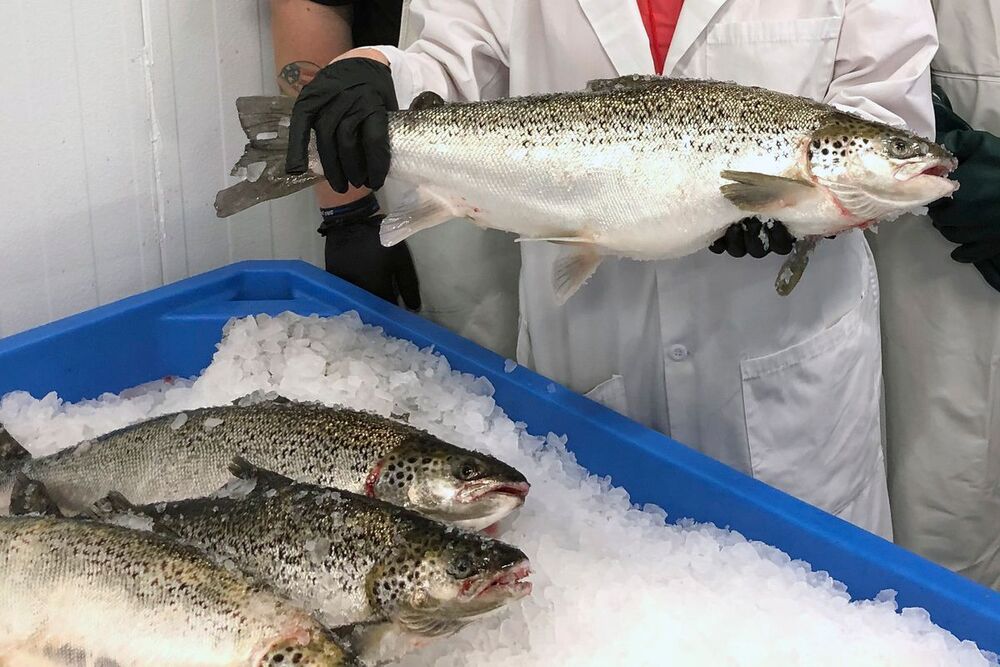
AquaBounty Technologies Inc. will initially send salmon to restaurants and away-from-home dining services where labeling as genetically engineered is not required, company CEO Sylvia Wulf said.


Critical advances in the investigation of brain functions and treatment of brain disorders are hindered by our inability to selectively target neurons in a noninvasive manner in the deep brain.
This study aimed to develop sonothermogenetics for noninvasive, deep-penetrating, and cell-type-specific neuromodulation by combining a thermosensitive ion channel TRPV1 with focused ultrasound (FUS)-induced brief, non-noxious thermal effect.
The sensitivity of TRPV1 to FUS sonication was evaluated in vitro. It was followed by in vivo assessment of sonothermogenetics in the activation of genetically defined neurons in the mouse brain by two-photon calcium imaging. Behavioral response evoked by sonothermogenetic stimulation at a deep brain target was recorded in freely moving mice. Immunohistochemistry staining of ex vivo brain slices was performed to evaluate the safety of FUS sonication.
The idea is simple: decades of research have found certain genes that seem to increase the chance of Alzheimer’s and other dementias. The numbers range over hundreds. Figuring out how each connects or influences another—if at all—takes years of research in individual labs. What if scientists unite, tap into a shared resource, and collectively solve the case of why Alzheimer’s occurs in the first place?
The initiative’s secret weapon is induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPSCs. Similar to most stem cells, they have the ability to transform into anything—a cellular genie, if you will. iPSCs are reborn from regular adult cells, such as skin cells. When transformed into a brain cell, however, they carry the original genes of their donor, meaning that they harbor the original person’s genetic legacy—for example, his or her chance of developing Alzheimer’s in the first place. What if we introduce Alzheimer’s-related genes into these reborn stem cells, and watch how they behave?
By studying these iPSCs, we might be able to follow clues that lead to the genetic causes of Alzheimer’s and other dementias—paving the road for gene therapies to nip them in the bud.

Many of the fundamental features of life don’t necessarily have to be the way they are. Chance plays a major role in evolution, and there are always alternate paths that were never explored, simply because whatever evolved previously happened to be good enough. One instance of this idea is the genetic code, which converts the information carried by our DNA into the specific sequence of amino acids that form proteins. There are scores of potential amino acids, many of which can form spontaneously, but most life uses a genetic code that relies on just 20 of them.
Over the past couple of decades, scientists have shown that it doesn’t have to be that way. If you supply bacteria with the right enzyme and an alternative amino acid, they can use it. But bacteria won’t use the enzyme and amino acid very efficiently, as all the existing genetic code slots are already in use.
