Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown great capabilities in various natural language tasks such as text summarization, question answering, generating code, etc., emerging as a powerful solution to many real-world problems. One area where these models struggle, though, is goal-directed conversations where they have to accomplish a goal through conversing, for example, acting as an effective travel agent to provide tailored travel plans. In practice, they generally provide verbose and non-personalized responses.
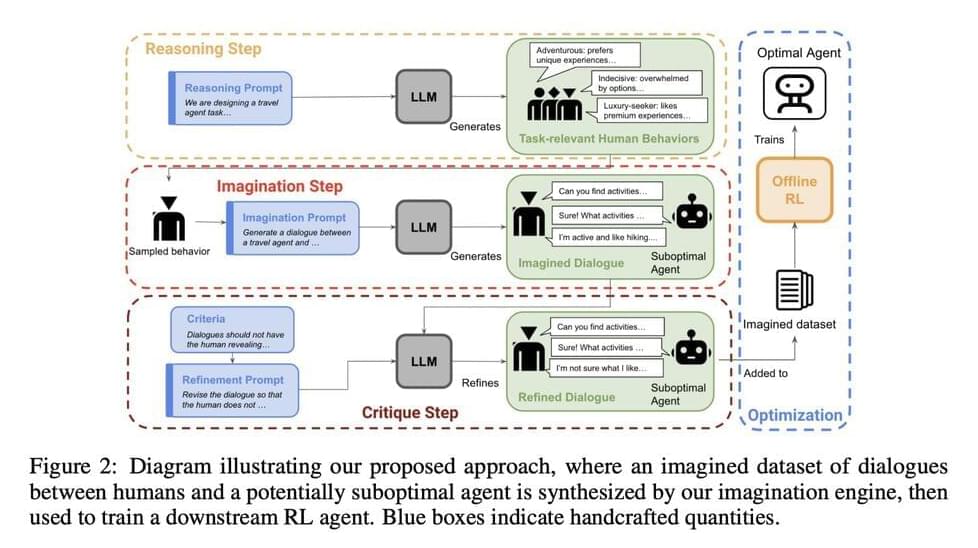
Models trained with supervised fine-tuning or single-step reinforcement learning (RL) commonly struggle with such tasks as they are not optimized for overall conversational outcomes after multiple interactions. Moreover, another area where they lack is dealing with uncertainty in such conversations. In this paper, the researchers from UC Berkeley have explored a new method to adapt LLMs with RL for goal-directed dialogues. Their contributions include an optimized zero-shot algorithm and a novel system called imagination engine (IE) that generates task-relevant and diverse questions to train downstream agents.
Since the IE cannot produce effective agents by itself, the researchers utilize an LLM to generate possible scenarios. To enhance the effectiveness of an agent in achieving desired outcomes, multi-step reinforcement learning is necessary to determine the optimal strategy. The researchers have made one modification to this approach. Instead of using any on-policy samples, they used offline value-based RL to learn a policy from the synthetic data itself.