercial airliner or spacecraft, according to new research. However, the research also shows these defenses must be designed to counter increasingly sophisticated algorithms used to break them.
Many aircraft, spacecraft and weapons systems have an onboard computer network known as military standard 1,553, commonly referred to as MIL-STD-1553, or even just 1553. The network is a tried-and-true protocol for letting systems like radar, flight controls and the heads-up display talk to each other.
Securing these networks against a cyberattack is a national security imperative, said Chris Jenkins, a Sandia cybersecurity scientist. If a hacker were to take over 1,553 midflight, he said, the pilot could lose control of critical aircraft systems, and the impact could be devastating.