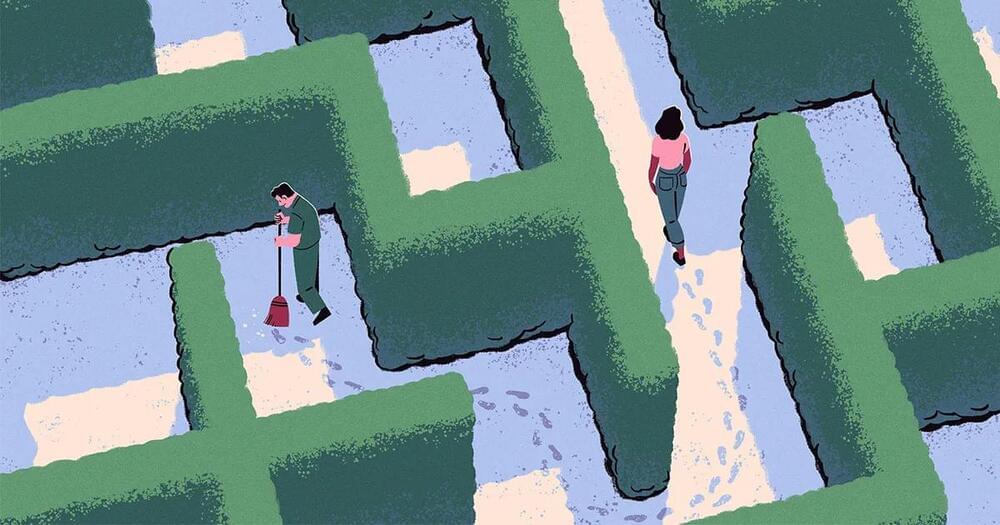
Quantum algorithms can find their way out of mazes exponentially faster than classical ones, at the cost of forgetting the path they took. A new result suggests that the trade-off may be inevitable.



The digital devices that we rely on so heavily in our day-to-day and professional lives today—smartphones, tablets, laptops, fitness trackers, etc.—use traditional computational technology. Traditional computers rely on a series of mathematical equations that use electrical impulses to encode information in a binary system of 1s and 0s. This information is transmitted through quantitative measurements called “bits.”
Unlike traditional computing, quantum computing relies on the principles of quantum theory, which address principles of matter and energy on an atomic and subatomic scale. With quantum computing, equations are no longer limited to 1s and 0s, but instead can transmit information in which particles exist in both states, the 1 and the 0, at the same time.
Quantum computing measures electrons or photons. These subatomic particles are known as quantum bits, or ” qubits.” The more qubits are used in a computational exercise, the more exponentially powerful the scope of the computation can be. Quantum computing has the potential to solve equations in a matter of minutes that would take traditional computers tens of thousands of years to work out.
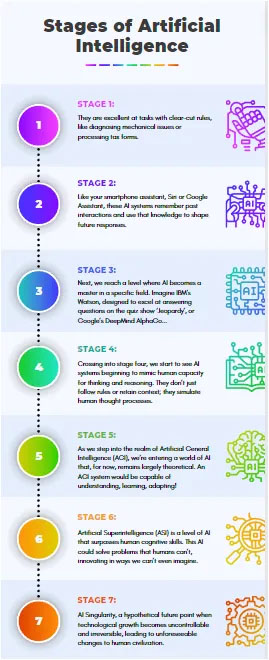
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed our world at an astounding pace. It’s like a vast ocean, and we’re just beginning to navigate its depths.
To appreciate its complexity, let’s embark on a journey through the seven distinct stages of AI, from its simplest forms to the mind-boggling prospects of superintelligence and singularity.
Picture playing chess against a computer. Every move it makes, every strategy it deploys, is governed by a predefined set of rules, its algorithm. This is the earliest stage of AI — rule-based systems. They are excellent at tasks with clear-cut rules, like diagnosing mechanical issues or processing tax forms. But their capacity to learn or adapt is nonexistent, and their decisions are only as good as the rules they’ve been given.
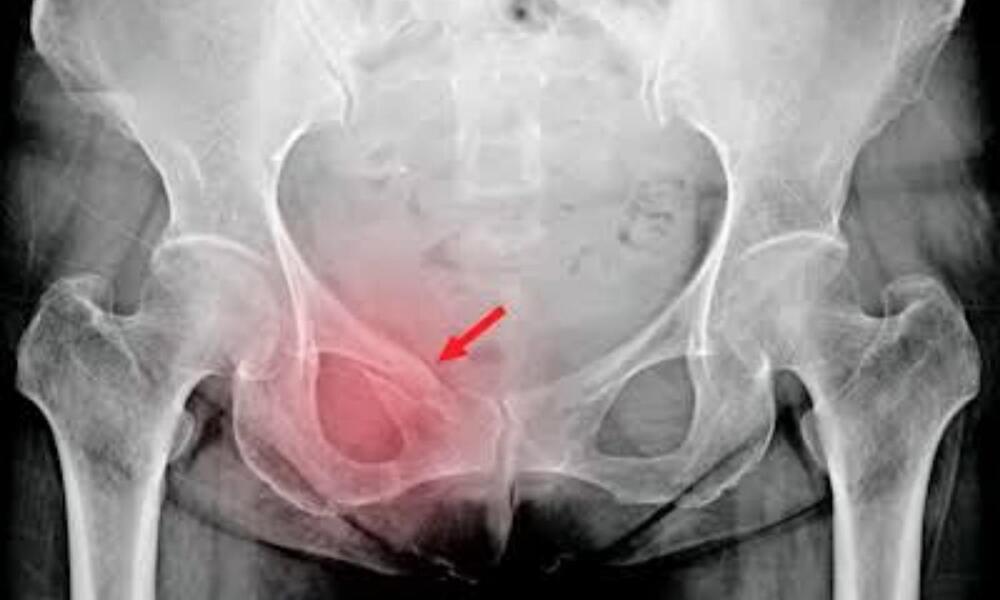
Singapore: A research paper, published in iScience, has decribed the development of a deep learning model for predicting hip fractures on pelvic radiographs (Xrays), even with the presence of metallic implants.
Yet Yen Yan of Changi General Hospital and colleagues at the Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore, and colleagues developed the AI (artificial intelligence) algorithm using more than fortythousand pelvic radiographs from a single institution. The model demonstrated high specificity and sensitivity when applied to a test set of emergency department (ED) radiographs.
This study approximates the realworld application of a deep learning fracture detection model by including radiographs with suboptimal image quality, other nonhip fractures and meta llic implants, which were excluded from prior published work. The research team also explored the effect of ethnicity on model performance, and the accuracy of visualization algorithm for fracture localization.