In a new work, researchers have managed to edit bacteria’s genetic code to free up a few new slots. They then filled those slots with unnatural amino acids, allowing the bacteria to produce proteins that would never be found in nature. One side effect of the reprogramming? No viruses could replicate in the modified bacteria.

PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROYAL SOCIETY • JUN 3, 2021
Culture drives human evolution more than genetics
I wonder about the thought that only humans do this, and perhaps that somehow culture is separate in some way from biological evolution enmeshed with the rest of the planet?
by University of Maine
Culture is an under-appreciated factor in human evolution, Waring says. Like genes, culture helps people adjust to their environment and meet the challenges of survival and reproduction. Culture, however, does so more effectively than genes because the transfer of knowledge is faster and more flexible than the inheritance of genes, according to Waring and Wood.
Waring and Wood say culture is also special in one important way: it is strongly group-oriented. Factors like conformity, social identity and shared norms and institutions—factors that have no genetic equivalent—make cultural evolution very group-oriented, according to researchers. Therefore, competition between culturally organized groups propels adaptations such as new cooperative norms and social systems that help groups survive better together.
According to researchers, “culturally organized groups appear to solve adaptive problems more readily than individuals, through the compounding value of social learning and cultural transmission in groups.” Cultural adaptations may also occur faster in larger groups than in small ones.
With groups primarily driving culture and culture now fueling human evolution more than genetics, Waring and Wood found that evolution itself has become more group-oriented.
“In the very long term, we suggest that humans are evolving from individual genetic organisms to cultural groups which function as superorganisms, similar to ant colonies and beehives,” Waring says. “The ‘society as organism’ metaphor is not so metaphorical after all.
The team says that the technique could be used to develop new vaccines against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and potentially even wipe out some dangerous strains in a similar way to how smallpox was eradicated.
Pathogens like bacteria and viruses are extremely good at evolving in response to drugs, which can render vaccines ineffective. But now, researchers at ETH Zurich have found a way to weaponize that ability against them, forcing the bugs down harmless evolutionary dead ends.
Microbes are living examples of evolution in action. Darwin’s classic theory says that when lifeforms are exposed to pressures from their environment, some of them will develop new genetic mutations that help them cope better. Since other individuals will be at a disadvantage, the mutations will eventually become the norm throughout a population.
In the world of bacteria and viruses, drugs and vaccines are the environmental pressures that they must overcome. And they do it with frustrating ease, quickly finding ways around the attacks and then swapping those genes like trading cards. The end result is the constant looming threat of antibiotic-resistant “superbugs” that render our best drugs ineffective.
CRISPR-based technologies offer enormous potential to benefit human health and safety, from disease eradication to fortified food supplies. As one example, CRISPR-based gene drives, which are engineered to spread specific traits through targeted populations, are being developed to stop the transmission of devastating diseases such as malaria and dengue fever.
But many scientists and ethicists have raised concerns over the unchecked spread of gene drives. Once deployed in the wild, how can scientists prevent gene drives from uncontrollably spreading across populations like wildfire?
Now, scientists at the University of California San Diego and their colleagues have developed a gene drive with a built-in genetic barrier that is designed to keep the drive under control. Led by molecular geneticist Omar Akbari’s lab, the researchers engineered synthetic fly species that, upon release in sufficient numbers, act as gene drives that can spread locally and be reversed if desired.
Hydraulic Instability Decides Who’s to Die and Who’s to Live
In many species including humans, the cells responsible for reproduction, the germ cells, are often highly interconnected and share their cytoplasm. In the hermaphrodite nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, up to 500 germ cells are connected to each other in the gonad, the tissue that produces eggs and sperm. These cells are arranged around a central cytoplasmic “corridor” and exchange cytoplasmic material fostering cell growth, and ultimately produce oocytes ready to be fertilized.
In past studies, researchers have found that C. elegans gonads generate more germ cells than needed and that only half of them grow to become oocytes, while the rest shrinks and die by physiological apoptosis, a programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Now, scientists from the Biotechnology Center of the TU Dresden (BIOTEC), the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG), the Cluster of Excellence Physics of Life (PoL) at the TU Dresden, the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems (MPI-PKS), the Flatiron Institute, NY, and the University of California, Berkeley, found evidence to answer the question of what triggers this cell fate decision between life and death in the germline.
