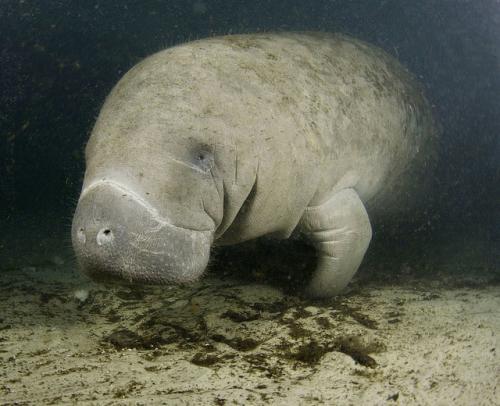
About 99 percent of human genes are shared with chimpanzees. Only the small remainder sets us apart. However, we have one important difference: The brain of humans is three times as big as the chimpanzee brain.
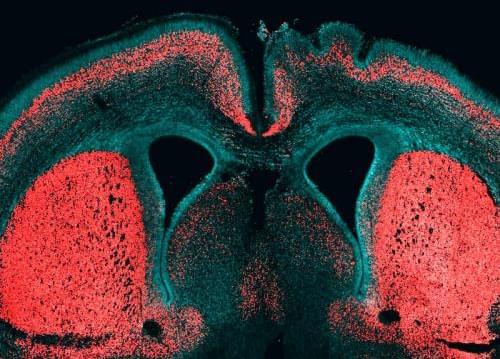
During evolution our genome must have changed in order to trigger such brain growth. Wieland Huttner, Director and Research Group Leader a the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG), and his team identified for the first time a gene that is only present in humans and contributes to the reproduction of basal brain stem cells, triggering a folding of the neocortex. The researchers isolated different subpopulations of human brain stem cells and precisely identified, which genes are active in which cell type. In doing so, they noticed the gene ARHGAP11B: it is only found in humans and in our closest relatives, the Neanderthals and Denisova-Humans, but not in chimpanzees. This gene manages to trigger brain stem cells to form a bigger pool of stem cells. In that way, during brain development more neurons can arise and the cerebrum can expand. The cerebrum is responsible for cognitive functions like speaking and thinking.
Wieland Huttner’s researchers developed a method that isolates and identifies special subpopulations of brain stem cells from the developing human cerebrum. No one has managed to do this so far. The scientists first isolated different stem and progenitor cell types from fetal mice and human cerebrum tissue. In contrast to the big and folded human brain, the brain of mice is small and smooth. After the isolation, the researchers compared the genes that are active in the various cell types and were able to identify 56 genes that are only present in humans and which play a role in brain development. “We noticed that the gene ARHGAP11B is especially active in basal brain stem cells. These cells are really important for the expansion of the neocortex during evolution,” says Marta Florio, PhD student in Wieland Huttner’s lab, who carried out the main part of the study.