A recent paper published in Nature Aging by researchers from Integrated Biosciences, a biotechnology company combining synthetic biology and machine learning.
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that deals with the development of algorithms and statistical models that enable computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning is used to identify patterns in data, classify data into different categories, or make predictions about future events. It can be categorized into three main types of learning: supervised, unsupervised and reinforcement learning.

Filmmakers may soon be able to stabilize shaky video, change viewpoints and create freeze-frame, zoom and slow-motion effects – without shooting any new footage – thanks to an algorithm developed by researchers at Cornell University and Google Research.
The software, called DynIBar, synthesizes new views using pixel information from the original video, and even works with moving objects and unstable camerawork. The work is a major advance over previous efforts, which yielded only a few seconds of video, and often rendered moving subjects as blurry or glitchy.
The code for this research effort is freely available, though the project is at an early stage and not yet integrated into commercial video editing tools.

Generative AI techniques like ChatGPT, DALL-e and Codex can generate digital content such as images, text, and the code. Recent progress in large-scale AI models has improved generative AI’s ability to understand intent and generate more realistic content. This text summarizes the history of generative models and components, recent advances in AI-generated content for text, images, and across modalities, as well as remaining challenges.
In recent years, Artificial Intelligence Generated Content (AIGC) has gained much attention beyond the computer science community, where the whole society is interested in the various content generation products built by large tech companies. Technically, AIGC refers to, given human instructions which could help teach and guide the model to complete the task, using Generative AI algorithms to form a content that satisfies the instruction. This generation process usually comprises two steps: extracting intent information from human instructions and generating content according to the extracted intentions.
Generative models have a long history of AI, dating to the 1950s. Early models like Hidden Markov Models and Gaussian Mixture Models generated simple data. Generative models saw major improvements in deep learning. In NLP, traditional sentence generation used N-gram language models, but these struggled with long sentences. Recurrent neural networks and Gated Recurrent Units enabled modeling longer dependencies, handling ~200 tokens. In CV, pre-deep learning image generation used hand-designed features with limited complexity and diversity. Generative Adversarial Networks and Variational Autoencoders enabled impressive image generation. Advances in generative models followed different paths but converged with transformers, introduced for NLP in 2017. Transformers dominate many generative models across domains. In NLP, large language models like BERT and GPT use transformers. In CV, Vision Transformers and Swin Transformers combine transformers and visual components for images.
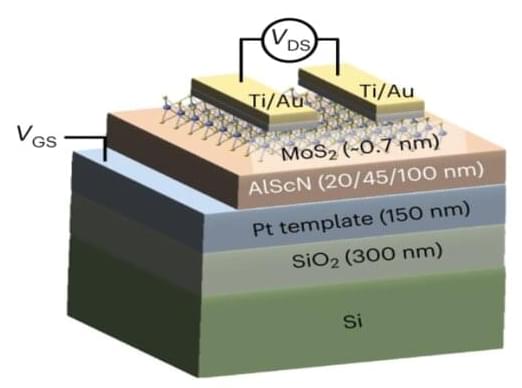
The Big Data revolution has strained the capabilities of state-of-the-art electronic hardware, challenging engineers to rethink almost every aspect of the microchip. With ever more enormous data sets to store, search and analyze at increasing levels of complexity, these devices must become smaller, faster and more energy efficient to keep up with the pace of data innovation.
Ferroelectric field effect transistors (FE-FETs) are among the most intriguing answers to this challenge. Like traditional silicon-based transistors, FE-FETs are switches, turning on and off at incredible speed to communicate the 1s and 0s computers use to perform their operations.
But FE-FETs have an additional function that conventional transistors do not: their ferroelectric properties allow them to hold on to electrical charge.

