Circa 2016
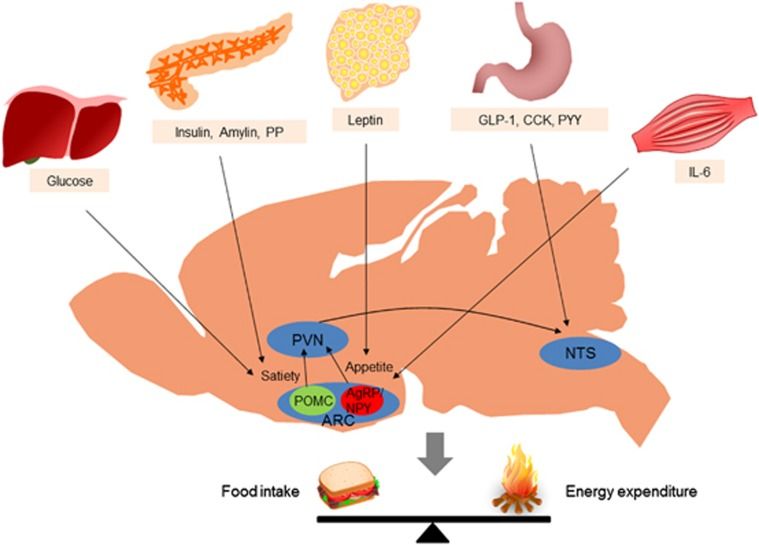
Accumulated evidence from genetic animal models suggests that the brain, particularly the hypothalamus, has a key role in the homeostatic regulation of energy and glucose metabolism. The brain integrates multiple metabolic inputs from the periphery through nutrients, gut-derived satiety signals and adiposity-related hormones. The brain modulates various aspects of metabolism, such as food intake, energy expenditure, insulin secretion, hepatic glucose production and glucose/fatty acid metabolism in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. Highly coordinated interactions between the brain and peripheral metabolic organs are critical for the maintenance of energy and glucose homeostasis. Defective crosstalk between the brain and peripheral organs contributes to the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Here we comprehensively review the above topics, discussing the main findings related to the role of the brain in the homeostatic regulation of energy and glucose metabolism.
In normal individuals, food intake and energy expenditure are tightly regulated by homeostatic mechanisms to maintain energy balance. Substantial evidence indicates that the brain, particularly the hypothalamus, is primarily responsible for the regulation of energy homeostasis.1 The brain monitors changes in the body energy state by sensing alterations in the plasma levels of key metabolic hormones and nutrients. Specialized neuronal networks in the brain coordinate adaptive changes in food intake and energy expenditure in response to altered metabolic conditions ( Figure 1 ).2, 3.