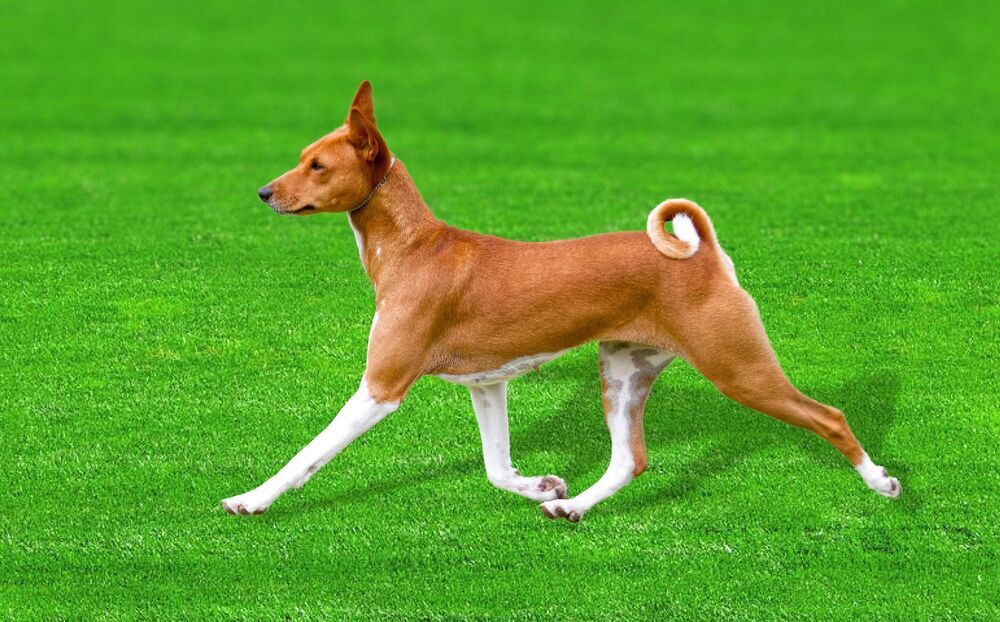

An international study led by UNSW researchers has mapped one of the most intact and complete dog genomes ever generated.
The genome sequence of the Basenji dog could have a big impact on the understanding of dog evolution, domestication and canine genetic diseases.
The Basenji—also known as the barkless dog—is an ancient African dog breed which still lives and hunts with tribesmen in the African Congo.
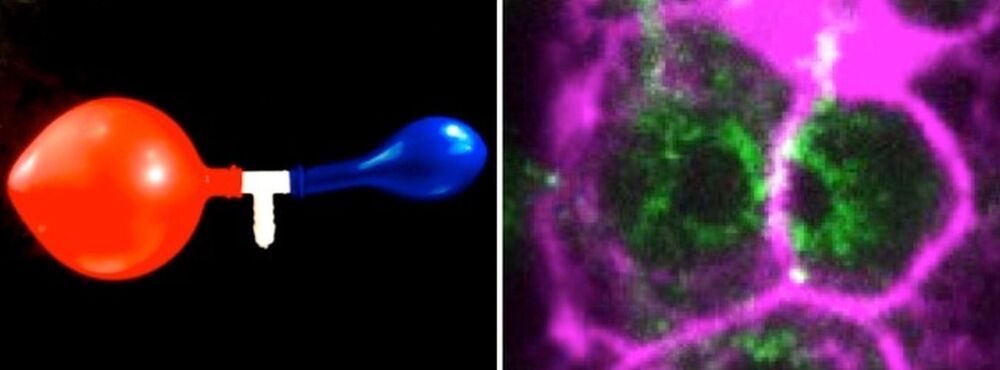
In many species including humans, the cells responsible for reproduction, the germ cells, are often highly interconnected and share their cytoplasm. In the hermaphrodite nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, up to 500 germ cells are connected to each other in the gonad, the tissue that produces eggs and sperm. These cells are arranged around a central cytoplasmic “corridor” and exchange cytoplasmic material fostering cell growth, and ultimately produce oocytes ready to be fertilized.
In past studies, researchers have found that C. elegans gonads generate more germ cells than needed and that only half of them grow to become oocytes, while the rest shrink and die by physiological apoptosis, a programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Now, scientists from the Biotechnology Center of the TU Dresden (BIOTEC), the Max Planck Institute of molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG), the Cluster of Excellence Physics of Life (PoL) at the TU Dresden, the Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems (MPI-PKS), the Flatiron Institute, NY, and the University of California, Berkeley, have found evidence to answer the question of what triggers this cell fate decision between life and death in the germline.
Prior studies revealed the genetic basis and biochemical signals that drive physiological cell death, but the mechanisms that select and initiate apoptosis in individual germ cells remained unclear. As germ cells mature along the gonad of the nematode, they first collectively grow in size and in volume homogenously. In the study just published in Nature Physics, the scientists show that this homogenous growth suddenly shifts to a heterogenous growth where some cells become bigger and some cells become smaller.