With artificial intelligence poised to assist in profound scientific discoveries that will change the world, Cornell is leading a new $11.3 million center focused on human-AI collaboration that uses mathematics as a common language.
The Scientific Artificial Intelligence Center, or SciAI Center, is being launched with a grant from the Office of Naval Research and is led by Christopher J. Earls, professor of civil and environmental engineering at Cornell Engineering. Co-investigators include Nikolaos Bouklas, assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at Cornell Engineering; Anil Damle, assistant professor of computer science in the Cornell Ann S. Bowers College of Computing and Information Science; and Alex Townsend, associate professor of mathematics in the College of Arts and Sciences. All of the investigators are field faculty members of the Center for Applied Mathematics.
With the advance of AI systems – built with tangled webs of algorithms and trained on increasingly large sets of data – researchers fear AI’s inner workings will provide little insight into its uncanny ability to recognize patterns in data and make scientific predictions. Earls described it as a situation at odds with true scientific discovery.
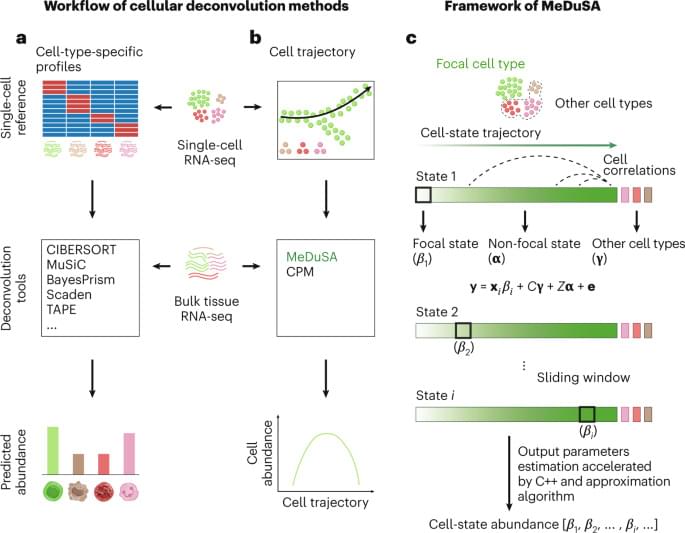
A recent work introduces a cellular deconvolution method, MeDuSA, of estimating cell-state abundance along a one-dimensional trajectory from bulk RNA-seq data with fine resolution and high accuracy, enabling the characterization of cell-state transition in various biological processes.
Single-cell transcriptomic techniques continue to revolutionize the resolution of cell analysis, determining discrete cell types and cell states with continuous dynamic transitions that can be related to development and disease progression5. Cells in different states can be computationally ordered according to a pseudo-time series, or cell trajectory6. Both MeDuSA and another method, Cell Population Mapping (CPM)7, were developed to exploit the rich spectrum of single-cell reference profiles to estimate cell-state abundance in bulk RNA-seq data, which enables fine-resolution cellular deconvolution (Fig. 1b). Although CPM effectively tackles the issue of estimating the abundance of cells in different states, MeDuSA further improves the estimation accuracy by employing a LMM (see the equation in Fig. 1c) that takes into account both the cell state of interest (focal state) and the remaining cells of the same cell type (non-focal state) as well as the other cell types.